Addiction is a complex and multi-faceted issue that affects individuals globally. It is important to understand the various factors and motivations that contribute to the development and perpetuation of addiction. By examining these factors and motivations, we can gain insight into the underlying causes and explore effective strategies for treatment and recovery. In this article, we will delve into the reasons for addiction and examine the different factors that play a role in its occurrence. We will explore genetic factors, environmental factors, and psychological factors that contribute to the vulnerability of addiction.
We will investigate the motivations that drive individuals towards addictive behaviors, such as seeking pleasure and reward, using addiction as a coping mechanism, succumbing to social influences and peer pressure, and seeking self-medication.
Furthermore, we will investigate the intricate relationship between mental health and addiction, as individuals with mental health disorders may be more susceptible to addictive behaviors. Understanding this relationship is vital in developing holistic treatment approaches and providing appropriate support. The effects and consequences of addiction can be far-reaching, impacting not only the individuals themselves but also their families, communities, and society as a whole. We will explore the detrimental effects of addiction on physical and mental health, relationships, and overall well-being. Finally, we will discuss the available treatment and recovery options for individuals struggling with addiction. From therapy and support groups to medications and rehabilitation programs, there are various resources and approaches that can aid in overcoming addiction and achieving long-term recovery.

Understanding Factors of Addiction
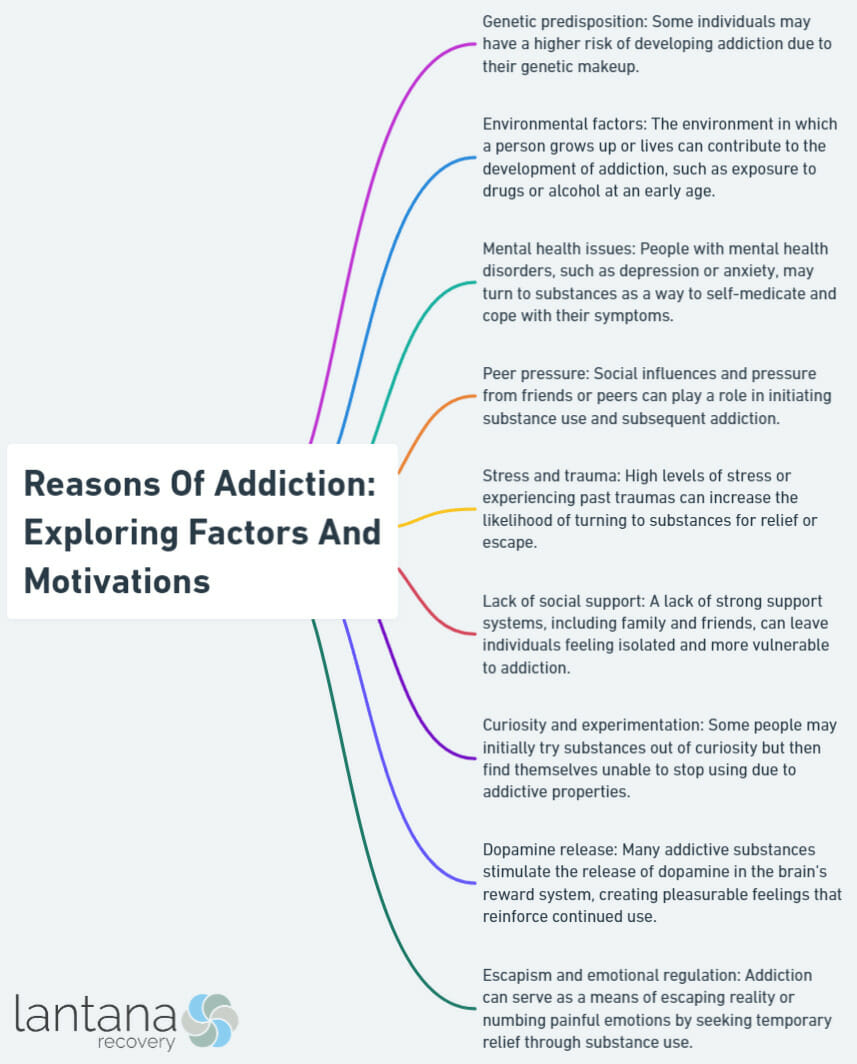
Addiction is a complex phenomenon influenced by various factors. In this section, we will deep dive into the fundamental aspects of addiction by examining its key factors. From genetics and environmental influences to psychological elements, we will uncover the intricate interplay between these factors, shedding light on why addiction manifests in different individuals and how.
Genetic Factors
Genetic factors play a significant role in the development of addiction. Research has shown that specific genes can predispose individuals to addiction by influencing the likelihood of developing substance use disorders and the response to different substances. Variations in the dopamine receptor gene (DRD2) are one important genetic factor that increases the risk of addiction.
Dopamine, a neurotransmitter involved in the brain’s reward system, is influenced by these gene variations and affects how the brain responds to rewards, which in turn makes individuals more inclined to seek substances for pleasure.
Additionally, addiction has been found to have a hereditary nature, as research indicates that it tends to run in families, highlighting the influence of genetic components. If an individual has a parent or sibling with addiction, their own likelihood of developing addiction increases.
However, it is important to note that while genetic factors contribute to vulnerability, they do not solely determine a person’s destiny. Environmental factors and individual choices also play a significant role in addiction development.
If someone has a family history of addiction, it is important for them to be aware of their increased susceptibility and develop healthy coping mechanisms, and seek support in order to decrease the risk. Educating oneself about addiction is also crucial in order to make informed choices regarding substance use.
Environmental Factors
Environmental factors play a significant role in contributing to addiction. These factors encompass external influences and circumstances that heighten the likelihood of drug or alcohol addiction. Understanding these factors is crucial for preventing and addressing addiction in individuals.
One key factor is the availability of drugs or alcohol in a particular environment, which strongly influences the risk of addiction. When substances are easily accessible, individuals are more prone to experiment with and regularly use them.
Another factor is peer influence, whereby social norms and peer pressure within a person’s social circle can impact their substance use. If peers engage in drug or alcohol use, individuals may feel compelled to join in to fit in or gain acceptance. “Several risk factors include early mental and behavioral health problems, peer pressure, under-resourced schools, poverty, inadequate parental supervision and relationships, unstable family structure, limited opportunities, social isolation, gender influences, and easy accessibility to drugs” (Risk and protective factors of drug abuse among adolescents: a systematic review, Nawi et al., 2021.)
Family dynamics also play a crucial role in addiction development. Growing up in a household where substance abuse is prevalent increases the risk of addiction. Factors such as parental neglect, abuse, or substance use contribute to an individual’s vulnerability to addiction.
Additionally, stressful environments can increase an individual’s susceptibility to using drugs or alcohol as a coping mechanism. High levels of stress, trauma, or adversity can trigger substance use as a way to escape or numb emotional pain. Stressful life events like divorce, loss, or financial difficulties can intensify this vulnerability.
Moreover, community factors such as poverty, crime rates, and lack of access to resources can contribute to addiction. Individuals residing in disadvantaged communities may face more stressors and have fewer opportunities for healthy coping mechanisms.
A true story exemplifying these environmental factors revolves around Sarah, who grew up in a neighborhood with easy access to drugs. Many of her friends experimented with substance use, and Sarah herself relied on drugs to escape her family issues and depression. Limited access to mental health resources and support further perpetuated her dependence on drugs. However, it was only when Sarah moved to a different neighborhood and sought professional help that she was able to recover and create a healthier environment for herself. This story underscores the profound impact of environmental factors on an individual’s journey toward addiction and recovery.
Psychological Factors
Psychological factors play a significant role in the development and progression of addiction. These factors, such as thoughts, emotions, and behaviors, contribute to substance use and addictive behaviors which is why some may experience cognitive dissonance when battling an addiction. Gaining an understanding of these psychological factors is crucial for preventing, treating, and supporting recovery from addiction.
One important psychological factor in addiction is the coping mechanism. Many individuals turn to substance use as a way to cope with stress, trauma, or emotional difficulties. Using substances temporarily relieves negative emotions and provides a sense of relief.
Social influences also have a strong impact on addictive behaviors. Peer pressure and social norms greatly influence a person’s decision to engage in addictive behaviors. The desire to fit in or be accepted often leads to substance use.
Another psychological factor is self-medication. Some individuals use substances to self-medicate mental health issues like depression, anxiety, or post-traumatic stress disorder. They believe that substances can temporarily numb emotions or alleviate symptoms.
The reinforcement and reward aspect of addiction is also significant. Addictive substances activate the brain’s reward system, leading to pleasurable sensations. This reinforcement then drives individuals to seek and use substances, ultimately resulting in addiction.
Psychological vulnerabilities can increase a person’s susceptibility to addiction. Some individuals have underlying psychological vulnerabilities, such as impulsivity, low self-esteem, or traumatic history. These vulnerabilities make it more likely for them to develop addiction.
Understanding these psychological factors is essential for healthcare professionals to create personalized treatment plans for individuals struggling with addiction. By addressing the root causes and providing psychological support, recovery can be strongly supported.
True Story: Sarah, a 28-year-old woman, battled addiction for years and faced childhood trauma and low self-esteem. She used drugs as a coping mechanism to numb her emotional pain. However, through therapy and support groups, she was able to address the psychological factors contributing to her addiction. Sarah learned healthier coping mechanisms, built self-esteem, and developed a support network. Today, she has been in recovery for three years and advocates for mental health and addiction awareness. Sarah’s story highlights the importance of addressing psychological factors in addiction recovery.

Addiction is a complex phenomenon, driven by various motivations that fuel its grip on individuals. In this section, we will dive into the different motivations behind addiction, peeling back the layers to understand what drives individuals toward harmful behaviors. From seeking pleasure and rewards to using substances as a coping mechanism, and even the powerful influence of social factors such as peer pressure and self-medication – we’ll explore the intricate facets that contribute to the motivations for addiction.
Pleasure and Reward
Pleasure and reward play a vital role in addiction. They serve as the driving force behind individuals’ participation in addictive behaviors. Activities like taking drugs, gambling, or consuming certain foods trigger the release of dopamine, a neurotransmitter closely linked to pleasure and motivation. This release generates a pleasurable sensation and reinforces the behavior, increasing the likelihood of repeating it.
Scientific research demonstrates that addiction directly involves the brain’s reward system. Repeated stimulation of this system through addictive substances or behaviors can result in changes in both brain structure and function. Consequently, individuals become more susceptible to addiction. With time, the brain becomes less responsive to natural rewards, leading to a continuous cycle of pursuing greater pleasure through addictive behaviors.
It is crucial to recognize that addiction is influenced by various environmental, psychological, and social factors. These factors interact with the brain’s reward system, rendering certain individuals more susceptible to addiction than others. For instance, in the case of social media addiction, a study by Vimala Balakrishnan and Azra Shamim in 2013 explored Malaysian Facebookers’ motives and addictive behaviors. The researchers found that Facebook can be addicting as the platform offers users the opportunity to enhance their self-esteem and popularity, gather information about others, and even alleviate feelings of loneliness.
Understanding the significance of pleasure and reward in addiction is essential for the development of more effective prevention and treatment strategies. Interventions can address the underlying motivations contributing to addiction, such as the pursuit of pleasure and reward. By promoting healthier ways to satisfy these needs and improve overall well-being, interventions can pave the way for successful outcomes.
Coping Mechanism
Coping mechanisms are commonly observed in addiction. People use addictive substances or behaviors to cope with stress, trauma, or difficult emotions. Understanding the role of coping mechanisms is important for effective treatment and support.
1. Escape from Reality: Coping mechanisms provide a temporary escape from overwhelming emotions or life circumstances. For example, people may use drugs or alcohol to numb painful experiences or temporarily forget their problems.
2. Self-Medication: Some individuals use addictive substances to self-medicate symptoms of mental health disorders like anxiety or depression. They may feel that the substance helps alleviate their symptoms or provides relief from emotional distress.
3. Emotional Regulation: Addictive behaviors can help regulate and manage emotions. For instance, excessive gambling or shopping may provide excitement or cope with feelings of boredom or emptiness.
4. Coping with Trauma: Individuals who have experienced trauma may turn to addictive substances or behaviors to cope with distressing memories and emotions associated with their past experiences.
5. Lack of Healthy Coping Skills: Some individuals haven’t learned healthy ways to cope with stress or difficult emotions. As a result, they resort to addictive substances or behaviors as their main coping mechanism.
Understanding the role of coping mechanisms is crucial for developing personalized treatment plans. Addressing underlying issues and providing alternative healthy coping strategies is essential to support individuals in their recovery journey.
True story: John, a successful businessman, had a high-stress job that left him overwhelmed and anxious. He lacked healthy coping mechanisms to manage his stress, so he turned to alcohol to relax and unwind after work. Over time, John’s reliance on alcohol increased, negatively impacting his personal and professional life. Through therapy and support groups, John learned new coping strategies like exercise, mindfulness, and seeking support from loved ones. Gradually, he overcame his addiction and developed healthier ways to cope with stress. Coping mechanisms played a significant role in John’s addiction journey, highlighting the importance of addressing and developing healthy coping skills in addiction recovery.
Social Influences
It is important to recognize how societal factors can impact an individual’s susceptibility to addiction. Here are key points to consider when exploring the role of social influences in addiction:
1. Peer pressure: Peer pressure can lead individuals to engage in substance abuse or addictive behaviors. The desire to fit in and be accepted by a social group can influence individuals to try drugs or engage in risky behaviors.
2. Social norms: Societal norms and cultural values shape an individual’s perceptions of substance use. If substance abuse is normalized or glamorized within a social group or community, individuals may be more likely to engage in such behaviors.
3. Social support: The presence or absence of a supportive social network significantly impacts an individual’s likelihood of developing an addiction. Strong social support systems that encourage healthy behaviors and discourage substance abuse serve as protective factors against addiction.
4. Accessibility: The availability and accessibility of addictive substances in a person’s social environment contribute to their likelihood of using drugs or becoming addicted. Easy access to drugs or alcohol increases the risk of substance abuse.
5. Stress and trauma: Social factors like poverty, discrimination, or trauma contribute to chronic stress, increasing vulnerability to addiction. Individuals may turn to substances as a coping mechanism to deal with difficult social circumstances.
True story: Laura was a teenager who had a healthy and drug-free lifestyle until she started hanging out with a new group of friends experimenting with drugs. Due to strong peer influence, Laura succumbed to using drugs. Over time, her social circle became centered around drug use, making it increasingly difficult for her to break free from addiction. The social influences she was exposed to played a significant role in her journey toward addiction, highlighting the importance of recognizing and addressing the impact of social factors in addiction prevention and treatment.
Peer Pressure
Peer pressure is a significant factor contributing to addiction. Addiction is often influenced by the pressure exerted by one’s peers or social group, compelling individuals to engage in potentially harmful behaviors. Succumbing to peer pressure can lead to substance abuse and risky behaviors.
When it comes to peer pressure, one important consideration is its impact on individuals, particularly adolescents who desire acceptance and fitting in. They may feel pressured to experiment with drugs or alcohol, being influenced by their peers to try substances they would not have otherwise considered.
Additionally, peer pressure plays a role in perpetuating addictive behaviors and making it difficult for individuals to break free from addiction. Being part of a group that abuses substances creates a social environment that normalizes and reinforces addictive habits. As a result, individuals may feel compelled to continue using substances in order to maintain their social relationships.
However, it is essential to note that not everyone succumbs to peer pressure. Factors such as self-esteem, assertiveness, and having a supportive network can help mitigate its influence. Developing strong decision-making skills and a sense of self-identity can empower individuals to resist the pressures to engage in addictive behaviors.z
Understanding the role of peer pressure in addiction is crucial for prevention and intervention efforts. By fostering a supportive and inclusive environment, educating individuals about the dangers of peer pressure, and promoting healthy coping mechanisms, we can empower individuals to make their own choices and resist negative influences.
Self-Medication
Self-medication is a prevalent reason for addiction, as individuals may use substances or behaviors to cope with physical or mental health symptoms. It is common for people to self-medicate in order to manage chronic pain or other physical problems. For instance, someone with persistent back pain may misuse opioids temporarily to relieve their discomfort.
Additionally, individuals with anxiety or depression often resort to self-medication as a means to alleviate distressing symptoms. They may turn to substances like alcohol or drugs in an attempt to temporarily reduce their anxiety or enhance their mood. Moreover, some individuals utilize self-medication as a way to address unmet emotional needs or underlying emotional issues. For example, individuals who feel lonely or have low self-esteem may seek comfort in substances.
Furthermore, individuals who have experienced trauma or abuse may turn to self-medication as a way to numb painful memories or emotions. These individuals use self-medication as a temporary relief or avoidance mechanism. Lastly, in situations where affordable or adequate healthcare is not accessible, self-medication may become the only option. This is often observed in low-income communities or areas with limited healthcare resources.
The story of Amy, a young woman in her mid-twenties, serves as a prime example of the risks associated with self-medication. Amy struggled with undiagnosed anxiety for years, experiencing feelings of unease, sleep troubles, and panic attacks. Due to her inability to afford therapy or medication, Amy resorted to self-medication. Initially, she turned to alcohol as a way to alleviate her anxiety and induce relaxation. However, her alcohol use gradually escalated, leading to addiction and exacerbated mental health issues. Only when Amy sought professional help and received appropriate treatment for her anxiety was she able to break free from her addictive behaviors and discover healthier coping mechanisms. This narrative highlights the importance of accessible mental healthcare and the potential dangers of self-medication in managing mental health concerns.

The Relationship Between Mental Health and Addiction
The complex relationship between mental health and addiction is crucial to understand. Mental health issues play a significant role in the development of addiction. Here are some important points to keep in mind:
1. Mental health disorders significantly heighten the risk of addiction: Individuals with these disorders are more susceptible to developing addiction compared to those without them. Conditions such as depression, anxiety, and bipolar disorder often lead to self-medication through substance abuse.
2. Dual diagnosis is prevalent: Many individuals battling addiction also struggle with co-occurring mental health disorders. Effective treatment for these cases requires a comprehensive approach that addresses both the addiction and the underlying mental health condition.
3. Self-medication is common: Some individuals with mental health issues resort to drugs or alcohol as a way to cope with their symptoms. Unfortunately, this destructive cycle can worsen their mental health and exacerbate substance abuse.
4. Relapse risk is heightened: Individuals with mental health disorders face a greater risk of relapse after addiction treatment. It is crucial to provide ongoing support and address underlying mental health issues to reduce the chances of relapse.
5. Integrated treatment approaches are key: Effective treatment for individuals with mental health and addiction problems typically involves addressing both issues simultaneously. This may involve therapy, medication management, and participation in support groups with the guidance of professionals at Lantana Recovery in Charleston.
Understanding the relationship between mental health and addiction is fundamental to developing efficient prevention and treatment strategies. By addressing both aspects, individuals have a better chance of achieving long-term recovery and improved mental well-being.

Effects and Consequences of Addiction
The effects and consequences of addiction can have detrimental impacts on individuals and society as a whole. Understanding these effects is crucial when it comes to addressing and combating addiction. Here are some important considerations to keep in mind:
- Health deterioration: Addiction can lead to severe health consequences, including organ damage, respiratory problems, and an increased risk of HIV and hepatitis. Furthermore, addiction often coexists with mental health disorders, resulting in the worsening of symptoms and an overall decline in well-being.
- Financial instability: Addiction can bring about significant financial burdens. The cost associated with addictive substances and behaviors can swiftly deplete savings, create debt, and even lead to unemployment or a decrease in income.
- Strained relationships: Addiction can strain relationships with family, friends, and romantic partners. Trust can be shattered, communication can break down, and conflicts can arise due to the individual’s addictive behaviors.
- Legal issues: Addiction frequently results in legal problems, such as DUI charges, possession, and distribution of illicit substances. Consequently, this can lead to criminal records, incarceration, and additional stress on both individuals and families.
- Social isolation: Individuals who are grappling with addiction may isolate themselves from social activities and loved ones. This isolation can contribute to feelings of loneliness, which can exacerbate mental health issues and diminish social support.
It is absolutely essential to comprehensively address the effects and consequences of addiction by providing support, treatment, and prevention strategies in order to mitigate its impact on individuals and society as a whole.
Treatment and Recovery Options
Treatment and recovery options for addiction include:
- Inpatient Rehabilitation: Stay at a treatment facility like Lantana for 30 to 90 days. Benefit from structured programs, 24/7 medical and emotional support, and a drug-free environment to aid in the recovery process.
- Outpatient Treatment: Live at home while attending treatment sessions during the day or evening. Receive therapy, counseling, and support while managing daily responsibilities.
- Support Groups: Narcotics Anonymous (NA) and Alcoholics Anonymous (AA) provide a supportive community for individuals seeking recovery. Gain peer support, advice, and a platform for sharing experiences.
- Therapy: Collaborate with a qualified addiction therapist to address the underlying causes and triggers of addiction. Common therapeutic approaches include cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), dialectical behavior therapy (DBT), and motivational interviewing.
- Medication-Assisted Treatment (MAT): Combine medications with therapy and counseling to effectively treat addiction. Medications such as methadone, buprenorphine, and naltrexone can help reduce cravings, alleviate withdrawal symptoms, and support long-term recovery.
- Aftercare Programs: Receive ongoing support and guidance after completing primary treatment. These programs may involve continued therapy, participation in support groups, and regular check-ins with a treatment professional. You can also use resources like addiction DVDs and other educational resources to overcome and understand addiction.
To determine the most suitable treatment and recovery options, individuals should evaluate their specific needs and consult with professionals. Identifying the right approach is essential for long-term success.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the factors that contribute to addiction?
Addiction is caused by a complex combination of biological, psychological, and social factors. These include feelings about oneself, emotional state, family relationships, social ties, community attributes, employment status, stress reactivity, coping skills, physical or emotional pain, personality traits, educational opportunities, goals, and access to rewards.
Why do some people become addicted while others do not?
There is no one factor that determines whether someone will become addicted. Addiction susceptibility can be influenced by various factors such as genetics, biology, personality traits, early life experiences, and social influences from family and peers.
What are the most commonly addictive substances?
Nicotine, found in tobacco, is the most widely used addictive substance worldwide. Alcohol is also widely used for pleasure but can lead to uncontrolled drinking and alcohol use disorder. In the US, painkillers, including prescription opiates and heroin, account for a significant number of addictions. Cocaine and methamphetamine are highly addictive stimulants.
How does addiction develop?
Addiction can start with experimental use in social situations and progress to more frequent use. As drug use increases, larger doses may be needed to achieve the desired effect. Eventually, the drug may be needed just to feel good. Attempts to stop can result in intense cravings and withdrawal symptoms, making it increasingly difficult to go without the drug.
What are the signs and symptoms of drug addiction?
Common signs of drug addiction include regularly feeling the need to use the drug, intense urges for the drug, needing more of the drug to achieve the same effect, taking larger amounts of the drug than intended, neglecting obligations and responsibilities, continuing to use the drug despite negative consequences, engaging in risky behaviors while under the influence, spending a significant amount of time obtaining and using the drug, and experiencing withdrawal symptoms when attempting to quit.
How can drug addiction be recognized in family members?
Recognizing drug use in family members can be challenging, but signs may include problems at school or work, physical health issues, neglected appearance, changes in behavior and relationships, money issues, and discovering missing items or money. Signs of drug use or intoxication can vary depending on the drug.









