Relapse can be a challenging and discouraging experience for individuals who are on the path to recovery from addiction. In order to prevent and manage relapse, it is crucial to identify and understand the triggers that can lead to a recurrence of addictive behaviors. This article aims to provide insights into the common triggers for relapse and strategies to effectively manage these high-risk situations.
Firstly, it is important to understand what exactly is meant by a relapse. A relapse refers to the resumption of substance use or engaging in addictive behaviors after a period of abstinence or recovery. It can be a setback in one’s journey towards sobriety and can significantly impact an individual’s physical, mental, and emotional well-being.
Identifying triggers for relapse is essential because they are the situations, emotions, or circumstances that increase the likelihood of engaging in addictive behaviors. By recognizing these triggers, individuals can develop effective coping strategies and relapse prevention plans to navigate through challenging situations.
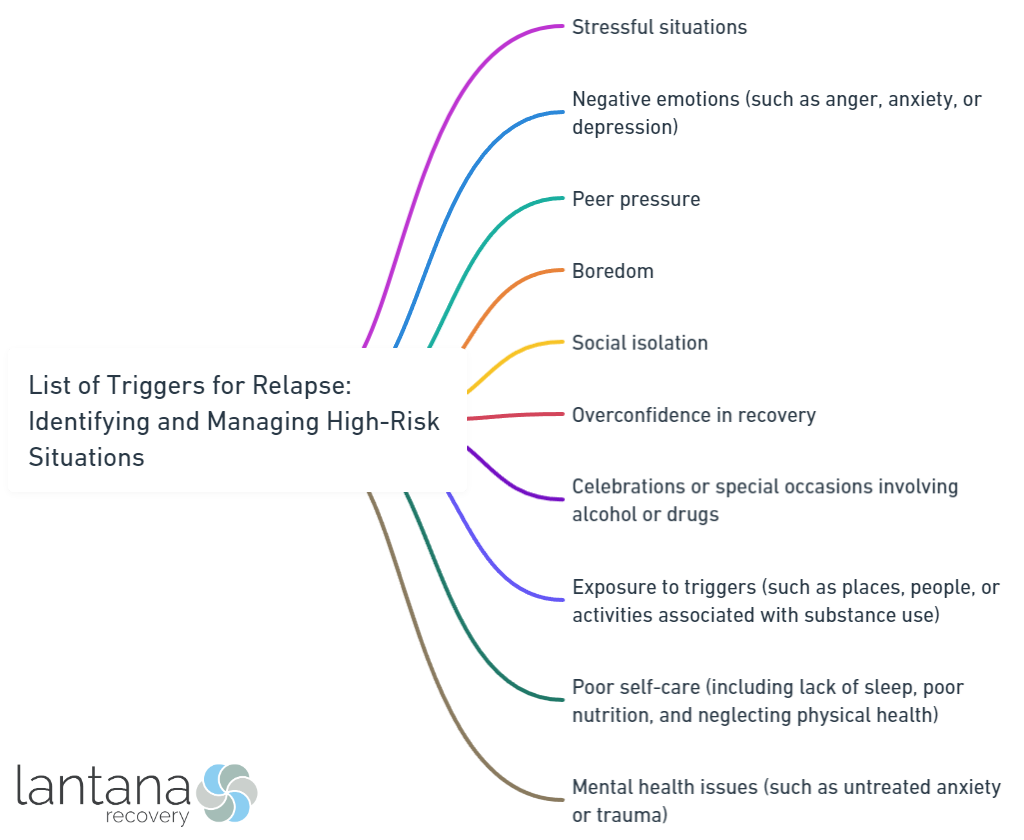
Some of the common triggers for relapse include:
- High-Risk Situations: Certain situations, such as being in environments where substances are easily accessible or being around individuals who encourage substance use, can put individuals at a higher risk of relapse.
- Emotional Distress: Emotional distress, including feelings of anxiety, depression, loneliness, or boredom, can contribute to increased vulnerability to relapse. These emotions may motivate individuals to turn to substances as a means of coping or escaping.
- Social Pressure and Peer Influence: Peer pressure and the influence of friends or social circles can have a significant impact on one’s decision to engage in addictive behaviors. Being in environments where substance use is normalized can increase the risk of relapse.
- Negative or Stressful Life Events: Major life events, such as loss, trauma, or financial difficulties, can act as triggers for relapse. These events can evoke intense emotions and destabilize an individual’s recovery progress.
- Environmental Cues: Environmental cues associated with past substance use, such as specific locations, objects, or even certain smells, can trigger cravings and make individuals more susceptible to relapse.
Identifying high-risk situations specific to an individual’s circumstances is crucial. By recognizing these situations, individuals can develop personalized strategies and coping mechanisms to manage or avoid these triggers altogether.
In order to effectively manage high-risk situations, it is important to develop a comprehensive relapse prevention plan. This plan may include strategies such as enhancing self-awareness, building a strong support system, practicing healthy coping mechanisms, and establishing a structured daily routine.
Seeking support from professionals, such as therapists or support groups, can provide valuable guidance and assistance in navigating through challenging situations.
By understanding the triggers for relapse, developing effective strategies, and seeking support, individuals can enhance their ability to maintain their recovery journey and minimize the risk of relapse.
Understanding Relapse
Understanding relapse is crucial for individuals recovering from addiction. It helps them recognize warning signs and develop strategies to prevent relapse. Here are some important points to consider:
1. Relapse is not a sign of failure. Addiction is a chronic, relapsing condition. Relapse is an opportunity for growth and learning.
2. Triggers and high-risk situations can lead to relapse. Common triggers include stress, negative emotions, social pressure, and environments associated with substance use. Avoiding these triggers reduces the risk.
3. Building a strong support system is crucial. Friends, family, support groups, and therapists provide essential support, understanding, and guidance during challenges.
4. Developing healthy coping mechanisms and self-care practices is essential. Activities like exercise, mindfulness, hobbies, and therapy help manage stress, cravings, and triggers.
5. Creating a relapse prevention plan is key. This plan includes identifying triggers, developing coping strategies, setting boundaries, and having an emergency plan.
What is a Relapse?
A relapse refers to returning to an unhealthy behavior or condition after improvement or recovery. It is important to understand what is a relapse and why it occurs. It commonly occurs in addiction, but it can also happen in mental health conditions or chronic illnesses.
During a relapse, individuals often go back to their old behavior and experience negative consequences. Relapses are normal and provide insights into the factors that contribute to the unhealthy behavior.
To prevent relapse, it is crucial to identify and understand triggers that can lead to the undesired behavior. Triggers can vary from high-risk situations to emotional distress, social pressure, negative life events, or environmental cues.
Recognizing and managing high-risk situations is essential in preventing relapse. “Relapse prevention (RP) is a crucial aspect of alcoholism treatment, aimed at addressing both immediate determinants and covert antecedents that contribute to relapse” (Relapse Prevention, Larimer et al., 2003.) This involves developing an effective prevention plan that includes strategies for coping. Seeking support from loved ones or professionals can also be beneficial in maintaining long-term recovery.
Why is it Important to Identify Triggers for Relapse?
Identifying triggers for relapse is crucial to maintain sobriety and prevent setbacks in recovery. Understanding these triggers allows individuals to be better prepared to handle challenging situations. By identifying specific situations, emotions, or people that increase the risk of relapse, individuals can develop strategies to manage these triggers. This may involve coping mechanisms like relaxation techniques or healthy distractions to handle cravings or emotional distress.
Identifying triggers also helps individuals build a support system and seek help when needed. Recognizing situations or circumstances that increase vulnerability to relapse allows individuals to reach out to counselors, sponsors, or support groups for guidance and assistance. Having a strong support system in place increases accountability and provides necessary resources to navigate high-risk situations.
Identifying triggers offers an opportunity for personal growth and self-reflection. By becoming aware of factors that may contribute to relapse, individuals can understand their own vulnerabilities and address underlying issues fueling the addiction. This self-awareness helps cultivate resilience and enhance overall well-being.
Jane, a recovering alcoholic, recognized the importance of identifying triggers for relapse early in her sobriety journey. She attended therapy sessions and support group meetings where she learned about common triggers and coping strategies. Through self-reflection, Jane discovered that certain social situations, particularly parties or gatherings where alcohol was present, posed a high risk for relapse. With this knowledge, she developed a relapse prevention plan that included avoiding such events, engaging in sober activities, and reaching out to her sponsor for support. Jane also focused on cultivating healthier coping mechanisms like exercise and mindfulness to manage stress and emotional distress. Actively identifying and managing her triggers allowed Jane to successfully maintain her sobriety and thrive in her recovery journey.

Common Triggers for Relapse
Discover the most influential factors that can lead to relapse and hinder recovery. In this section, we uncover the common triggers that increase the risk of relapse, ranging from high-risk situations to emotional distress, social pressure, negative life events, and environmental cues. By understanding the power of these triggers, we can empower ourselves and others with the knowledge needed to identify and effectively manage these challenges on the path to long-term sobriety.
1. High-Risk Situations
High-risk situations increase relapse likelihood for individuals in recovery. It is crucial for individuals to identify and understand these high-risk situations in order to effectively manage and prevent relapse.
Some examples of high-risk situations include being around substances, such as parties, bars, or environments where drugs or alcohol are accessible. Emotional distress, such as stress, anxiety, or depression can also lead to relapse.
Additionally, social pressure and peer influence from friends who use substances can tempt individuals to relapse. Negative or stressful life events like job loss, relationship problems, or financial struggles can drive individuals to substances. Environmental cues, such as places, objects, or activities associated with past substance use, can also trigger cravings.
Therefore, it is important for individuals in recovery to develop coping strategies for these high-risk situations according to G. Alan Marlatt in Taxonomy of high-risk situations for alcohol relapse. Strategies may involve avoiding triggers, seeking support, practicing stress management, and developing healthy coping mechanisms. Seeking professional help and joining support groups can also provide guidance in managing high-risk situations and preventing relapse.
2. Emotional Distress
Emotional distress serves as a triggering factor for relapse among individuals in recovery from addiction. It is crucial to acknowledge the significant impact of emotional distress and establish efficient strategies for coping with it.
Strong negative emotions such as sadness, anger, frustration, or loneliness substantially augment the risk of relapse. Moreover, unresolved trauma from the past often resurfaces during the recovery process, leading to emotional distress. This unresolved trauma acts as a catalyst for the urge to numb emotions through substance use.
Excessive stress is another critical factor that overwhelms individuals in recovery, making them more likely to turn to substances in search of relief. Additionally, personal or professional setbacks present a considerable emotional challenge, thus increasing vulnerability to relapse.
Issues in relationships, such as conflicts, broken connections, or lack of support, have a significant impact on emotional well-being. The absence of a robust support system further heightens the susceptibility to relapse.
True Story: After successfully completing six months of sobriety following his rehabilitation, John unfortunately relapsed due to the sudden death of his close friend. Overwhelmed with grief and emotional pain, John resorted to substance use as a means to numb his anguish. This unfortunate incident serves as a stark reminder of the utmost importance to address emotional distress and establish effective coping mechanisms in order to prevent relapse.
3. Social Pressure and Peer Influence
Social pressure and peer influence are significant factors that can lead to relapse. Managing these influences is essential for individuals in recovery. Here are some key points to consider:
- Social pressure: The influence of peers can be powerful and may cause individuals to engage in harmful behaviors or consume substances they are trying to avoid.
- Peer influence: Surrounding oneself with peers who use substances normalizes and encourages relapse. It is important to be mindful of the company we keep.
- Vulnerability to influence: People in early recovery or those with limited support systems are more susceptible to social pressure and peer influence. It is crucial to acknowledge and address this vulnerability.
- Recognizing triggers: Identifying the people, places, or situations that exert social pressure or peer influence empowers individuals to develop strategies to avoid or navigate them effectively.
- Building a support network: Surrounding oneself with friends and mentors who understand the challenges of recovery is crucial in countering peer influence. This support network provides encouragement and guidance.
It is important to note that individuals in recovery have the power to resist and make choices that align with their recovery goals. By being aware of these influences and developing coping strategies, they can protect their sobriety and maintain a healthy, drug-free lifestyle.
Studies have shown that social support and connection play a crucial role in preventing relapse. Building a strong support network is key to countering the negative influences of social pressure and peer influence.
4. Negative or Stressful Life Events
Denial is the first step to recovery. Negative or stressful life events can significantly increase the risk of relapse in individuals. It is crucial to be mindful of these triggers and develop effective coping strategies to combat them. Various examples of such events include:
1. Loss of a loved one: Experiencing the unfortunate death of a close individual can serve as a major triggering factor for relapse.
2. Relationship problems: Difficulties encountered in relationships, such as breakups or divorces, can lead to emotional distress and intensify the risk of relapse.
3. Financial problems: Struggling with financial issues like unemployment or debt can be overwhelming and contribute to relapse.
4. Work-related stress: Experiencing high levels of stress at work, including job loss or excessive workload, can have adverse effects on mental health and increase vulnerability to relapse.
5. Legal issues: Dealing with legal problems, such as arrests or court proceedings, can generate immense stress and act as a trigger for relapse.
In order to effectively manage these events and reduce the risk of relapse, consider the following steps:
- Seek support: Reach out to friends, family, or support groups for guidance and understanding during challenging times.
- Practice self-care: Engage in activities that promote overall well-being, such as regular exercise, sufficient sleep, and a nutritious diet.
- Develop healthy coping mechanisms: Look for healthy ways to deal with stress, such as meditation, journaling, or pursuing hobbies.
- Consider therapy: Professional assistance from therapists at Lantana, for example, can provide valuable tools and strategies for managing stress and preventing relapse.
By recognizing negative or stressful life events as potential triggers for relapse and taking proactive measures to manage them, individuals can significantly enhance their chances of maintaining their recovery journey.
5. Environmental Cues
Environmental cues play a significant role in triggering relapse for individuals in recovery from addiction. These cues can vary from person to person; however, understanding them is essential for developing effective strategies to prevent relapse.
1. Familiar Places: It is crucial to avoid environments where substance abuse occurred because returning to these locations can evoke memories and cravings. For instance, regularly going to a bar or nightclub where alcohol was consumed can be a substantial trigger for relapse.
2. People and Associations: Interacting with individuals who were part of the substance abuse lifestyle can act as a strong trigger. The influence of friends who still use substances or peer pressure can undermine efforts towards recovery.
3. Triggers in the Home: Objects or situations within the home can serve as cues for relapse. This may include drug paraphernalia, prescription medications, or specific rooms where substance abuse took place.
4. Media and Entertainment: Exposure to movies, TV shows, songs, or advertisements that depict substance use can trigger cravings and nostalgic associations. Minimizing exposure to media content that showcases substance abuse can help reduce the impact of these cues.
5. Emotional States: Emotional distress, such as stress, anxiety, or sadness, can also act as a cue for relapse. Developing healthy coping mechanisms and emotional resilience can decrease vulnerability to these triggers.
By being aware of these environmental cues, individuals in recovery can actively avoid or minimize their impact. Building a strong support network and engaging in activities that promote a healthy and substance-free lifestyle are vital for effectively managing and overcoming these triggers.

Identifying High-Risk Situations
Identifying high-risk situations is of utmost importance in the management and prevention of relapse. It is crucial for individuals to recognize and understand these situations, as this enables them to develop effective strategies to either avoid or cope with them. Here are some key points to consider when it comes to identifying high-risk situations:
1. Social settings: Parties, bars, or events where alcohol or drugs are present can pose as high-risk situations. Being aware of these environments and planning alternative activities or opting to avoid them altogether can greatly help in minimizing temptation and potential relapse.
2. Emotional triggers: Stress, anxiety, loneliness, or intense emotions can make individuals more vulnerable to relapse. It is essential to recognize one’s personal emotional triggers and create healthy coping mechanisms. Engaging in hobbies, exercise, or seeking support from others can be beneficial when navigating through these challenging situations.
3. Negative influences: Surrounding oneself with people who use substances or engage in unhealthy behaviors significantly raises the risk of relapse. Identifying and steering clear of negative influences, as well as building a supportive network of sober friends and family members, can greatly enhance the chances of maintaining sobriety.
4. Familiar environments: Returning to places or situations associated with substance use can be precarious. It is important to identify and avoid environments that may trigger cravings or memories of drug or alcohol use.
5. Routine disruptions: Major life changes, such as job loss, relationship issues, or financial difficulties, can disrupt routines and potentially lead to relapse. Developing a plan to manage and cope with such changes, seeking professional help when needed, and maintaining healthy daily routines can provide stability during challenging times.
By actively identifying and addressing high-risk situations, individuals can proactively manage their recovery journey and reduce the likelihood of relapse. It is crucial to remember that everyone’s triggers may vary, and personalized strategies play a vital role in achieving long-term success.
What are High-Risk Situations?
Why is relapse part of recovery and what are high-risk situations? High-risk situations refer to circumstances that increase the probability of relapse for individuals in addiction recovery. It is crucial to identify and understand these situations in order to support the recovery process and ensure progress. By recognizing and comprehending these scenarios, individuals can effectively develop strategies to manage or avoid them.
One example of a high-risk situation is social settings. Parties, bars, and other places where alcohol or drugs are present can be particularly risky for individuals with addiction. The presence of substances in these settings can make the temptation to use them stronger.
Emotional distress is another high-risk situation. Stress, anxiety, depression, and intense emotions can trigger relapse. Individuals experiencing these emotions may feel compelled to seek solace or escape through substance use.
Negative life events are also considered high-risk situations. Significant events such as loss, trauma, or financial difficulties can increase vulnerability to relapse. These situations can disrupt emotional well-being and coping mechanisms, making individuals more susceptible to resorting to substance use.
Environmental cues can also trigger relapse. Being around people, places, or objects associated with past substance use can be a risk. For example, visiting a location where drug use was common or being in the presence of individuals who still use substances can evoke cravings and lead to relapse.
Peer pressure is another high-risk situation to be aware of. Friends, acquaintances, or social circles that engage in substance use can pose a significant risk. The fear of missing out and the pressure from peers may tempt individuals to revert to their old habits.
To effectively manage high-risk situations, it is essential for those in recovery to develop a relapse prevention plan. This plan involves identifying triggers, implementing coping strategies such as stress management techniques, seeking support from a therapist or support group, and avoiding situations that could contribute to relapse. Recognizing high-risk situations and taking proactive steps to protect one’s recovery journey are crucial for long-term success.
Examples of High-Risk Situations
- Attending social events with alcohol or drugs
- Being around friends who use substances
- Stressful situations at work or home
- Feeling intense emotions like anger, sadness, or anxiety
- Encountering reminders of past substance use
- Being exposed to cues linked to substance use
- Going through major life events like loss, divorce, or job loss
- Feeling bored or having free time
- Financial difficulties or other problems that increase stress
- Experiencing conflicts or strained relationships with friends, family, or partners

Managing High-Risk Situations
Managing high-risk situations is crucial in navigating the journey of recovery. In this section, we will explore practical approaches to effectively handle these challenges. From developing an effective relapse prevention plan to implementing strategies for coping with high-risk situations, we will uncover actionable insights to support your recovery journey. Additionally, we will delve into the importance of seeking support and professional help, ensuring a comprehensive approach to successfully managing high-risk situations. So, let’s dive in and equip ourselves with the tools needed for a resilient recovery.
Developing an Effective Relapse Prevention Plan
Developing an effective relapse prevention plan is essential for maintaining sobriety and minimizing the risk of relapse. Follow these crucial steps to incorporate keywords naturally:
1. Education: Acquire knowledge about relapse factors and understand your personal triggers. This will help you identify potential risks and develop effective management strategies.
2. Realistic goals: Establish clear sobriety goals and create a comprehensive plan with specific actions to achieve them. Break down these goals into manageable steps to increase your chances of success.
3. Support network: Surround yourself with supportive individuals who can help you on your journey. Join support groups, attend therapy sessions, and connect with peers who have triumphed over similar challenges to gain invaluable encouragement and guidance.
4. Healthy coping mechanisms: Discover healthy ways to cope with stress, negative emotions, and cravings. Engage in hobbies, practice mindfulness or meditation, exercise regularly, or seek professional help to manage these challenges positively.
5. Avoid high-risk situations: Recognize and steer clear of places, people, or activities associated closely with substance use that might trigger cravings or temptations. For example, in a study by David M. Price titled Relapse prevention and risk reduction, the researcher discussed how the prevailing high-risk situations identified were associated with unsettling or distressing emotions and cognitive distortions.
6. Relapse prevention plan: Develop a detailed plan outlining specific actions to take if you feel at risk of relapsing. This may include reaching out to a trusted friend, utilizing distraction techniques, or seeking immediate professional assistance from experts at Lantana.
7. Regular self-assessment: Continuously monitor your progress and evaluate the effectiveness of your coping strategies. Make adjustments to your relapse prevention plan as needed to stay proactive in maintaining your sobriety.
Remember, developing an effective relapse prevention plan requires dedication, self-awareness, and a commitment to personal growth. By incorporating these steps, you can significantly increase your chances of sustaining long-term sobriety and leading a healthier, happier life.
Strategies for Coping with High-Risk Situations
When faced with high-risk situations, it is crucial to have effective strategies in place. Here are some strategies for coping with high-risk situations:
1. Identify triggers: Recognize specific situations or experiences that increase the risk of relapse. This may include certain people, places, or emotions.
2. Develop healthy coping mechanisms: Find alternative ways to manage stress and emotions, such as engaging in physical activity, practicing mindfulness or meditation, or seeking support from friends and family.
3. Create a relapse prevention plan: Work with a professional to develop a plan that includes strategies for avoiding or managing high-risk situations. This plan may involve setting boundaries, creating a support network, or engaging in therapy or counseling.
4. Avoid temptation: Remove yourself from environments where substance use is prevalent, such as parties or social gatherings that may trigger cravings or temptations.
5. Practice self-care: Take care of your physical and mental well-being by getting enough sleep, eating nutritious meals, and engaging in activities that bring you joy and relaxation.
6. Seek professional help: If you are struggling to cope with high-risk situations on your own, reach out to a therapist, support group, or treatment center for additional support and guidance.
7. Stay accountable: Establish accountability measures, such as regular check-ins with a sponsor or therapist, to help you stay on track and address any issues or concerns.
Remember, everyone’s journey is unique, and it is important to find strategies that resonate with your long-term recovery goals.
Seeking Support and Professional Help
Seeking professional help and support from institutions like Lantana Recovery is crucial for individuals experiencing or at risk of relapse. Addiction, a complex issue, often requires intervention and guidance. When seeking help, it is important to:
-
Recognize the need for assistance: Acknowledging the need for professional help is the first step towards recovery.
-
Find a qualified professional: Look for professionals specializing in addiction treatment who can provide the necessary guidance, therapy, and personalized relapse prevention plans.
-
Join support groups: Participate in groups like Alcoholics Anonymous or Narcotics Anonymous to find a sense of community and understanding, which can greatly support the journey towards recovery.
-
Build a supportive network: Surround yourself with individuals who understand addiction and can offer the needed encouragement and accountability for maintaining recovery.
-
Continue therapy and counseling: Regular sessions with professionals can address underlying issues contributing to addiction and teach effective strategies to prevent relapse.
Remember, seeking support and professional help from addiction rehab services near you is a positive step towards healing and a healthier, addiction-free life. There are numerous resources available to assist individuals on their journey towards recovery.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are high-risk incidents in relation to relapse?
High-risk incidents refer to situations that pose a significant threat to a successful recovery from addiction. These incidents can be interpersonal conflicts, social pressure, negative emotional states, or positive emotional states. It is important to anticipate and avoid these incidents in order to maintain sobriety.
How can I identify and manage high-risk situations for relapse?
Identifying and managing high-risk situations is essential for preventing relapse. It involves recognizing triggers, both internal (emotions) and external (people, places, things), that may bring back thoughts, feelings, or memories of addiction. Strategies for managing these triggers include mindfulness, exercise, social support, and self-care. It is also crucial to have a relapse prevention plan in place.
How can avoiding people and places associated with substance misuse help in relapse prevention?
Avoiding people and places associated with substance misuse is a key strategy for relapse prevention. Being in such environments can trigger cravings and temptations, making it more difficult to resist the urge to use drugs or alcohol. By distancing oneself from these triggers, individuals can create a safer and healthier environment that supports their recovery.
What is the role of cognitive therapy and mind-body relaxation in relapse prevention?
Cognitive therapy and mind-body relaxation techniques are important tools in developing healthy coping skills and preventing relapse. Cognitive therapy helps individuals address negative thinking patterns and develop positive thought patterns that support recovery. Mind-body relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing and meditation, can help manage stress and reduce the inclination to resort to substance use as a coping mechanism.
Can support groups play a role in managing high-risk situations and preventing relapse?
Yes, support groups can be immensely helpful in managing high-risk situations and preventing relapse. Joining self-help groups like Narcotics Anonymous, Alcoholics Anonymous, or other similar groups can provide individuals with strategies for successful recovery and a safe space to discuss their struggles and triumphs. These groups offer support, guidance, and a sense of community that can be invaluable in sustaining sobriety.
What are the five rules of recovery that can help prevent relapse?
The five rules of recovery are essential guidelines for preventing relapse. They include changing your life, being completely honest, asking for help, practicing self-care, and not bending the rules. By implementing these rules, individuals can create a supportive and responsible framework that promotes long-term recovery and helps navigate through challenging situations without turning to substance use.









