Addiction is a complex and multifaceted phenomenon that affects individuals across various aspects of their lives. It is crucial to have a comprehensive understanding of addiction in order to effectively address and support those struggling with it. In this in-depth exploration of the concept of addiction, we will delve into its definition, causes, the science behind it, common types, signs and symptoms, impact, treatment, and prevention strategies.
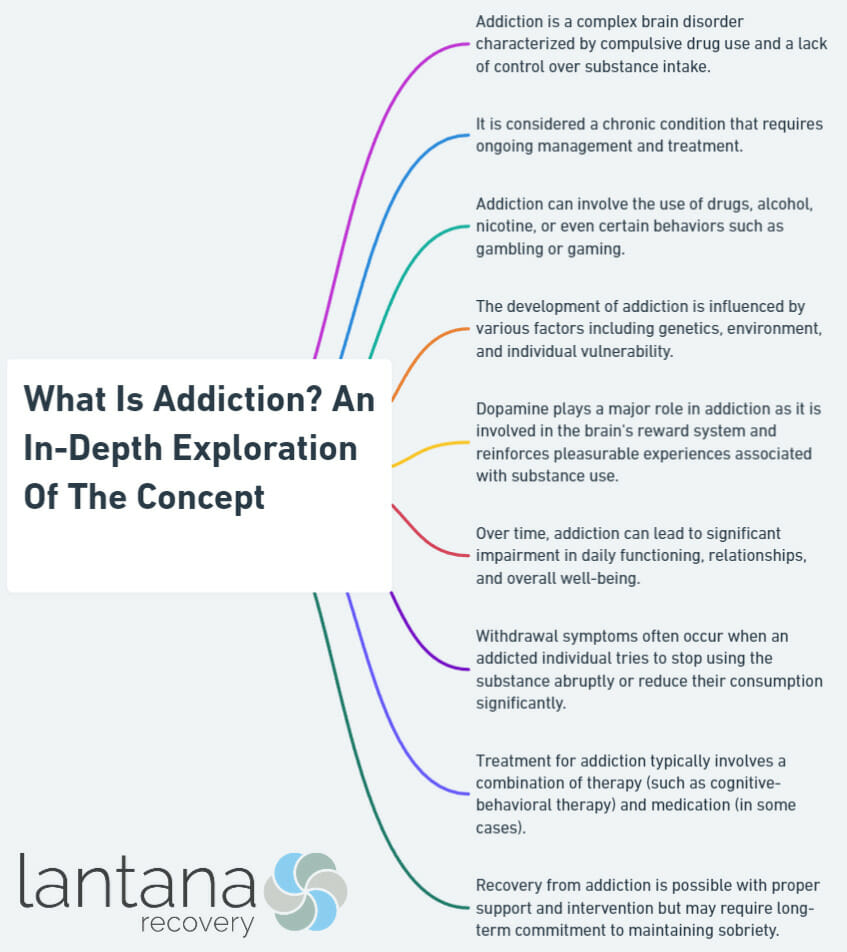
Understanding addiction begins with defining the term itself. Addiction can be described as a chronic and relapsing brain disorder characterized by compulsive drug seeking and use, despite harmful consequences. It is both a behavioral and physiological phenomenon that involves changes in the brain’s reward circuitry.
There are different types of addiction that individuals can experience. Substance addiction, such as drugs and alcohol, is perhaps the most well-known. However, behavioral addictions, such as gambling, gaming, or compulsive shopping, can also have a profound impact on individuals’ lives.
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of addiction is crucial for early intervention. These symptoms can manifest physically, psychologically, and socially. Physical symptoms may include tolerance and withdrawal, while psychological symptoms may involve cravings, impaired judgment, and emotional instability. Social and behavioral symptoms may manifest as secrecy, isolation, and strained relationships.
The impact of addiction extends to various aspects of an individual’s life. Health consequences can range from physical ailments to mental health disorders. Relationships and social life often suffer due to strained interactions and a lack of trust. addiction can negatively impact work, school, and financial stability.
Treatment and recovery play a vital role in combating addiction. Seeking professional help is often necessary, and there are several treatment approaches available, including therapy, medication, and support groups. Building a strong support system is essential for sustaining recovery and preventing relapse.
Prevention strategies focus on educating individuals about the risks and consequences of addiction through educational programs. Early intervention is crucial in identifying and addressing risk factors before addiction develops. Building resilience and fostering healthy coping mechanisms can also be effective prevention strategies.
By exploring addiction from various angles, we can gain a deeper understanding of this complex issue and contribute to fostering a healthier and more supportive environment for individuals struggling with addiction.

Understanding Addiction
Addiction, a complex and pervasive phenomenon that affects millions worldwide. In this section, we’ll dive deep into understanding addiction, exploring its defining characteristics and uncovering its underlying causes. Brace yourself for a thought-provoking journey as we dissect this intricate subject and shed light on what drives individuals down the path of addiction. So grab a cup of coffee, fasten your seatbelt, and prepare to unravel the mysteries of this captivating topic.
Defining Addiction
Defining addiction is crucial as it is a complex condition characterized by compulsive engagement in a substance or behavior, despite negative consequences. Addiction involves a loss of control, making it difficult for individuals to restrain their use of substances or engagement in behaviors. This chronic condition affects the brain’s reward system, leading to persistent cravings and a strong desire to repeat the behavior.
Furthermore, individuals with addiction often prioritize substance use or addictive behaviors above other aspects of their lives, including relationships, work, and health. It is important to note that addiction is not simply a matter of willpower or character flaw. It is influenced by genetic predisposition and environmental factors.
Addiction can manifest in different forms, such as substance addiction (involving drugs or alcohol) or behavioral addiction (involving activities like gambling or gaming). Understanding the definition of addiction helps to recognize its signs and symptoms. Some indicators include tolerance, withdrawal symptoms upon discontinuation, and unsuccessful attempts to cut down or control substance use or behavior.
By defining addiction clearly, individuals and healthcare professionals can take appropriate steps to address it, seek professional help, and promote recovery and well-being. If you suspect someone is struggling with addiction, it is important to seek professional help and support. Addiction is a treatable condition, and recovery is possible with the right assistance and resources.
The Causes of Addiction
The causes of addiction can be complex. Addiction is not solely a result of personal choice or moral failing, but rather a combination of various factors. Here are some key factors that contribute to addiction:
1. Genetic predisposition: According to American Psychological Association, genes play a significant role in developing substance abuse disorder as some individuals may be more susceptible due to their genetic makeup.
2. Environmental factors: The environment can play a significant role in addiction development. Factors such as drug use exposure, unstable family dynamics, and trauma can increase the risk.
3. Mental health disorders: Individuals with depression, anxiety, or ADHD are more likely to develop addiction. Substance use may be a way to self-medicate or cope with symptoms.
4. Peer influence: Peer pressure and the influence of friends or social groups can contribute to addiction. Individuals may be more likely to use substances if surrounded by peers who also do.
5. Lack of coping skills: Some individuals turn to substances to cope with stress or emotional pain. Inability to effectively manage stress can contribute to addiction.
6. Early exposure: The age at which a person first experiments with drugs or alcohol can impact their risk. Starting substance use earlier increases the risk of addiction later in life.
Understanding the causes of addiction is crucial for developing prevention and treatment strategies. By addressing these factors, we can reduce the impact of addiction on individuals and society.

The Science Behind Addiction
Delve into the fascinating world of addiction as we explore the science behind this complex phenomenon. Unravel the intricate relationship between addiction and the brain, the impact of dopamine and reward circuitry, and the interplay of genetic and environmental factors. Discover the compelling research and insightful findings that shed light on the inner workings of addiction. Get ready for a captivating journey into the science behind addiction and gain a deeper understanding of this pervasive issue.
How Addiction Affects the Brain
Addiction rewires neural pathways. Substance addiction alters the brain’s structure and function. Prolonged substance abuse changes the wiring of the brain’s reward system, making individuals more susceptible to cravings and compulsive drug-seeking behavior.
Dopamine plays a crucial role. Dopamine, a neurotransmitter associated with pleasure and reward, is heavily involved in addiction. Substance abuse triggers the release of dopamine, leading to feelings of euphoria. Over time, the brain becomes reliant on the substance to release dopamine, leading to addiction.
Genetic and environmental factors contribute. Addiction is influenced by genetic and environmental factors. Some individuals have a genetic predisposition to addiction, making them more susceptible to substance abuse disorders. Environmental factors, such as stress or exposure to substance abuse, can also contribute to addiction by affecting brain chemistry.
The science behind addiction reveals how it affects the brain. As per a recent neuroscientific study by Nora D. Volkow (Director of National Institute of Drug Abuse) and colleagues titled The Neuroscience of Drug Reward and Addiction, addiction hijacks the brain’s natural reward and motivation systems, primarily involving the neurotransmitter dopamine and other related chemicals. Genetic and environmental factors also play a significant role in a person’s vulnerability to addiction.
Addiction affects cognitive function. Prolonged drug or alcohol abuse can impair cognitive function, including memory, attention, and decision-making. Changes in the brain’s structure and function caused by addiction can result in difficulties in controlling impulses and making sound judgments.
Withdrawal symptoms and cravings. When addicted individuals try to stop using the substance, they often experience withdrawal symptoms and intense cravings. These cravings are a result of the brain’s adaptation to the substance and its reliance on it to function properly.
Understanding how addiction affects the brain helps develop more effective treatments and interventions. By targeting the neurological aspects of addiction, it becomes possible to address the underlying causes and promote recovery.
Dopamine and Reward Circuitry
Dopamine and reward circuitry play a crucial role in addiction. The brain’s reward system is reinforced by pleasurable behaviors and is influenced by the release of dopamine. When individuals engage in rewarding activities, like drug use or certain behaviors, dopamine is released in the brain.
1. Dopamine release: In the brain, drugs and specific behaviors trigger the release of dopamine. This release generates pleasure and reinforces the behavior, making it more likely to occur again.
2. Reward pathway: The brain’s reward pathway, which includes the prefrontal cortex, limbic system, and nucleus accumbens, involves dopamine. This pathway regulates emotions, motivation, and pleasure.
3. Sensitization: Repeated exposure to addictive substances or behaviors sensitizes the reward circuitry. This sensitivity increases the responsiveness to the substance or behavior, thus raising the risk of addiction.
4. Cravings and withdrawal: Dopamine also plays a role in cravings and withdrawal symptoms. When individuals with addiction cease using the substance or engaging in the behavior, dopamine levels decrease, resulting in intense cravings and withdrawal symptoms.
5. Tolerance: Dopamine is also involved in the development of tolerance. Continued substance use or addictive behaviors cause the brain to adapt by reducing dopamine receptors. This adaptation necessitates larger amounts of the substance or behavior to achieve the same level of pleasure.
Understanding the role of dopamine and reward circuitry in addiction is crucial for the development of effective treatment and prevention programs. By targeting the reward system and dopamine release, interventions can assist individuals in overcoming addiction and restoring balance to the brain’s reward system.
Genetic and Environmental Factors
Genetic and environmental factors play a significant role in the development of addiction. It is important to consider the following key points:
1. Genetic factors: Certain genes can increase vulnerability to addiction. Research indicates that individuals with a family history of addiction have a higher risk of developing it. Genetic variations impact the brain’s reward system, making some individuals more susceptible to the effects of substances.
2. Environmental factors: The environment in which a person grows up contributes to their risk of addiction. Factors such as peer influence, exposure to traumatic events, availability of drugs, and socioeconomic status can all influence the likelihood of developing addiction. Research with rodents and humans suggests that “heavy use of alcohol during adolescence can result in neurocognitive changes that increase the likelihood of subsequent abuse of alcohol in adulthood.” (Genetic and Environmental Risk Factors for Adolescent-Onset Substance Use Disorders, Meyers, Dick, 2013)
3. Interaction between genetics and environment: Genetics and environment interact in complex ways. While genetics may predispose someone to addiction, the environment can either enhance or mitigate this risk. A supportive and stable family environment can help protect against the development of addiction.
4. Epigenetics: Epigenetic modifications, including DNA methylation, are influenced by both genetics and the environment. These modifications regulate gene expression and have the potential to impact susceptibility to addiction.

Common Types of Addiction
Addictions come in various forms, each with its own unique characteristics and impact. In this section, we’ll dive into the common types of addiction, exploring substance addiction, behavioral addiction, and the signs and symptoms that accompany this complex condition. Brace yourself for an eye-opening journey as we uncover the gripping realities behind these addictive behaviors, shedding light on the challenges individuals face in their daily lives. Let’s uncover the truth about addiction together!
Substance Addiction
Substance addiction is a complex issue that affects individuals in various ways. Here are some key points to consider:
- Definition: Substance addiction, also known as drug or alcohol addiction, is the compulsive and uncontrollable use of substances despite negative consequences. It is characterized by a physical and psychological dependence on these substances.
- Causes: Substance addiction can have multiple causes, including genetic predisposition, environmental factors, and mental health issues. It is important to note that substance addiction is a disease and not simply a result of weak willpower.
- Physical Symptoms: Substance addiction can manifest through cravings, withdrawal symptoms, increased tolerance, and the inability to control or reduce substance use.
- Psychological Symptoms: Individuals with substance addiction may experience increased anxiety, depression, mood swings, and impaired judgment and decision-making.
- Social and Behavioral Symptoms: Substance addiction can significantly impact an individual’s social life and relationships, leading to strained relationships, difficulties at work or school, financial problems, and a loss of interest in once-enjoyable activities.
Understanding substance addiction is crucial for developing effective prevention strategies and providing support for individuals struggling with substance addiction.
Behavioral Addiction
Behavioral addiction refers to compulsive behaviors that interfere with daily life. These addictions do not involve substances but are characterized by a strong impulse to engage in a certain behavior.
- Gaming addiction: Excessive involvement in playing video games. It can lead to neglect of responsibilities, poor performance, and a decline in social interactions.
- Internet addiction: Excessive use of the internet, leading to neglect of important tasks and social isolation.
- Compulsive gambling: Uncontrollable urge to gamble, leading to financial problems, relationship issues, and legal troubles.
- Compulsive shopping: Excessive and uncontrollable urge to shop and spend money. It can lead to financial difficulties and strained relationships.
- Food addiction: Unhealthy relationship with food, leading to weight gain, emotional distress, and health problems.
- Sleep addiction: Sleep addiction, also known as sleep onset association disorder, is a condition where individuals become excessively dependent on specific actions or conditions to fall asleep. This behavioral sleep disorder can involve relying on external stimuli like screens, music, or certain bedtime rituals, leading to difficulties in falling asleep without them.
Recognize the signs of behavioral addiction and seek help if needed. Treatment options include therapy, counseling, support groups, and behavioral interventions to regain control over these compulsive behaviors.
The Signs and Symptoms of Addiction
- Physical Symptoms: Common physical symptoms of addiction include increased tolerance, withdrawal symptoms, changes in appetite or weight, and deteriorating physical health.
- Psychological Symptoms: Addiction can also manifest in intense cravings, difficulty controlling or stopping substance use, impaired judgment, and withdrawal symptoms when attempting to quit.
- Social and Behavioral Symptoms: Addiction often leads to changes in social behavior such as withdrawal from social activities, strained relationships, neglecting responsibilities, and engaging in secretive or deceptive behavior to obtain or use the substance.
Did you know that addiction is a complex brain disease that affects both the brain and behavior? It is characterized by compulsive substance use or engaging in certain behaviors, despite harmful consequences.
Physical Symptoms
Physical symptoms often accompany addiction and can vary depending on the substance or behavior involved. These physical symptoms serve as warning signs of addiction. When addicted individuals try to stop using the substance or engaging in the behavior, they may experience withdrawal symptoms, such as nausea, tremors, sweating, and muscle aches.
Many people with addiction may also have changes in appetite and sleep patterns. Some may experience a decreased appetite and significant weight loss, while others may have an increased appetite and weight gain. Sleep disturbances, including insomnia and oversleeping, are also common. Substance abuse can cause gastrointestinal issues, including nausea, vomiting, constipation, and diarrhea. These symptoms can result from the substances’ direct effects on the digestive system or be a side effect of addiction treatment medication.
Addiction can negatively impact physical health, leading to a weakened immune system, frequent illnesses, and poor wound healing. Substance abuse can also contribute to chronic pain or worsen existing pain conditions, making it difficult for individuals to stop using substances and seek recovery. Recognizing these physical symptoms is crucial for identifying and addressing addiction.
Seeking professional help and support systems for recovery can assist individuals in managing and overcoming these physical symptoms, resulting in improved overall health and well-being.
Psychological Symptoms
Psychological symptoms significantly impact the mental well-being of individuals struggling with addiction. These symptoms, which vary in intensity, encompass several key aspects:
-
Cravings: Addiction triggers intense cravings for the addictive substance or behavior. These cravings bring about obsessive thoughts and difficulties in maintaining focus.
-
Emotional instability: Addiction causes mood swings, irritability, and heightened levels of anxiety or depression. These emotional fluctuations disrupt daily life and strain relationships.
-
Compulsive behaviors: Addiction drives individuals to engage repeatedly in the addictive substance or behavior, despite experiencing negative consequences. This loss of control makes it incredibly challenging to break free from addiction.
-
Withdrawal symptoms: When individuals attempt to quit or reduce substance use, they experience restlessness, irritability, insomnia, and intense cravings. These symptoms add an extra layer of difficulty in overcoming addiction.
-
Denial and avoidance: Many individuals with addiction tend to deny or avoid acknowledging the existence of the problem. They often downplay or rationalize their behavior, making it challenging to recognize the severity and seek appropriate help.
Addressing these psychological symptoms and seeking professional help is an essential step in successfully overcoming addiction. With the right treatment and support, individuals can regain control over their lives and improve their overall mental well-being.
Social and Behavioral Symptoms
Addiction often presents social and behavioral symptoms that heavily impact personal and social lives. Some examples of these symptoms include:
- Social withdrawal and isolation: Individuals with addiction may withdraw from social activities, hobbies, and relationships and prefer to spend time alone or engage in addictive behaviors.
- Neglecting important responsibilities: Addiction often leads to neglecting important responsibilities like work, school, or family obligations, resulting in missed deadlines, skipped school or work, and difficulties in meeting commitments.
- Financial instability: Addictive behaviors can be costly, leading to financial problems or debt due to excessive spending on substances or engaging in addictive behaviors.
- Changes in social circles: Addiction can cause individuals to gravitate towards peers who enable or engage in addictive behaviors, resulting in a distancing from concerned friends or family members.
- Risky behaviors: People with addiction may engage in activities they would typically avoid, such as driving under the influence, unprotected sex, or participating in illegal activities to obtain substances.
It’s crucial to seek professional help if you or someone you know is experiencing these social and behavioral symptoms associated with addiction. Please note that these symptoms may vary depending on the individual and the specific addiction.

The Impact of Addiction
Addiction can have a profound impact on various aspects of our lives. From our health and relationships to work and finances, its influence is far-reaching. In this section, we’ll dive into the consequences of addiction, exploring its effects on our physical well-being, the dynamics of our relationships and social life, as well as the toll it takes on our work, school, and financial stability. Brace yourself for an eye-opening exploration of the true cost of addiction.
Health Consequences
The health consequences of addiction can have severe implications and affect an individual’s well-being. Some of the health consequences that can emerge from addiction include:
-
Physical health issues: Addiction to drugs and alcohol can have adverse effects on the liver, cardiovascular system, respiratory system, immune function, and increase the risk of infectious diseases like HIV/AIDS or hepatitis.
-
Mental health disorders: Addiction is frequently linked to co-occurring mental health disorders such as depression, anxiety, and psychosis. Substance abuse can exacerbate existing mental health conditions or even trigger the onset of new ones.
-
Increased risk of injuries: Substance abuse can impair judgment and coordination, leading to a higher possibility of accidents and injuries. Intoxication or impaired decision-making can contribute to incidents such as falls, car accidents, and self-inflicted harm.
-
Neurological damage: Prolonged drug or alcohol abuse can cause significant harm to the brain, resulting in cognitive impairments, memory issues, difficulties in concentration, and a decline in overall brain function.
-
Poor nutrition and organ damage: Substance addiction can disrupt eating patterns, resulting in malnourishment, weight fluctuations, vitamin deficiencies, and harm to organs like the liver and kidneys.
-
Increased vulnerability to other diseases: Drug abuse can weaken the immune system, rendering individuals more susceptible to infections, certain cancers, and other chronic health conditions.
The health consequences of addiction underscore the significance of seeking timely help and support to address the underlying causes and break free from the harmful cycle of substance abuse.
According to the 2019 National Survey on Drug Use and Health, approximately 20.2 million adults in the United States had a substance use disorder in 2019. This highlights the widespread impact of addiction in our society. It is important to approach addiction with empathy and understanding, as it is a complex issue that requires comprehensive support and treatment. By addressing the underlying causes and providing effective interventions, we can help individuals overcome addiction and lead healthy lives.
Relationships and Social Life
In relationships and social life, addiction can significantly impact individuals. It strains relationships with family, friends, and romantic partners, causing conflicts and trust issues. Substance addiction causes individuals to prioritize obtaining and using drugs or alcohol over maintaining healthy connections, resulting in feelings of isolation and loneliness.
Moreover, addiction leads to social consequences like job loss, financial instability, and legal issues. Individuals neglect their responsibilities, straining work relationships and negatively impacting their professional lives. Additionally, addiction is costly and can lead to financial difficulties.
Furthermore, addiction affects overall social functioning. Individuals withdraw from social activities and hobbies they once enjoyed, choosing substance use or addictive behaviors instead. This isolation worsens feelings of loneliness and perpetuates the addiction cycle.
However, it’s important to remember that recovery and treatment can help rebuild and cultivate healthier connections within relationships and social life. Seeking professional help and accessing support systems are crucial steps towards regaining social functioning. Strong support systems, therapy, and community resources aid in developing healthier coping mechanisms and rebuilding relationships damaged by addiction.
Work, School, and Finances
When it comes to addiction, it can significantly impact work, school, and finances. Consider the following:
- Work: Addiction greatly affects an individual’s ability to perform well, leading to absences, decreased productivity, and impaired decision-making. It can strain relationships with colleagues and result in demotion or job loss.
- School: Addiction has severe consequences for students, including poor academic performance, increased absenteeism, and difficulty concentrating. Students struggling with addiction may face disciplinary actions or be at risk of dropping out.
- Finances: Addiction takes a toll on an individual’s financial situation. Substance abuse is expensive, leading to financial instability and debt. Neglecting financial responsibilities can worsen the issue, putting individuals at risk of financial hardship and bankruptcy.
Treatment and Recovery
Seeking professional help, exploring different treatment approaches, and building a robust support system are key elements in the journey of addiction treatment and recovery. In this section, we’ll dive into the various strategies and resources available to individuals grappling with addiction. Whether it’s through therapy, medications, or community programs, finding the right path towards recovery requires understanding the available options and building a strong network of support. Let’s explore the tools and approaches that can pave the way towards a healthier and more fulfilling life.
Seeking Professional Help
Seeking professional help is essential for individuals grappling with addiction. Finding the right professional is key in this process. It is crucial to seek assistance from qualified and experienced counselors, therapists, or doctors who specialize in addition treatment and have expertise in addiction and recovery.
One of the first steps in seeking professional help is undergoing a comprehensive assessment and diagnosis. This evaluation helps professionals understand the severity of the addiction, identify underlying causes, and develop an appropriate treatment plan.
Professionals offer a range of tailored treatment options, including therapy, medication-assisted treatment, support groups, and evidence-based approaches. They recommend the most effective treatment plan based on the assessment conducted.
Throughout the recovery journey, professional help provides valuable support and guidance. Regular counseling, therapy sessions, and check-ins are offered to monitor progress and provide assistance.
A holistic approach is taken by professionals when treating addiction. They address not only the physical aspects but also the psychological and social aspects of well-being. The focus is on cultivating long-term recovery and overall wellness.
Seeking professional help ensures confidentiality and privacy. Professionals adhere to strict ethical codes and regulations to protect client privacy.
Remember, taking the brave step of seeking professional help is vital for overcoming addiction and achieving a healthier, happier life.
Types of Treatment Approaches
When treating addiction, there are various effective approaches. Here are some common types:
1. Medication-Assisted Treatment (MAT): This approach combines medication, such as methadone or buprenorphine, with counseling and behavioral therapies. MAT is often used for opioid addiction and helps manage withdrawal symptoms and cravings.
2. Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT): CBT helps individuals identify and change negative thoughts and behaviors associated with addiction. It focuses on developing coping skills, managing triggers, and preventing relapse.
3. 12-Step Programs: Programs like Alcoholics Anonymous (AA) and Narcotics Anonymous (NA) follow a structured set of principles and offer support from peers who have also struggled with addiction. They emphasize accountability, self-reflection, and spiritual growth.
4. Motivational Interviewing: This approach aims to enhance an individual’s motivation to change by exploring their thoughts and feelings about addiction. It involves empathetic listening, supporting self-efficacy, and resolving ambivalence.
5. Contingency Management: This treatment uses positive reinforcement to motivate individuals to abstain from substance use. They receive rewards or incentives for meeting specific treatment goals, such as passing drug tests or attending therapy sessions.
It’s important to note that each person’s recovery journey is unique, and what works for one may not work for another. Consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most suitable treatment approach.
In addition to these treatment approaches, here are suggestions to maximize the effectiveness of addiction treatment:
- Commit to the treatment plan and actively participate in therapy sessions.
- Build a strong support system of family, friends, or support groups who understand and provide encouragement.
- Avoid triggers and high-risk situations that could lead to relapse.
- Practice self-care and engage in activities that promote overall well-being and reduce stress.
- Stay connected to treatment resources and continue to educate yourself about addiction and recovery.
Support Systems for Recovery
Support Systems for Recovery are crucial in helping individuals overcome addiction and maintain long-term sobriety. These systems offer various forms of assistance and support to individuals on their recovery journey. Here are some important aspects to consider:
1. Peer Support: Peer support groups like Alcoholics Anonymous (AA) or Narcotics Anonymous (NA) provide a safe and non-judgmental space for individuals to share their experiences, receive support, and learn from others who have been through similar struggles.
2. Counseling and Therapy: Counseling and therapy provide individuals with tools and coping strategies to address underlying issues that contribute to addiction. Therapists can help individuals manage triggers and stressors that might lead to a relapse.
3. Sober Living Houses: Sober living houses are structured environments where individuals in recovery live in a supportive community that emphasizes sobriety. These houses offer a drug-free living environment and provide accountability and support during the early stages of recovery.
4. Family and Friends: The support of loved ones is crucial in the recovery process. Family and friends can offer emotional support and encouragement, and help individuals navigate challenges and make healthy choices.
5. Aftercare Programs: After completing a treatment program, aftercare programs provide ongoing support to help individuals maintain sobriety. These programs may include regular check-ins, counseling sessions, and access to resources and referrals.
It is important to note that everyone’s recovery journey is unique, and different individuals may require different types and levels of support. With the right support systems in place, individuals can enhance their chances of successful recovery and regain control of their lives.
Prevention Strategies
Prevention is always better than cure! In this section, we’ll dive into the various strategies to combat addiction. From educational programs that aim to equip individuals with knowledge and awareness, to early intervention efforts that catch addiction in its early stages, and building resilience to strengthen individuals against the pull of addictive behaviors. So let’s explore these powerful prevention approaches and take proactive steps towards a healthier and addiction-free future!
Educational Programs
Educational programs play a vital role in addressing addiction. They aim to raise awareness, provide knowledge, and promote prevention strategies. When discussing these programs, it is important to consider the following:
1. Informative content: Educational programs should provide accurate and up-to-date information on addiction, including its causes, effects, and available treatment options. They should cover various types of addiction, such as substance and behavioral addiction.
2. Evidence-based approach: It is crucial to base educational programs on scientific research and evidence. Credible sources and expert opinions should be relied upon to ensure the accuracy and effectiveness of the programs.
3. Targeted audience: Educational programs should be tailored to specific audiences, such as schools, workplaces, healthcare providers, and community organizations. They should address the unique needs and challenges faced by each audience.
4. Interactive and engaging methods: To enhance understanding and retention, educational programs should utilize interactive methods such as presentations, discussions, workshops, and multimedia resources.
5. Encouraging open dialogue: Educational programs should create a safe and non-judgmental space for discussing addiction. The goal should be to reduce stigma associated with addiction and encourage help-seeking behavior.
6. Collaboration and partnerships: Collaborating with schools, healthcare providers, community organizations, and law enforcement agencies can strengthen the impact of educational programs. It ensures a comprehensive approach to addiction prevention and treatment.
7. Evaluation and continuous improvement: Regular evaluation of program effectiveness is crucial. Based on feedback and outcomes, necessary adjustments should be made to ensure that the programs remain relevant and impactful.
8. Promotion of healthy coping mechanisms: Educational programs should focus on promoting healthy coping mechanisms and resilience-building strategies. This includes stress management, emotional regulation, and positive peer influences.
By incorporating these key elements, educational programs can effectively address addiction and contribute to the well-being of individuals and communities.
Early Intervention
Early intervention plays a pivotal role in addressing and managing addiction, as research emphasizes its significant impact on improving outcomes for individuals struggling with addiction. By promptly identifying and addressing addiction, individuals are more likely to achieve successful recovery.
One crucial aspect of early intervention is raising awareness and educating people about the warning signs of addiction. These signs encompass physical symptoms like changes in appetite or sleep patterns, psychological symptoms like mood swings or irritability, and social and behavioral symptoms like withdrawal from social activities or engagement in risky behaviors.
Early intervention also involves implementing strategies to halt the progression of addiction. This may entail offering resources and support networks for individuals at risk, such as counseling services or support groups. Additionally, it involves promoting resilience and developing coping skills to assist individuals in managing stress and averting substance use or addictive behaviors.
Moreover, early intervention may necessitate the involvement of addiction counselors or therapists. These professionals can conduct assessments, provide interventions, and devise personalized treatment plans to aid individuals in navigating the challenges of addiction and recovery.
Building Resilience
Building resilience is crucial for overcoming challenges and adversities in life. Here are some strategies to help in building resilience:
-
Embrace a positive mindset: Maintaining a positive outlook greatly impacts your ability to bounce back from difficult situations. Focus on the opportunities within adversity and cultivate gratitude for what you have.
-
Seek support: Building a strong support system is crucial during periods of stress. Surround yourself with trusted friends, family, or mentors who offer encouragement, empathy, and guidance. Sharing your thoughts and feelings with them helps navigate tough times.
-
Practice self-care: Taking care of your physical, emotional, and mental well-being is vital for resilience. Engage in activities that bring you joy and help you relax. Prioritize sleep, exercise regularly, and eat a balanced diet.
-
Develop problem-solving skills: Building resilience involves learning how to effectively solve problems and make decisions. Break challenges into manageable tasks and focus on finding practical solutions instead of dwelling on the problem itself.
-
Cultivate adaptability: Life is full of unexpected twists and turns, and being adaptable helps navigate uncertainties. Embrace change, learn from past experiences, and develop flexibility in your thinking and actions.
-
Foster a strong sense of purpose: Having a clear sense of purpose and meaning in life provides motivation and resilience during difficult times. Identify your values, set achievable goals, and work towards them with determination and perseverance.
Remember, building resilience is a continuous process that requires effort and self-reflection. By implementing these strategies, you can enhance your ability to adapt, grow, and thrive in the face of adversity.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is addiction and how is it defined by the American Society of Addiction Medicine?
Addiction is a treatable, chronic medical disease characterized by compulsive substance use or behaviors, despite harmful consequences. The American Society of Addiction Medicine (ASAM) defines addiction as a complex condition involving brain circuits, genetics, the environment, and an individual’s life experiences.
What are the causes and risk factors for addiction?
Addiction can be influenced by various factors, including genetics, brain circuits, environment, and life experiences. Risk factors for addiction include early life experiences such as childhood abuse or exposure to parental substance misuse, as well as genetic predispositions to addictive behaviors.
How are addiction and mental health related?
There is a bidirectional relationship between addiction and mental health. Individuals may use substances to cope with mental health issues, and addiction can worsen mental health conditions. Substance use can provide temporary relief but ultimately exacerbate mental health problems.
What are the main treatment approaches for addiction?
Treatment approaches for addiction include comprehensive support services that address both mental health and substance use issues. These may involve a combination of counseling, therapy, medication, and recovery support services. These treatments can either be received in an inpatient or an outpatient rehab by Lantana Recovery in Charleston. It is important to consider early intervention, prevention strategies, and access to evidence-based treatment services.
What is the role of stigma and barriers to treatment in addiction?
Stigma surrounding addiction can create barriers to treatment, limiting access and contributing to the negative perception of individuals with addiction. Limited availability of treatment services can also pose challenges. However, accessing treatment is beneficial, providing necessary support and a non-judgmental environment for recovery.
What are the consequences of substance misuse and addiction?
Substance misuse and addiction have devastating consequences, including negative impacts on individuals’ physical and mental health, relationships, employment, and overall quality of life. Substance misuse also imposes significant economic costs on society, contributing to healthcare expenses, crime, and lost productivity.









