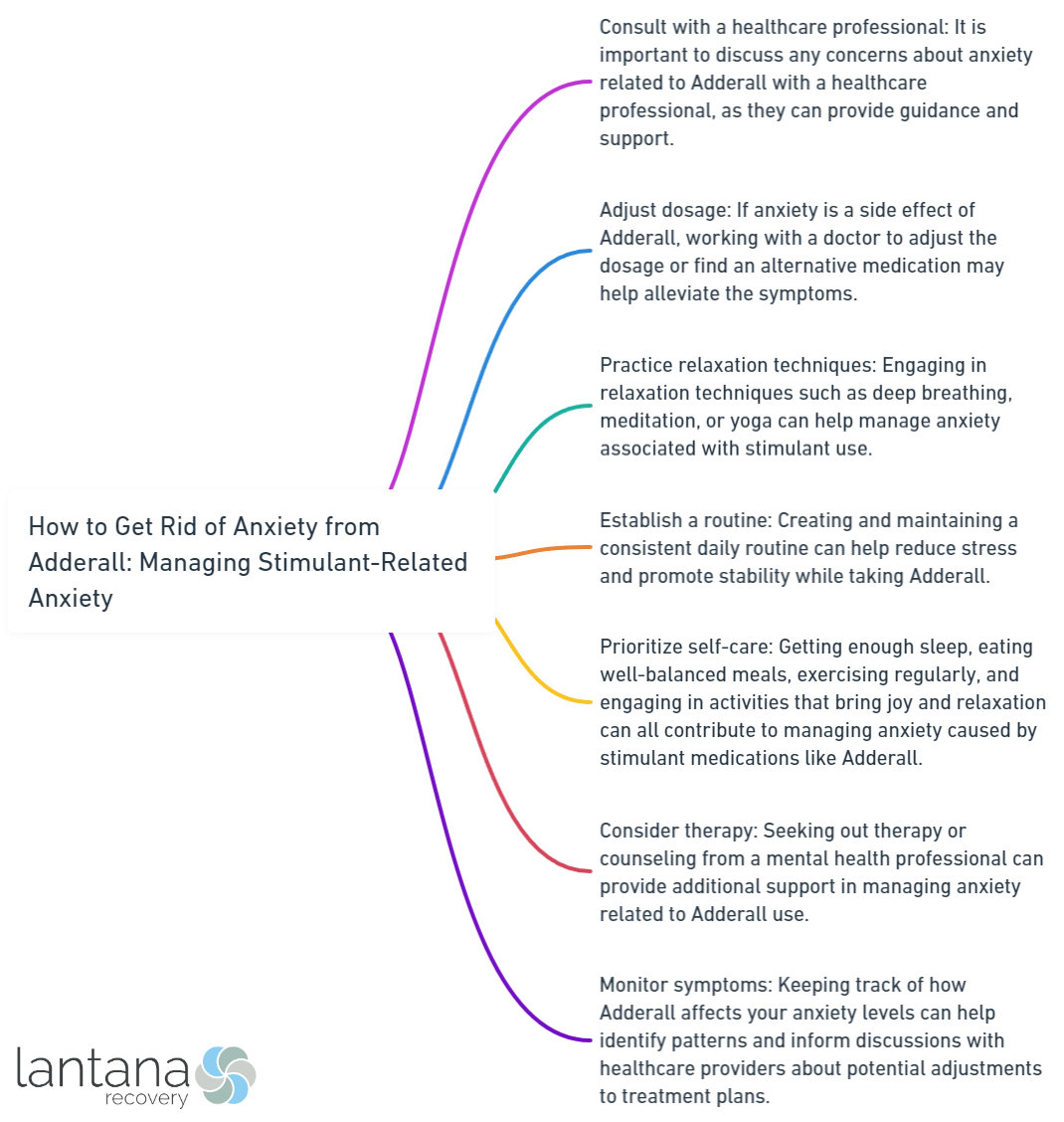
Anxiety is a common side effect experienced by individuals taking Adderall, a prescription stimulant medication used to treat attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). Understanding the relationship between Adderall and anxiety is crucial in effectively managing stimulant-related anxiety.
To start, it’s important to have a comprehensive understanding of Adderall and its effects. Adderall is a central nervous system stimulant that works by increasing the levels of certain chemicals in the brain, improving focus and reducing impulsivity. Along with its desired effects, Adderall can also produce various side effects, including anxiety.
The relationship between Adderall and anxiety stems from the impact of the medication on brain chemistry. Adderall affects the levels of neurotransmitters like dopamine and norepinephrine, which play a role in the regulation of mood and anxiety. These changes in brain chemistry can lead to increased feelings of anxiety and restlessness.
Fortunately, there are strategies and techniques that can help manage stimulant-related anxiety. Communication with your prescribing doctor is vital in discussing your symptoms and finding the most suitable treatment plan. This may involve adjusting the dosage of Adderall or exploring alternative medications that have a lower risk of anxiety as a side effect.
In addition to medication adjustments, incorporating relaxation techniques such as deep breathing exercises, mindfulness, and meditation can help reduce anxiety. Engaging in regular physical exercise is also beneficial as it helps release endorphins and promotes overall well-being. Stress-management strategies like proper sleep hygiene, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and seeking support from friends and family can further contribute to anxiety reduction.
If stimulant-related anxiety persists and significantly impacts daily functioning, it may be necessary to seek professional help. Consulting a doctor or mental health professional can provide further guidance and support. Therapy and other forms of treatment, along with medication adjustments, may be recommended to address the underlying anxiety issues.
By understanding the relationship between Adderall and anxiety and employing effective management strategies, individuals can find relief from stimulant-related anxiety and experience improved overall well-being. Remember, seeking professional help when necessary is crucial for personalized and comprehensive care.
Understanding Adderall and its Effects
Understanding Adderall and its effects is crucial. Here are some key points to consider:
- Adderall is a prescription stimulant medication used to treat ADHD. It contains amphetamine and dextroamphetamine.
- This medication increases certain neurotransmitters in the brain, improving focus, attention, and impulse control.
- Adderall can have effects like increased alertness, improved concentration, enhanced productivity, decreased appetite, and increased heart rate.
- The effects of Adderall vary based on dosage, metabolism, and other factors like concurrent substance use or medical conditions.
- It is essential to take Adderall as prescribed to avoid serious health consequences such as addiction and cardiovascular problems.
- Understanding the potential side effects of Adderall is important, including insomnia, dry mouth, irritability, and increased blood pressure.
- Adderall may interact with other medications or substances, like certain antidepressants or alcohol. Consult with a healthcare provider for safe use.
- Individuals should be aware of the risks and benefits of taking Adderall and have open communication with their healthcare provider.
What is Adderall and How Does it Work?
Adderall is a prescription medication that is used to treat attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD).
It contains amphetamine and dextroamphetamine, which are central nervous system stimulants.
These stimulants work by stimulating chemicals in the brain to improve focus, reduce impulsivity, and decrease hyperactivity in individuals with ADHD.
The amphetamine component of Adderall increases the levels of specific neurotransmitters like dopamine and norepinephrine in the brain.
These neurotransmitters play a crucial role in regulating attention, concentration, and impulse control.
By increasing the levels of these neurotransmitters, Adderall helps to improve communication between brain cells and enhance the ability of individuals with ADHD to maintain attention and control their behaviors.
It is important to remember that Adderall is a prescription medication and should only be taken under the guidance and supervision of a healthcare professional.
The dosage and duration of treatment should be tailored to meet the specific needs of each individual and should follow the prescribed guidelines.
If you have any concerns or questions about taking Adderall or its potential effects, it is advisable to consult with a mental health specialist.
They can provide you with guidance and assistance in managing any anxiety or side effects that may be associated with the medication.
Common Side Effects of Adderall
The common side effects of Adderall include dry mouth, lack of sleep, increase in heart rate, difficulty concentrating, anxiety symptoms, slowed speech, and increased blood pressure. Users often experience dry mouth, which can be alleviated by staying hydrated. Adderall can interfere with sleep patterns, leading to difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep, with users experiencing sleep problems.
It is a stimulant that can raise heart rate, with users experiencing a rapid or elevated heart rate. Despite being prescribed to help with concentration, some users may have difficulty focusing as a side effect.
Adderall can also cause or worsen anxiety symptoms, such as restlessness, rapid breathing, and a sense of unease. In some cases, Adderall can make speech slower or more deliberate. Additionally, it can elevate blood pressure levels, which may be concerning for individuals with high blood pressure or cardiovascular conditions.
If you experience any of these side effects while taking Adderall, it is important to discuss them with your prescribing doctor. They can adjust your dosage or explore alternative treatment options. Remember to always follow prescribed guidelines and communicate any concerns or changes in symptoms with your healthcare professional.

The Relationship Between Adderall and Anxiety
The relationship between Adderall and anxiety is a complex one. Adderall, which is a stimulant medication prescribed for ADHD, has the ability to improve focus and attention. However, it can also exacerbate symptoms of anxiety in certain individuals.
One of the effects of Adderall is that it increases levels of dopamine and norepinephrine in the brain. These neurotransmitters play a role in regulating mood and anxiety.
It is possible for individuals to experience more restlessness, nervousness, or irritability when taking Adderall, especially if they already have a tendency towards anxiety.
However, the impact of Adderall on anxiety can vary from person to person. While some individuals may experience increased anxiety, others may not notice any change in their anxiety levels. In fact, some individuals may even feel calmer and more focused when taking Adderall.
Epidemiological investigations on comorbid anxiety among children with ADHD have shown that 25% to 50% of children diagnosed with ADHD also experience a concurrent anxiety disorder.
If significant anxiety occurs while taking Adderall, it may be necessary to adjust the dosage or try a different medication. This is particularly important for individuals who are more susceptible to anxiety.
In addition to medication adjustments, there are also strategies for managing anxiety while taking Adderall. Engaging in stress-reducing activities such as exercise, mindfulness techniques, and relaxation exercises can be beneficial. It is also crucial to maintain open communication with healthcare providers to address any concerns and explore potential treatment adjustments.
It is important to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice on the relationship between Adderall and anxiety. Each individual’s experience is unique, and tailored recommendations can be provided to optimize the benefits of Adderall while minimizing any potential negative effects on anxiety levels.
Why Does Adderall Cause Anxiety?
Adderall causes anxiety by stimulating the sympathetic nervous system, which triggers the body’s fight or flight response. This is the reason why Adderall causes anxiety. It leads to increased heart rate, rapid breathing, and heightened alertness, all contributing to anxiety.
The reason why Adderall causes anxiety is because it increases the levels of neurotransmitters like dopamine and norepinephrine in the brain, which are important for focus and attention. However, excessive levels of these neurotransmitters can result in overstimulation and anxiety.
Another reason why Adderall causes anxiety is because it can also disrupt the balance of other neurotransmitter systems involved in regulating mood and anxiety, such as serotonin and GABA.
Various factors like dosage, duration of use, personal susceptibility, and existing mental health conditions can influence the likelihood and intensity of anxiety symptoms. So, it is important to consider why Adderall causes anxiety and communicate with your doctor to consider adjustments to the dosage or alternative medications if you experience anxiety while taking Adderall.
In addition, relaxation techniques, regular physical exercise, and stress-management strategies may also help manage stimulant-related anxiety. It is highly recommended to consult a mental health specialist as they can provide guidance and support in effectively managing symptoms.
The Impact of Adderall on Brain Chemistry
The impact of Adderall on brain chemistry is a crucial factor in its effectiveness for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). Adderall affects neurotransmitter systems by increasing dopamine and norepinephrine levels in the brain. These neurotransmitters regulate attention, focus, and impulse control. By enhancing their availability, Adderall helps individuals with ADHD concentrate and manage hyperactivity.
“Stimulants such as methylphenidate and amphetamine are currently the most common treatment for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). It is now known that low doses of stimulants focus attention and improve executive function in both normal and ADHD subjects.” (Stimulants: Therapeutic Actions in ADHD, Amy Arnsten, 2006)
Additionally, Adderall stimulates the central nervous system (CNS), speeding up brain activity. This leads to increased alertness and wakefulness, assisting individuals with ADHD in staying focused and reducing excessive activity levels. The medication primarily targets the prefrontal cortex, which is associated with executive functions such as decision-making, impulse control, and working memory. Enhancing activity in this area can improve cognitive functioning in individuals with ADHD.
It is important to note that Adderall can cause changes in heart rate and blood pressure due to its stimulant properties. Monitoring these effects closely, especially in individuals with pre-existing cardiovascular conditions, is essential. It is also important to understand that Adderall’s effects on brain chemistry are temporary. As the medication is metabolized and eliminated from the body, its impact gradually wears off. To maintain its effectiveness, regular dosing and adherence to prescribed guidelines are crucial.
If you experience concerning side effects or have questions about the impact of Adderall on brain chemistry, it is recommended to consult a healthcare professional or your prescribing doctor. They can provide guidance and make adjustments to your care plan if necessary.

Managing Stimulant-Related Anxiety
Discover effective ways to manage stimulant-related anxiety and regain a sense of calm. We’ll explore practical strategies that can make a difference in alleviating the negative impact of anxiety caused by stimulant medications. From open communication with your doctor to incorporating relaxation techniques and engaging in regular exercise, this section offers valuable insights to help you navigate the challenges of managing anxiety while using stimulant medications. Say goodbye to stress and hello to a more balanced, peaceful mindset.
Communicate with Your Prescribing Doctor
When managing stimulant-related anxiety, it is important to communicate with your prescribing doctor. Your doctor plays a crucial role in understanding your needs and concerns. By openly discussing your experiences with anxiety and the effects of Adderall, your doctor can provide guidance and personalized recommendations.
During these discussions, avoid using modal verbs and stick to factual statements. Be explicit with numerical details and percentages when necessary, without using vague terms.
By communicating with your prescribing doctor, you can address concerns or side effects you may be experiencing. This includes discussing common side effects such as dry mouth, rapid heartbeat, or difficulties sleeping. It also allows you to explore potential dosage adjustments to better manage anxiety symptoms.
Furthermore, your doctor can provide insights into relaxation techniques, stress-management strategies, or non-stimulant options that may be beneficial for your situation.
Remember, your prescribing doctor is there to support you in managing anxiety related to Adderall. By maintaining open communication, you can develop a care plan that suits your needs and promotes your well-being.
Adjusting the Dosage
Consult your prescribing doctor for guidance on adjusting your Adderall dosage to alleviate anxiety symptoms. Start with a lower dosage to see if it reduces anxiety and gradually increase as needed. Monitor changes in anxiety levels and report them to your doctor. Consider adding anti-anxiety medication to your treatment plan if necessary. Fine-tune your Adderall dosage to find the optimal level for reducing anxiety without compromising benefits. Always follow your doctor’s instructions when adjusting the dosage. Be aware of any new or worsening side effects and report concerns to your doctor. Seek the help of a mental health professional if adjusting the dosage does not effectively manage anxiety symptoms. Adjusting the dosage is important to find the right balance for treating anxiety while benefiting from Adderall.
Incorporating Relaxation Techniques
Incorporating relaxation techniques can help manage stimulant-related anxiety caused by Adderall. Effective relaxation techniques to consider include:
-
Deep Breathing: Practice diaphragmatic or belly breathing by taking slow, deep breaths through your nose and exhaling through your mouth. This calms the nervous system and reduces anxiety.
-
Progressive Muscle Relaxation: Tense and release each muscle group from toes to head to release tension and promote relaxation.
-
Mindfulness Meditation: Focus your attention on the present moment to reduce racing thoughts and promote calmness.
-
Guided Imagery: Visualize peaceful scenes like a beach or forest to redirect your thoughts away from anxiety.
-
Yoga or Tai Chi: Engage in gentle activities that combine breath control, meditation, and flowing movements to promote relaxation and reduce anxiety.
It’s important to find techniques that work best for you. Incorporating these techniques into your daily routine can effectively manage stimulant-related anxiety and improve overall well-being.
Engaging in Regular Physical Exercise
Engaging in regular physical exercise helps manage stimulant-related anxiety. Here are some ways exercise can help:
- Regular physical exercise stimulates the release of endorphins, known as “feel-good” hormones. These hormones improve mood and reduce anxiety.
- Through regular exercise, you can release muscle tension caused by anxiety, promoting relaxation and calm.
- Lack of quality sleep can worsen anxiety. Incorporating regular physical activity into your routine helps regulate sleep patterns, leading to better sleep quality and reduced anxiety.
- Exercise not only benefits your physical health but also contributes to your overall well-being. It boosts self-esteem, self-confidence, and reduces stress, positively impacting your emotional well-being and counteracting anxiety.
- Engaging in physical activity serves as a healthy distraction from anxious thoughts. By focusing on your body’s movements during exercise, you shift your attention away from anxiety.
Incorporating regular physical exercise into your routine is beneficial for managing stimulant-related anxiety. Choose exercises that you enjoy and consult a healthcare professional before starting any new exercise regimen, especially if you have underlying health conditions.
Research by German scientists published in Frontiers in Psychology consistently shows the positive impact of engaging in regular physical exercise on mental health. The study have reported that regular physical exercise is known for alleviating symptoms of anxiety and depression.
Just 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise, such as brisk walking or cycling, significantly reduces anxiety levels. Exercise not only improves cognitive function and resilience to stress but also promotes the release of mood-enhancing neurotransmitters. It also helps improve sleep quality, reduce muscle tension, and enhance overall well-being. However, it’s important to note that exercise should be part of a comprehensive approach to managing anxiety, and personalized advice from a mental health specialist or healthcare professional is recommended.
Practicing Stress-Management Strategies
Practicing stress-management strategies is crucial for individuals with Adderall-induced anxiety. It is important to incorporate the following strategies in order to effectively manage stress, if you can’t function without Adderall:
- Utilize deep breathing exercises to activate the body’s relaxation response and effectively reduce anxiety.
- Engage in regular physical exercise, such as cardio or yoga, to effectively reduce stress and enhance overall well-being.
- Establish a consistent sleep schedule and practice good sleep hygiene to ensure adequate sleep.
- Explore relaxation techniques like progressive muscle relaxation, guided imagery, or meditation to effectively calm the mind and reduce anxiety symptoms.
- Prioritize tasks and create a realistic schedule to effectively reduce stress and improve organization.
- Seek support from loved ones to effectively alleviate stress by sharing feelings and concerns.
It is important to note that strategies for managing stress may vary for each individual. It is advised to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized guidance and support in managing Adderall-induced stress and anxiety.
In fact, a clinical trial has shown that implementing stress-management techniques alongside medication-assisted treatment programs improves outcomes for individuals with anxiety and substance use disorders.
Considering Non-Stimulant Alternatives
When managing stimulant-related anxiety, it is important to consider non-stimulant alternatives that can help alleviate symptoms. Here are some options:
- Behavioral therapy: Working with a mental health professional can provide techniques and strategies to manage anxiety without using stimulant medications. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and other forms of therapy can help individuals develop coping mechanisms and address underlying causes of anxiety.
- Relaxation techniques: Incorporating relaxation techniques such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, and mindfulness practices can help reduce anxiety and promote a sense of calm. These techniques can be used alongside or instead of stimulant medications.
- Alternative medications: Non-stimulant medications available for treating anxiety include selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs). These medications regulate the levels of serotonin in the brain and effectively reduce anxiety symptoms.
- Lifestyle changes: Making healthy lifestyle choices can have a positive impact on anxiety levels. Regular exercise, a balanced diet, adequate sleep, and stress management techniques contribute to overall well-being and reduce anxiety symptoms.
- Support groups and therapy groups: Engaging in therapy groups or support groups provides individuals with a safe space to share experiences and learn from others who have similar struggles. This social support is beneficial for managing anxiety and finding non-stimulant alternatives.
Considering non-stimulant alternatives is essential for addressing stimulant-related anxiety. It allows individuals to explore different avenues for managing their symptoms and finding strategies that work best for them. These alternatives offer effective solutions without relying solely on stimulant medications.

Seeking Professional Help
Struggling with anxiety caused by Adderall? Don’t worry, you’re not alone. In this section, we’ll explore the importance of seeking professional help when dealing with stimulant-related anxiety. Discover when it’s time to consult a doctor or a mental health professional, and the role that therapy and medication can play in finding relief. Get ready to regain control of your mental well-being and get back to living your best life.
When to Consult a Doctor or Mental Health Professional
Consulting a doctor or mental health professional is vital if you are experiencing concerning symptoms or side effects from Adderall. It is important to promptly seek professional help in order to evaluate and address any potential complications.
If you notice severe psychological symptoms such as panic attacks, difficulty focusing, or persistent anxiety, it is advisable to consult a mental health specialist. They will be able to assess your condition and provide appropriate guidance and treatment options.
In addition, if you experience physical symptoms such as rapid heart rate, sleep problems, or high blood pressure, it is important to consult a healthcare professional. They can evaluate your symptoms in context and help determine the most suitable course of action.
In certain cases, a doctor or mental health professional may suggest adjustments to medication dosage or alternative treatments to manage Adderall-related anxiety. They are also able to provide information about potential side effects and develop a personalized care plan based on your specific needs.
Always remember that seeking professional guidance is crucial for your well-being and safety. When experiencing symptoms related to Adderall, it is essential to seek the expertise of a doctor or mental health professional for proper evaluation, management, and support.
If your are thinking of quitting nicotine smoking while taking Adderall, read our article on how to quit smoking while taking Adderall to see the various ways this ADHD medication can help in your cessation journey,
The Role of Therapy and Medication
Therapy and medication play a crucial role in managing stimulant-related anxiety. Here are some important points to consider:
- Therapy can be beneficial: Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) helps individuals identify and address anxiety triggers associated with the use of Adderall. It equips them with coping strategies and tools to alleviate anxiety symptoms.
- Medication options: Medication can be prescribed to tackle anxiety symptoms. Benzodiazepines may be considered for short-term relief, but their usage should be supervised by a mental health professional due to the potential for dependence and side effects.
- Combination approach: In cases of severe anxiety or co-occurring mental health conditions, a combination of therapy and medication may be recommended. This approach addresses both the underlying anxiety and any other mental health issues.
- Regular monitoring: It is important for individuals receiving therapy and medication to have regular check-ins with their healthcare professional. This allows for adjustments to the treatment plan and prompt addressing of potential side effects or new symptoms.
- Holistic approaches: Alongside therapy and medication, complementary techniques such as relaxation exercises, regular physical activity, and a healthy lifestyle can aid in managing anxiety.
Remember, the role of therapy and medication in managing stimulant-related anxiety may differ for each person. It is crucial to consult with a mental health specialist for personalized guidance based on your specific needs and circumstances.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Adderall cause anxiety?
Yes, Adderall can cause or worsen anxiety symptoms in some individuals. The stimulant effects of Adderall, such as increased heart rate and blood pressure, can contribute to feelings of anxiety. Additionally, dependence on Adderall can lead to anxiety when the medication is not available.
What are the side effects of Adderall?
Common side effects of Adderall include nervousness, restlessness, headaches, problems sleeping, and decreased appetite. More severe side effects can include uncontrollable shaking or seizures, hallucinations, paranoia, and worsening mental health conditions like depression or anxiety.
How long does Adderall stay in your system?
The length of time Adderall stays in the body can vary depending on factors such as age, weight, dosage, and metabolism. Generally, Adderall can be detected in urine for up to two days, in blood for up to 46 hours, and in saliva for up to 20-50 hours.
What are some natural remedies for anxiety caused by Adderall?
To manage anxiety caused by Adderall, some natural remedies that may help include maintaining a regular sleep schedule, reducing caffeine consumption, engaging in regular aerobic exercise, practicing meditation and yoga, spending time outdoors, using essential oils with anxiety-relieving properties, and deep breathing exercises.
Can Adderall be used to treat anxiety?
Adderall is not commonly used to treat anxiety and may actually worsen anxiety symptoms in some individuals. It is primarily prescribed for attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and narcolepsy. Individuals with co-occurring ADHD and anxiety may benefit from a combination of therapy and medication specifically targeted at addressing both conditions.
What is the best treatment for managing stimulant-related anxiety?
The best treatment for managing stimulant-related anxiety will depend on the individual and their specific needs. Options may include therapy, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), and potentially anti-anxiety medication. It is important to consult with a healthcare or mental health professional at an outpatient treatment center to determine the most appropriate treatment plan.