Relapse can be a challenging and disheartening experience for individuals striving to overcome addiction or unhealthy behaviors. It is important to understand what relapse means and the common triggers that may lead to it. knowing coping strategies and seeking help is crucial in navigating through this difficult period.
To begin, it is essential to understand what relapse means in the context of addiction or unhealthy behaviors. Relapse refers to a recurrence of the problematic behavior after a period of abstinence or progress. It can be disheartening, but it is important to remember that it is a common part of the recovery process.
There are various triggers that can contribute to relapse. Firstly, it is important to identify personal triggers, which may include emotional distress, negative thoughts or self-talk, or encountering certain people or places associated with the addictive behavior. Similarly, social and environmental triggers, such as being in social situations where the behavior is present or experiencing high levels of stress, can also contribute to relapse.
When facing a relapse, it is important to have coping strategies in place to effectively deal with the situation. Recognizing and accepting the relapse is an important first step, as it allows individuals to acknowledge the setback and move forward. Seeking support from loved ones is crucial, as having a strong support system can provide encouragement, guidance, and accountability.
Engaging in self-care and healthy habits is also important during this time. This can include practicing mindfulness, engaging in physical activity, getting sufficient rest and sleep, and maintaining a balanced and nutritious diet. finding stress-relieving activities that work for you, such as meditating, journaling, or engaging in hobbies, can help manage stress and prevent further relapse.
Developing and utilizing coping skills is another important aspect of dealing with relapse. This may involve learning healthy ways to manage emotions, such as through deep breathing exercises or relaxation techniques. seeking professional help from therapists or counselors who specialize in addiction recovery can provide valuable guidance and support.
For those experiencing relapse, seeking professional help is crucial in navigating through this challenging period. Therapeutic interventions and counseling can provide individuals with the necessary tools, techniques, and support to address the underlying issues contributing to their relapse. Support groups and peer recovery networks can also be beneficial, as they offer a sense of community and understanding from individuals who have had similar experiences.
Furthermore, rehabilitation programs and treatment centers can provide a structured and supportive environment for individuals struggling with relapse. These programs often incorporate a range of therapies, educational resources, and holistic approaches to support recovery. medication-assisted treatment options may be available for certain individuals, which can help manage withdrawal symptoms and cravings.
Identifying and managing triggers, building a strong support system, continuously practicing self-care, and developing healthy coping mechanisms is also important. By addressing underlying issues, seeking ongoing support, and implementing healthy lifestyle changes, individuals can greatly reduce the risk of relapse and maintain their progress toward a healthier and more fulfilling life.

Understanding Relapse: What Does It Mean?
Understanding relapse is crucial for individuals recovering from addiction or maintaining a healthy lifestyle. Here are key points to consider as you prevent relapse and build resilience:
- Relapse is common in addiction recovery. It refers to returning to substance use or engaging in unhealthy behaviors after abstinence.
- Relapse does not mean failure. It is a temporary setback that can be overcome with support and coping strategies.
- Certain factors, such as stress, negative emotions, peer pressure, or environmental cues, often trigger relapse.
- Recognizing warning signs of relapse is crucial, including cravings, withdrawal symptoms, changes in behavior, or loss of interest in previously enjoyable activities.
- Seeking help and support is essential when dealing with relapse. This can involve reaching out to a therapist, counselor, or support group to address underlying issues and develop effective coping strategies.
Common Triggers for Relapse
Relapses can be challenging, but understanding common triggers can help in preventing them. Let’s explore two key aspects: identifying personal triggers and the influence of social and environmental factors. By recognizing the unique triggers that can lead to relapse, we can develop effective coping strategies and seek the right support. Stay tuned to discover practical tips to navigate these triggers and maintain a strong path to recovery.
Identifying Personal Triggers
Identifying personal triggers, such as emotional cues, environmental factors, social influences, and thought patterns and beliefs, is crucial in preventing relapse. By reflecting on past experiences and recognizing common themes or situations that led to using them again, individuals can determine specific triggers unique to them.
Paying attention to emotional states and identifying the emotions that often precede cravings or urges to use, such as stress, sadness, anger, or boredom, helps in developing strategies to cope with them. Considering the settings, people, places, or events associated with substance use, and being aware of environmental triggers, allows individuals to make conscious decisions to avoid or modify them.
Evaluating the influence of certain people or relationships in life, and surrounding oneself with supportive and positive influences, reduces the risk of relapse. Additionally, examining thoughts and beliefs about substance use and challenging negative ones can lead to healthier coping mechanisms.
Identifying personal triggers is an ongoing process that requires self-awareness and reflection, enabling individuals to take proactive steps to prevent relapse and maintain their recovery journey.
Social and Environmental Triggers
Social and environmental triggers are key factors that significantly influence the possibility of relapse. It is crucial to have an awareness of these triggers in order to effectively deal with them and minimize the risk of relapsing.
- One important trigger is stressful situations, which can include high-stress environments or significant life events. These situations increase the chances of relapse. Therefore, it is essential to develop healthy coping mechanisms to manage stress and avoid turning to substances for relief.
- Another trigger is peer pressure. Being in social settings where substance use is common can easily trigger a relapse. To counteract this influence, it is important to surround oneself with a supportive network of individuals who prioritize sobriety.
- Emotional distress is also a significant trigger for relapse. Feelings of sadness, anger, or loneliness can lead someone to turn to substances for temporary relief. It is crucial to learn healthy ways to manage emotions, such as therapy or support groups, in order to avoid this.
- Enabling environments, such as being in settings that promote substance use or having access to drugs and alcohol, pose a great danger for individuals in recovery. To reduce the risk of relapse, it is important to create a supportive and substance-free living environment.
- Unhealthy relationships, especially toxic or codependent ones, also contribute to relapse. Setting boundaries and seeking support through therapy or counseling can help individuals navigate these relationships in a healthy manner.
By being mindful of these social and environmental triggers, individuals in recovery can take proactive steps to avoid or effectively manage these situations, thereby decreasing the likelihood of relapse. Building a strong support system, practicing healthy coping skills, and remaining committed to recovery are all essential components in overcoming the challenges posed by these triggers.

Coping Strategies for Dealing with Relapse
When it comes to dealing with relapse, it’s essential to have effective coping strategies in place. In this section, we’ll dive into various approaches that can help you navigate this challenging situation. From recognizing and accepting the relapse to seeking support from loved ones, practicing self-care, engaging in stress-relieving activities, and developing coping skills, we’ll explore a range of techniques to aid you on your journey to recovery. So buckle up, because we’re about to equip you with the tools you need to conquer relapse head-on.
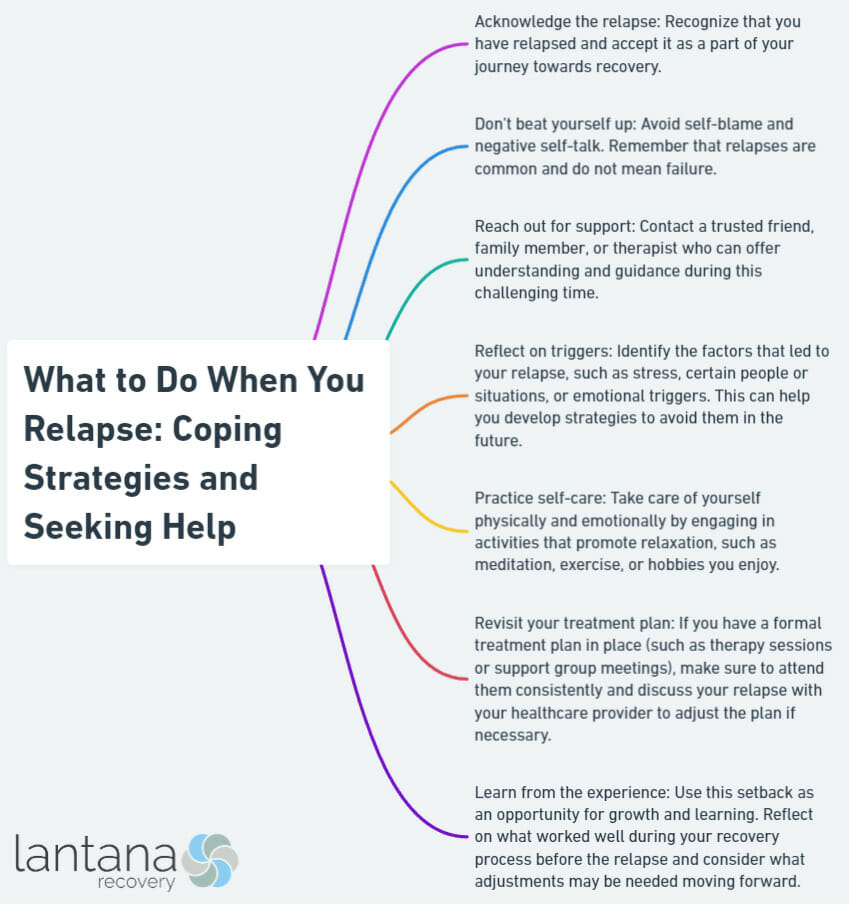
Recognizing and Accepting the Relapse
Recognizing and accepting relapse is crucial in the recovery journey. Relapse is common and should be seen as a learning experience. Consider these key points in recognizing and accepting the relapse:
1. Recognize the signs: Be aware of cravings, thoughts of using again, and changes in behavior or mood.
2. Accept the reality: Acknowledge the signs and don’t deny or resist relapse.
3. Seek support: Reach out to loved ones, support groups, or healthcare providers for guidance and support.
4. Take action: Get back on track by reevaluating the prevention plan, seeking therapy or counseling, and using effective coping skills.
5. Develop resilience: View relapse as a minor setback and maintain a positive mindset to navigate through the process.
By recognizing and accepting the relapse, individuals can prevent future relapses and continue their recovery journey.
Seeking Support from Loved Ones
When facing a relapse, it is important to naturally seek support from loved ones.
1. Communicate openly: It is crucial to reach out to your loved ones and let them know about your current situation. Discuss your struggles, triggers, and emotions. Having someone who can listen and offer support can make a significant difference.
2. Create a support network: Identify and lean on the understanding and non-judgmental people in your life. Surround yourself with individuals who can provide encouragement and hold you accountable.
3. Attend support groups: Join organizations such as Alcoholics Anonymous or Narcotics Anonymous to connect with others who have gone through similar experiences. Share your challenges and accomplishments, and gain insight and guidance from those who have been in your shoes.
4. Involve family therapy: Engaging in therapy or counseling sessions can help improve communication, strengthen relationships, and address underlying issues that may contribute to relapse.
5. Set healthy boundaries: Establish boundaries with your loved ones that support your recovery. Clearly communicate your needs and what is beneficial or triggering for you, and ensure they understand and respect your boundaries.
6. Seek emotional support: Reach out to loved ones who can offer emotional support. Express your feelings and concerns, allowing them to provide comfort and encouragement during difficult times.
7. Encourage involvement in your recovery: Ask your loved ones to actively participate in your recovery process. This may include attending therapy sessions, providing accountability, or simply being there to listen and offer encouragement.
Remember, seeking support from loved ones is not a sign of weakness, but rather a crucial step towards healing and recovery. Their love, understanding, and support can make a significant difference in your journey.
Practicing Self-Care and Healthy Habits
Practicing self-care and healthy habits is crucial when managing relapse. Here are some key strategies to keep in mind:
1. Prioritize your physical well-being: Make sure to engage in regular exercise, consume nutritious meals, and get enough rest. Taking care of your physical health not only enhances overall well-being but also minimizes the chances of relapse.
2. Give importance to your mental health: Set aside time for relaxation techniques like mindfulness meditation and deep breathing exercises. These practices effectively manage stress and promote mental well-being.
3. Establish a daily routine: Creating a structured daily routine provides stability and a sense of purpose, decreasing the likelihood of relapse behaviors. Make sure to include activities that you find enjoyable and fulfilling.
4. Create a support network: Surround yourself with individuals who support your recovery. Seek out self-help groups such as Alcoholics Anonymous or Narcotics Anonymous, as well as understanding friends and family.
5. Practice self-compassion: Be kind to yourself and cultivate a positive mindset. When confronted with challenges, view relapse as a learning experience rather than a failure.
Remember, practicing self-care and healthy habits is an ongoing process. Continuously implementing these strategies helps maintain a strong foundation for your recovery journey.
Engaging in Stress-Relieving Activities
Engaging in stress-relieving activities is important for coping with and preventing relapse. These activities, such as exercise, mindfulness meditation, breathing exercises, engaging in hobbies, connecting with nature, socializing, and practicing self-care, can effectively reduce anxiety, promote relaxation, and improve overall well-being. By incorporating these stress-relieving activities into your routine, you can better cope with stress and reduce the risk of relapse. It is crucial to find activities that suit your interests and preferences so that they become enjoyable and sustainable in the long run.
Developing and Utilizing Coping Skills
Developing and Utilizing Coping Skills is crucial for individuals who have experienced a relapse. Here are important steps to consider when dealing with relapse to develop and utilize coping skills effectively:
1. Recognizing and Accepting the Relapse: Acknowledge and accept that a relapse has occurred without judgment. This self-awareness is the first step toward recovery.
2. Seeking Support from Loved Ones: Reach out to trusted family and friends who can provide emotional support during this challenging time. Their understanding and encouragement can greatly assist in the recovery process.
3. Practicing Self-Care and Healthy Habits: Engage in activities that promote physical and mental well-being, such as regular exercise, a balanced diet, and sufficient sleep. These habits reduce stress and enhance overall resilience.
4. Engaging in Stress-Relieving Activities: Explore different stress-relieving techniques, such as mindfulness meditation, deep breathing exercises, or hobbies that bring joy and relaxation. These activities help manage triggers and promote emotional well-being.
5. Work with a therapist or counselor to identify effective coping strategies. This may involve cognitive-behavioral therapy techniques, challenging negative thoughts, or learning new skills to manage high-risk situations. For instance, former smokers heavily rely on cognitive coping responses as essential components of their coping strategies, which seem to be less affected by situational factors compared to behavioral coping as discussed by Saul Shiffman in Relapse following smoking cessation.
True Story: Jennifer, a former substance abuser, relapsed after a triggering life event caused emotional distress. She immediately recognized her relapse and reached out to her support group for help. Jennifer engaged in mindfulness-based relapse prevention therapy and learned coping skills to manage her cravings and emotional relapse. By practicing deep breathing exercises and grounding techniques, Jennifer regained control of her recovery journey. She also found solace in attending regular meetings at Alcoholics Anonymous. Jennifer’s dedication to developing and utilizing coping skills helped her overcome the relapse and empowered her to maintain abstinence.

Seeking Professional Help for Relapse
When it comes to dealing with relapse, seeking professional help from experts in rehab and recovery can make all the difference. In this section, we’ll explore various avenues for getting the support you need. From therapeutic interventions and counseling to support groups and peer recovery networks, we’ll uncover the different paths you can take toward recovery. Additionally, we’ll discuss the benefits of rehabilitation programs and treatment centers, as well as medication-assisted treatment options. By understanding these resources, you’ll gain valuable insights into preventing future relapses, building a strong support system, and developing healthy coping mechanisms.
Therapeutic Interventions and Counseling
Therapeutic interventions and counseling play a crucial role in the treatment of relapse. These approaches are designed to target the underlying causes of relapse behaviors and provide individuals with the necessary support and tools to avoid future instances of relapse.
1. Counseling: Trained therapists assist individuals in identifying and addressing the psychological, emotional, and behavioral factors that contribute to relapse. Through cognitive therapy, individuals are able to challenge negative thought patterns and develop healthier coping mechanisms. Counseling also provides a safe space for individuals to process their emotions, gain insight into their addiction, and receive guidance. For example, “structured psychological treatments for depression, particularly cognitive therapy, can reduce subsequent relapse after initial treatment” (Coping Strategies of Female Victims of Child Abuse in Treatment for Substance Abuse Relapse: Their Advice to Other Women and Healthcare Professionals, Smith, 2009.)
2. Group Therapy: Support groups and programs like Alcoholics Anonymous offer individuals a supportive environment where they can share their experiences, struggles, and successes. Being part of a supportive community helps to alleviate feelings of isolation and provides invaluable insight and encouragement.
3. Family Therapy: Involving loved ones in therapy enhances communication, rebuilds trust, and establishes healthier dynamics within the family. Family therapy also educates family members about addiction and equips them with the necessary tools to support the individual’s recovery.
4. Medication-Assisted Treatment: Medications such as methadone or buprenorphine, when combined with counseling and support services, can be effective in assisting individuals dealing with substance use disorders. This type of treatment helps to reduce cravings, manage withdrawal symptoms, and stabilize both physical and mental health.
5. Aftercare Programs: After completing primary treatment, aftercare programs offer ongoing support and guidance. These programs include counseling sessions, support groups, training in relapse prevention skills, and progress monitoring. They are designed to help individuals maintain sobriety and minimize the risk of relapse.
By actively engaging in therapeutic interventions and counseling, individuals can address the root causes of their addiction and develop the necessary skills and support systems to prevent future relapses. Therapy and counseling are essential components of achieving long-term recovery and leading a fulfilling life.
Support Groups and Peer Recovery Networks
Support groups and peer recovery networks are essential for individuals who have experienced relapse on their journey to recovery. These groups provide a safe and understanding environment where people can share their experiences and receive support from others who have faced similar challenges. By participating in support groups and peer recovery networks, individuals can connect with others who have struggled with addiction and find a sense of camaraderie and reassurance, knowing that they are not alone.
The emotional support offered in these groups allows individuals to openly express their feelings without fear of judgment. Members provide empathy, understanding, and encouragement, which boosts morale and motivation. Moreover, support groups and peer recovery networks hold individuals accountable for their actions by offering honest feedback, guidance, and advice to help them stay on track and make positive changes.
In these groups, individuals learn effective coping strategies from others who have successfully overcome relapse. These strategies include mindfulness meditation, grounding techniques, deep breathing exercises, and other self-care practices. By sharing their experiences and the lessons they have learned, individuals in these groups also help prevent future relapses and provide valuable insights to others.
Participating actively in support groups and peer recovery networks allows individuals to develop a strong support system, cultivate essential coping skills, and reduce the likelihood of relapse. These groups serve as a valuable resource throughout the recovery journey, guiding individuals through the challenging process of addiction recovery and supporting them in living a fulfilling and sober life.
Rehabilitation Programs and Treatment Centers
Rehabilitation programs and treatment centers are designed to offer a wide range of therapeutic interventions and counseling services to individuals in need. These programs include various forms of therapy, such as individual therapy, group therapy, family therapy, and specialized therapy modalities like cognitive-behavioral therapy or dialectical behavior therapy. The ultimate goal of these programs is to effectively address the underlying causes of addiction and equip individuals with the necessary tools for their recovery journey.
In addition to therapy, support groups, and peer recovery networks are also seamlessly integrated into these rehabilitation programs. These support systems provide a sense of community, invaluable support, and a strong sense of accountability for those who are struggling with addiction. Moreover, medication-assisted treatment options, such as methadone or buprenorphine combined with counseling and behavioral therapies, are also available to assist individuals in reducing substance use and enhancing their overall well-being.
To ensure a smooth transition back into everyday life, discharge planning is given utmost priority within these programs. This includes the development of relapse prevention strategies, connecting individuals with aftercare resources, and providing ongoing support. The comprehensive treatment approaches employed by rehabilitation programs and treatment centers address not only the physical aspects of addiction but also the mental and emotional aspects. These approaches encompass detoxification, individualized treatment plans, education on addiction and relapse prevention, as well as holistic therapies like mindfulness meditation or mind-body relaxation techniques.
Overall, rehabilitation programs and treatment centers aim to provide individuals with the necessary tools, support, and guidance to overcome addiction and achieve long-term recovery.
Medication-Assisted Treatment Options
When dealing with relapse, medication-assisted treatment options aid recovery and reduce the risk of relapsing. These options include:
- Methadone: Methadone is a synthetic opioid that reduces withdrawal symptoms and cravings. It is administered in an outpatient clinic.
- Buprenorphine: Buprenorphine is a medication prescribed by qualified healthcare providers for opioid addiction. It reduces cravings and withdrawal symptoms.
- Naltrexone: Naltrexone is an opioid receptor antagonist that blocks the effects of opioids. It can prevent relapse by reducing the rewarding effects of opioids during a relapse.
- Antabuse: Antabuse is a medication used to treat alcoholism. It causes unpleasant symptoms, like nausea and vomiting, when alcohol is consumed, discouraging alcohol use.
- Acamprosate: Acamprosate is a medication used to support abstinence in individuals with alcohol addiction. It reduces cravings and stabilizes brain chemistry.
Medication-assisted treatment options should always be used with other therapeutic interventions and support systems. These medications enhance the recovery process. Working closely with healthcare professionals like specialists at Lantana and following a comprehensive relapse prevention plan increases the chances of successful recovery. Seeking support from loved ones and developing healthy coping mechanisms are also crucial components of the recovery journey.
Preventing Future Relapses
To prevent future relapses, it is important to take proactive steps and implement effective strategies. Here are some key measures to consider:
- Identify and manage triggers: It is crucial to recognize the factors or situations that may cause relapse. Make a list of these triggers and develop strategies to either avoid or cope with them.
- Build a strong support system: Surround yourself with a reliable support network comprising family, friends, or support groups. They can offer encouragement, understanding, and guidance during challenging times.
- Practice self-care: Prioritize activities that promote physical, emotional, and mental well-being. This may include engaging in regular exercise, maintaining proper nutrition, getting adequate sleep, practicing mindfulness meditation, or participating in hobbies and activities that bring you joy.
- Develop healthy coping mechanisms: Learn and cultivate skills to effectively deal with stress and emotions. This may involve practicing deep breathing exercises, mindfulness, attending therapy sessions, or utilizing relaxation techniques like grounding exercises.
By implementing these strategies, individuals can significantly reduce the chances of relapse and maintain a healthy and fulfilling life in recovery.
Identifying and Managing Triggers
Identifying and managing triggers is paramount for preventing relapse. By staying mindful of factors that can lead to relapse, individuals in recovery can develop effective coping strategies and diminish their chances of relapse. Here are the essential steps in identifying and managing triggers:
-
Recognize personal triggers: Each person may have different triggers that tempt them to relapse, such as specific individuals, locations, or situations associated with substance use.
-
Avoid high-risk situations: Once personal triggers are identified, it is crucial to steer clear of situations that amplify the risk of relapse, such as particular social gatherings, parties, or places where substance use is prevalent.
-
Develop healthy coping mechanisms: Engaging in activities and coping skills like exercise, mindfulness meditation, deep breathing, or hobbies can effectively manage triggers.
-
Create a support system: Building a strong support network of friends, family, or support groups can provide encouragement, guidance, and accountability when triggers arise.
-
Continuously practice self-care: Take care of physical, emotional, and mental well-being by maintaining a balanced and healthy lifestyle, getting adequate sleep, managing stress, and seeking professional help when needed.
By identifying and managing triggers, individuals can decrease the risk of relapse and sustain their recovery journey. It is important to remember that relapse prevention is a challenging process, but with the right strategies and support, individuals can overcome obstacles and continue on the path to sobriety.
True story: Sarah, who successfully completed an addiction treatment program, identified family gatherings as a trigger for her substance use. She acknowledged that being around certain family members who were still using drugs and alcohol tempted her to relapse. To manage this trigger, she limited her interactions with those family members and attended support group meetings during family events. In doing so, she created a healthier environment for herself and minimized her risk of relapse.
Building a Strong Support System
Building a strong support system is crucial during recovery from a relapse. Reliable and understanding individuals can provide the necessary support and guidance. Here are some strategies to consider:
- Inform your loved ones: Let close friends and family know about your relapse. They can offer emotional support and encouragement during your recovery.
- Join support groups: Participate in self-help groups like Alcoholics Anonymous or Narcotics Anonymous. Connect with others who have faced similar challenges. Share your experiences, gain insights, and receive support from those who understand your struggles.
- Include professionals in your support system: Seek assistance from healthcare providers, therapists, or counselors specializing in addiction recovery like Lantana Recovery in Greenville, SC. They can provide therapeutic interventions, counseling, and relapse prevention tools to help you stay on track.
- Consider an addiction treatment program: Inpatient treatment centers or outpatient programs can offer comprehensive care and support. Address the physical, mental, and emotional aspects of addiction. These programs typically provide relapse prevention skills and coping mechanisms.
- Develop a strong daily routine: Create a structured daily routine that includes healthy habits like exercise, proper nutrition, and sufficient rest. Promote physical health and overall well-being. Engage in activities that bring joy and reduce stress levels.
Building a strong support system is essential for maintaining long-term recovery and reducing the chances of relapse. Surround yourself with individuals who understand your journey and can offer support, guidance, and encouragement. This significantly enhances your chances of overcoming difficulties and achieving a happy and fulfilling life.
Continuously Practicing Self-Care
Practicing self-care is crucial for well-being and relapse prevention. It is important to continuously practice self-care to ensure overall wellness.
- Continuously take care of your physical health by exercising regularly, eating nutritiously, and getting enough sleep. Prioritize activities that boost physical well-being.
- Invest in your mental health by continuously practicing mindfulness meditation or deep breathing exercises to reduce stress and promote relaxation.
- Continuously attend to your emotional needs by journaling or talking to a trusted friend or therapist. Healthy outlets for processing emotions are continuously important.
- Establish a daily routine that includes self-care activities like hobbies, joyful activities, and self-reflection. Continuously prioritize these activities in your daily routine.
- Cultivate a strong support network with positive influences and like-minded individuals through support groups or self-help groups. Continuously seek support and connect with others.
- Practice self-compassion and forgiveness, recognizing that relapse is common. Continuously be kind to yourself and avoid self-judgment.
- Identify high-risk situations and continuously develop coping skills, such as using the 5 4 3 2 1 coping technique or practicing mindfulness-based relapse prevention therapy.
- Seek professional help when necessary, through therapy, counseling, or addiction aftercare programs. Continuously prioritize seeking professional help when needed.
- Continuously acknowledge that self-care is an ongoing process and commit to practicing it daily for personal growth and relapse prevention.
Developing Healthy Coping Mechanisms
When it comes to developing healthy coping mechanisms for relapse, effective strategies exist. Consider the following options:
1. Utilize mindfulness techniques: Mindfulness meditation and grounding techniques bring awareness to the present moment, reducing stress and anxiety.
2. Seek support from a support system: Having a strong support system, such as friends, family, or a support group, provides encouragement and guidance during challenging times.
3. Engage in self-care activities: Taking care of physical and emotional well-being is crucial. This includes regular exercise, a healthy diet, enough sleep, and enjoyable and relaxing activities.
4. Develop healthy coping skills: Identify coping skills that work for you, such as deep breathing exercises, journaling, or engaging in hobbies that distract from substance urges.
5. Build resilience: Focus on building resilience by practicing self-compassion, setting realistic goals, and learning from past experiences. Look for supportive resources and relapse prevention classes near you!
Remember, developing healthy coping mechanisms is an ongoing process. Be patient and seek support from healthcare providers or addiction treatment professionals, if necessary. Consistently implementing these strategies and prioritizing well-being can reduce the chances of relapse and lead to a happier, healthier life.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the stages of relapse?
Relapse occurs in three stages: emotional, mental, and physical. During emotional relapse, individuals are not thinking about using, but their emotions and behaviors set them up for relapse. Signs of emotional relapse include bottling up emotions, isolating, not attending meetings, and poor self-care. Mental relapse involves a war within the mind, where individuals have conflicting desires to use or not. Signs of mental relapse include cravings, thinking about past use, and planning a relapse. Physical relapse is when an individual starts using again, often due to a lapse in self-control.
What are the main triggers for relapse?
Triggers for relapse include stress, boredom, depression, anxiety, and cravings for drugs or alcohol. Life events, both expected and unexpected, can also trigger a relapse. It’s important to identify your personal triggers and develop coping strategies to avoid or manage them.
What should I do if I relapse?
If you relapse, it’s important to reach out for help and support. Contact a treatment provider, counselor, or a supportive person in your life. Be gentle with yourself and avoid shame or self-blame. Use it as an opportunity to learn and strengthen your relapse prevention plan.
What are some coping strategies for preventing relapse?
Coping skills for relapse prevention include distracting oneself with other activities, talking to a supportive person, releasing negative feelings in a non-destructive way, treating oneself to something nice, writing in a journal, practicing gratitude, reaching out to a support system, finding a sponsor or role model, attending support group meetings, exercising regularly, eating a healthy diet, and getting enough sleep. Thinking of addiction as a bully and not giving it power can also help in avoiding relapse.
Why is post-acute withdrawal syndrome (PAWS) a concern after relapse?
Post-acute withdrawal syndrome (PAWS) refers to a prolonged period of withdrawal symptoms that can occur after the acute phase of withdrawal. If you relapse, you may experience PAWS, which can make recovery more challenging. It’s important to seek professional help and support to manage PAWS and prevent further relapses.
Why is it crucial to have an emergency contact list after a relapse?
An emergency contact list is important because it provides you with a network of healthy family members or friends who can provide support when cravings arise. These contacts understand the challenges of recovery and can offer guidance and encouragement. Having a support system in place increases your chances of staying sober and getting back on track after a relapse.









