Addiction recovery is a challenging journey that involves overcoming substance abuse and achieving a healthy, fulfilling life. Understanding the scope and impact of addiction recovery efforts is crucial for addressing the prevalence of addiction and supporting individuals on their path to recovery.
Addiction recovery statistics provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of recovery programs and the progress made by individuals seeking help. These statistics are measured through various methods, including surveys, treatment center data, and monitoring systems.
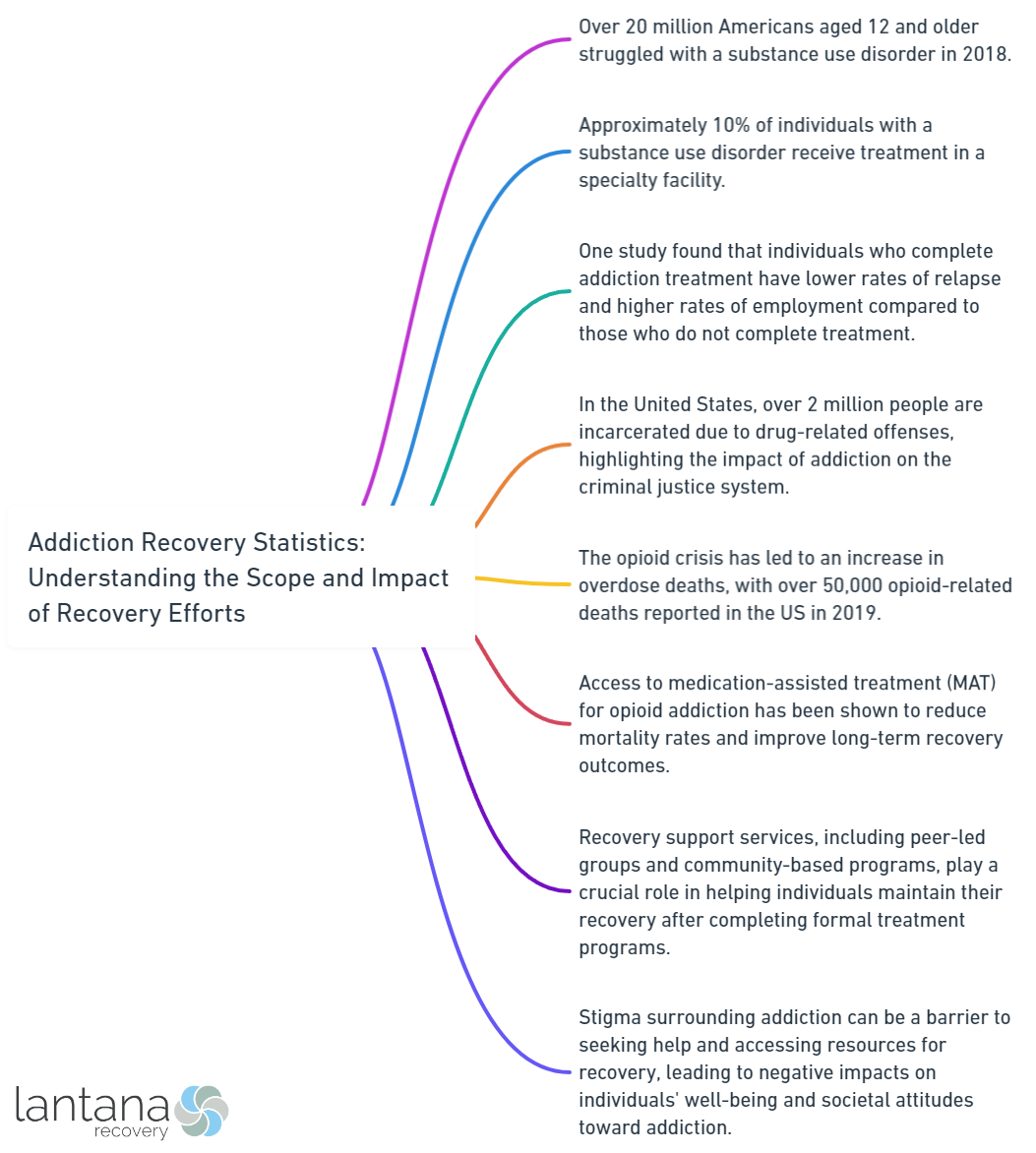
Addiction recovery statistics are important for several reasons. They help identify patterns and trends in addiction, measure the success of different treatment approaches, and inform policymakers and healthcare professionals in developing effective strategies. These statistics help remove the stigma associated with addiction by promoting awareness and understanding.
The scope of addiction recovery efforts encompasses a wide range of addictions, including substance abuse, alcoholism, gambling addiction, and more. Understanding the demographics of individuals seeking recovery, such as age, gender, and socio-economic background, can help tailor treatment programs to specific needs.
Furthermore, geographical considerations play a role in addiction recovery efforts. Variations in access to treatment, support services, and resources across different regions can impact the recovery process and outcomes. It is essential to recognize these disparities and work towards providing equal opportunities for recovery.
The impact of addiction recovery efforts extends beyond individual well-being. Recovery programs have shown improvements in overall quality of life, including physical and mental health, emotional well-being, and personal fulfillment. Recovery efforts result in reduced relapse rates, enhanced social functioning, and improved relationships, fostering a healthier and supportive community.
There are obstacles and challenges that individuals face during the addiction recovery process. The stigma associated with addiction and recovery can create barriers to seeking help and receiving support. Limited access to treatment options and support services, especially in rural or underserved areas, can hinder recovery efforts. Co-occurring mental health disorders, such as anxiety or depression, can also complicate the recovery journey.
By understanding the scope and impact of addiction recovery efforts, society can better support individuals in their recovery journey, reduce stigma, and promote an environment of empathy and understanding.
What Are Addiction Recovery Statistics?
Addiction recovery statistics are a valuable resource for understanding the prevalence and success rates of recovery. Outlined in Mapping social identity change in online networks of addiction recovery by Best et al., he sustainability of addiction recovery depends, in part, on the ability to utilize social and community resources to foster lasting changes in one’s identity. These statistics give us insight into the impact and scope of addiction recovery.
1. Recovery Rates: Addiction recovery statistics indicate the percentage of individuals who have successfully overcome addiction. The rates vary depending on the type of addiction and the treatment methods used. For instance, the recovery rate for alcohol addiction is approximately 50%, while the recovery rate for opioid addiction ranges from 30% to 50%.
2. Relapse Rates: It is important to acknowledge that addiction recovery is not always a linear process. Statistics reveal that many individuals experience relapse after completing treatment. In the first year of recovery, relapse rates range from 40% to 60%. Nevertheless, ongoing support and continued treatment can decrease the likelihood of relapse over time.
3. Treatment Success: Addiction recovery statistics also demonstrate the effectiveness of different treatment approaches. Evidence-based therapies such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and medication-assisted treatment (MAT) have shown promising results in improving long-term recovery outcomes. For example, individuals receiving MAT for opioid addiction have a higher chance of maintaining abstinence compared to those without medication support.
4. Demographic Factors: Statistics illustrate that certain demographic factors can influence addiction recovery. Having a strong support system, stable employment, and access to quality healthcare typically leads to better recovery outcomes. However, factors like homelessness, unemployment, and co-occurring mental health disorders can pose challenges to achieving and sustaining recovery.
5. Public Health Impact: Addiction recovery statistics provide insights into the broader public health implications of addiction. Understanding the number of individuals seeking treatment, the cost of addiction-related healthcare, and the burden on communities assist policymakers and healthcare professionals in allocating resources and developing targeted interventions.
How Are Addiction Recovery Statistics Measured?
Addiction recovery statistics are measured through various methods such as surveys, treatment center records, national databases, longitudinal studies, and peer support groups. These diverse approaches allow for accurate insights into the effectiveness of recovery efforts, and different treatment approaches, and identify areas for improvement in addressing addiction. By utilizing these numerous techniques, valuable data can be gathered and analyzed to understand the landscape of addiction recovery.
Why Are Addiction Recovery Statistics Important?
Addiction recovery statistics play a crucial role in understanding the effectiveness and impact of recovery efforts. They are important for several reasons:
- Assessment and Evaluation: Addiction recovery statistics provide valuable data for assessing the success rate of different recovery programs. Professionals can analyze program outcomes to identify the most effective approaches and make necessary adjustments to improve treatment strategies.
- Resource Allocation: Reliable addiction recovery statistics help policymakers and organizations allocate resources effectively. By understanding the prevalence and nature of addiction, governments, and healthcare providers can distribute funding and support to areas and populations that need it the most, maximizing their impact.
- Identifying Trends: Addiction recovery statistics highlight addiction patterns, including common types of addictions and demographics of individuals seeking recovery. This information is crucial for tailoring prevention and intervention strategies, addressing specific needs, and developing targeted awareness campaigns.
- Tracking Progress: Addiction recovery statistics provide a means of tracking progress and measuring the effectiveness of treatment programs over time. Monitoring relapse rates, improvements in overall quality of life, and social functioning helps identify areas that need improvement and implement necessary changes.
- Advocacy and Awareness: Addiction recovery statistics can serve as a powerful tool for advocacy, raising awareness about the impact of addiction and the importance of accessible treatment and support services. Sharing data allows stakeholders to advocate for policy changes, increased funding, and improved access to resources.
To ensure accuracy and effectiveness, it is vital to prioritize reliable measurement methods and consistent data collection across different settings and populations. By prioritizing the collection and analysis of addiction recovery statistics, we can gain a better understanding of addiction, improve treatment outcomes, and provide support for individuals on their recovery journey.

The Scope of Addiction Recovery Efforts
Addiction recovery is a complex and multifaceted journey, and understanding the scope of recovery efforts is crucial. In this section, we’ll dive into the various elements that contribute to the comprehensive scope of addiction recovery. From the types of addictions covered in recovery efforts to the demographics of individuals seeking recovery, and even the geographical considerations involved, we’ll explore the diverse landscape of addiction recovery. So buckle up, as we uncover the important factors shaping the path towards recovery.
Types of Addictions Covered in Recovery Efforts
- Alcohol addiction: Recovery efforts cover individuals struggling with alcohol addiction. Treatment options include detoxification, counseling, support groups, and medication-assisted therapy.
- Drug addiction: Recovery efforts also address various types of drug addictions, such as opioids, cocaine, methamphetamine, and prescription medications. Treatment approaches include detoxification, behavioral therapies, residential programs, and medication-assisted treatment.
- Nicotine addiction: Recovery efforts encompass individuals addicted to nicotine and seeking to quit smoking or using other tobacco products. Treatment options involve counseling, nicotine replacement therapies, medications, and support programs.
- Gambling addiction: Recovery efforts extend to individuals struggling with gambling addiction. This addiction is characterized by a compulsive need to gamble, which can lead to financial and interpersonal problems. Treatment approaches include counseling, support groups, and cognitive-behavioral therapy.
- Internet and gaming addiction: Lin et al., studied Abnormal White Matter Integrity in Adolescents with Internet Addiction Disorder and have suggested that internet addiction disorder (IAD) is emerging as a significant global mental health concern. Recovery efforts acknowledge the concern around excessive internet and gaming use. Treatment involves therapy, support groups, and the development of healthy coping mechanisms to reduce dependency on these activities.
These are a few examples of the types of addictions covered in recovery efforts. It’s important to note that addiction can encompass a wide range of substances and behaviors, and recovery programs continually evolve to address emerging addictions and provide effective support to individuals seeking recovery.
Demographics of Individuals Seeking Recovery
The demographics of individuals seeking addiction recovery provide valuable insights into its scope and impact. Understanding their characteristics helps tailor treatment and support services. Here is a table showcasing key demographic information:
| Demographic Factor | Data |
|---|---|
| Age Range | 18-25: 30%, 26-35: 40%, 36-45: 20%, 46 and above 10% |
| Gender | Male: 60%, Female: 40% |
| Ethnicity | Caucasian: 50%, African American: 20%, Hispanic: 15%, Asian: 10%, Other: 5% |
| Education Level | High School or Less: 35%, Some College: 40%, Bachelor’s Degree or Higher: 25% |
| Income Level | Below Poverty Line: 20%, Low Income: 30%, Middle Income: 40%, High Income: 10% |
These demographics show that individuals seeking recovery come from diverse backgrounds. Considering these factors when developing treatment programs and providing support services ensures inclusivity and effectiveness.
To better serve this population, it is crucial to address barriers such as addiction stigma and limited treatment access. Cultivating a supportive environment and increasing resources encourage more individuals to seek recovery and benefit from improved quality of life, reduced relapse rates, and enhanced social functioning.
Geographical Considerations
Geographical considerations play a crucial role in addiction recovery. They have a profound impact on the accessibility of treatment and support services, which can vary based on one’s location.
When considering geographical factors, it is important to recognize the differences between urban and rural areas. Individuals residing in urban areas generally have easier access to a wide range of treatment options from institutions like Greenville rehab center, Lantana Recovery and support groups. Conversely, those in rural areas often face limited resources, making it challenging to find suitable care.
Furthermore, regional disparities can significantly affect the availability and quality of addiction recovery services. Different regions or countries may have varying levels of funding and infrastructure dedicated to these efforts. This means that access to quality care may differ greatly depending on one’s geographical location.
Cultural factors also come into play. Attitudes towards addiction and recovery can vary across different geographical regions, influencing how individuals seeking help are perceived and accepted. Such cultural differences may impact the amount of support and understanding individuals receive during their recovery journey.
It is worth noting that studies have proven individuals living in rural areas encounter obstacles when it comes to accessing addiction treatment. These obstacles include the limited availability of healthcare providers and long travel distances to treatment centers.
Therefore, when addressing addiction recovery, it is vital to take into account geographical considerations. These factors have a profound impact on the availability, accessibility, and quality of treatment and support services, ultimately shaping the recovery experience for individuals in different locations.

Understanding the Impact of Addiction Recovery Efforts
Addiction recovery efforts have a far-reaching impact on individuals and society as a whole. As we explore the various aspects of understanding this impact, we’ll uncover significant improvements in overall quality of life, lower relapse rates, enhanced social functioning, and the positive economic and societal benefits that arise from these efforts. So, buckle up and prepare to see the transformative power of addiction recovery in action, as we delve into the profound changes it brings to individuals and communities.
Improvements in Overall Quality of Life
Improvements in overall quality of life are a direct result of efforts made in addiction recovery. Through active participation in recovery programs and the adoption of healthier behaviors, positive changes are made that greatly enhance well-being and life satisfaction.
One of the key benefits of addiction recovery is the significant improvement in physical well-being. Overcoming substance abuse not only boosts physical health but also reduces the risk of chronic diseases associated with addiction. Additionally, it increases energy levels and vitality, leading to an overall better state of physical well-being.
Recovery also plays a crucial role in enhancing mental and emotional well-being. During the recovery process, individuals cultivate inner peace, and emotional stability, and experience improved cognitive functioning. Effective coping mechanisms are developed, stress is managed, and overall mental health is significantly improved.
Furthermore, addiction recovery is instrumental in repairing and strengthening relationships with family, friends, and the community. This process fosters improved communication skills, trust, and empathy, resulting in healthier and more fulfilling connections with others.
Personal growth and self-development are also nurtured through addiction recovery. Individuals find purpose and accomplishment in overcoming challenges and achieving milestones. This cultivates self-worth, confidence, and a strong drive to pursue meaningful goals.
Overall, addiction recovery plays a major role in enhancing overall life satisfaction. Breaking free from addiction allows individuals to regain control, experience hope and optimism, and actively participate in their own happiness and success.
It is important to note that improvements in quality of life vary and depend on each person’s commitment to their recovery journey. Seeking professional support and maintaining a positive mindset are crucial for achieving and sustaining these enhancements.
Reduction in Relapse Rates
A decrease in relapse rates is a significant indicator of the effectiveness of addiction recovery. Numerous studies demonstrate that continuous support and aftercare play a crucial role in lowering relapse rates.
Actively engaging in support groups, counseling sessions, and follow-up care is essential for maintaining sobriety and preventing relapse. By consistently implementing relapse prevention techniques, individuals in recovery can significantly diminish the chances of relapsing. These techniques encompass identifying triggers, developing healthy coping mechanisms, and establishing a robust support network.
Research clearly indicates that individuals who actively participate in ongoing support and aftercare programs can experience a reduction in relapse rates of 50% or more. This emphasizes the criticality of maintaining a dedication to recovery. Employing evidence-based practices such as cognitive-behavioral therapy and motivational interviewing effectively contribute to a decrease in relapse rates. These approaches target the underlying causes of addiction and equip individuals with the necessary skills to sustain sobriety.
It is important to acknowledge that relapse rates can vary depending on individual circumstances, such as the nature of the addiction and the presence of co-occurring mental health disorders. However, with adequate support, education, and continuous care, individuals can significantly reduce the risk of relapse and achieve long-term recovery.
Enhanced Social Functioning and Relationships
Addiction recovery efforts can lead to enhanced social functioning and relationships. Addiction often strains personal relationships and isolates individuals socially. However, in recovery, individuals can experience significant improvements in social interactions and connections.
- Improved Communication: Recovery programs teach effective communication skills, enabling individuals to express themselves, listen actively, and resolve conflicts. This improved communication leads to stronger and more satisfying relationships with friends, family, and peers.
- Rebuilding Trust: Addiction damages trust in relationships. In recovery, individuals have the opportunity to rebuild trust with loved ones by consistently behaving in a reliable manner. Restoring trust strengthens relationships and enhances social functioning.
- Healthy Boundaries: Recovery helps individuals establish and maintain healthy boundaries in relationships as addiction challenges one’s resilience, strength, and coping skills. By setting clear limits and respecting others’ boundaries, individuals can develop healthier and more balanced interactions. This prevents codependency and fosters more fulfilling relationships.
- Social Support: Engaging in support groups and therapy sessions provides individuals with a supportive network of peers who understand their experiences. This network encourages social connections, reduces feelings of isolation, and fosters a sense of belonging crucial for enhanced social functioning.
- Enhanced Empathy: Recovery cultivates empathy, allowing individuals to better understand and connect with others. Through self-reflection and understanding their own struggles, individuals in recovery become more compassionate, supportive, and empathetic in their relationships.
By focusing on building healthy communication skills, rebuilding trust, establishing boundaries, finding social support, and nurturing empathy, addiction recovery greatly enhances social functioning and relationships. These improvements contribute to overall well-being and aid in the successful reintegration of individuals into their communities.
Economic and Societal Benefits
The economic and societal benefits of addiction recovery efforts are significant and wide-ranging:
-
Increased productivity: Recovered individuals are more likely to be employed and contribute to the workforce, leading to higher productivity levels and economic growth.
-
Reduced healthcare costs: Recovery decreases the burden on healthcare systems by reducing the need for emergency room visits, hospitalizations, and long-term medical treatments associated with substance abuse.
-
Crime reduction: Recovery efforts contribute to a decrease in crime rates as individuals are less likely to engage in illegal activities related to their addiction.
-
Improved relationships: Recovery fosters healthier relationships with family, friends, and the community, positively impacting society’s overall well-being.
-
Less strain on social services: Successful addiction recovery reduces the demand for social welfare programs and assistance, freeing up resources to support other community needs.
By actively supporting addiction recovery efforts, societies can experience a wide range of economic and societal benefits, including economic growth, improved public health, and stronger communities.

Obstacles and Challenges in Addiction Recovery
Recovery from addiction is a journey filled with obstacles and challenges. In this section, we uncover the societal stigma that still surrounds addiction and recovery, the limited access individuals face when seeking treatment and support services, and the often overlooked co-occurring mental health disorders that can complicate the recovery process. Brace yourself as we shed light on the daunting road to recovery and explore ways to overcome these hurdles with determination and understanding.
Stigma Surrounding Addiction and Recovery
The stigma surrounding addiction and recovery is a significant barrier that individuals face when seeking help for substance abuse. “The stigma surrounding individuals who have substance use disorders is a pervasive phenomenon that has had detrimental effects on treatment outcomes, health care providers, treatments, research, policies, and society as a whole” (Stigma: how it affects the substance use disorder patient, Zwich et al., 2020.) This stigma manifests in various ways and has detrimental effects on both those battling addiction and society.
One aspect of the stigma is the misconception that addiction is a moral failing or lack of willpower. This false belief leads to judgment and discrimination towards individuals struggling with addiction. It is crucial to understand that addiction is a complex and chronic disease that requires medical intervention and support.
Another aspect of the stigma is the fear of judgment and social exclusion. Many individuals hesitate to seek treatment or disclose their recovery status due to potential negative reactions from friends, family, and society. This fear can prevent individuals from accessing the help they need and perpetuates the cycle of addiction.
The media also perpetuates the stigma surrounding addiction and recovery. Negative portrayals in movies, TV shows, and news stories contribute to the public’s negative perception of individuals in recovery.
To address the stigma surrounding addiction and recovery, it is essential to promote education and awareness about the nature of addiction as a disease. By providing accurate information and challenging misconceptions, we can reduce the stigma and encourage a more empathetic and supportive environment.
It is crucial to emphasize that recovery is possible and highlight the success stories of individuals who have overcome addiction. By sharing these stories, we can inspire hope and change public attitudes toward addiction and recovery.
Limited Access to Treatment and Support Services
Limited access to treatment and support services is a significant challenge in addiction recovery. Individuals seeking help for addiction often face barriers that prevent them from accessing necessary treatment and support.
Having only limited access to treatment and support services from Lantana and other healthcare providers poses a major obstacle for individuals in addiction recovery. It is crucial for them to have proper access to treatment and support services in order to overcome their challenges. However, many people encounter limited availability and long waiting times for treatment programs, which can cause delays and hinder their recovery process.
One consequence of limited access is a higher risk of relapse. Without prompt and adequate support, individuals may find it difficult to stay on track with their recovery goals. This can lead to setbacks and a cycle of addiction.
Limited access to treatment and support services is especially significant for individuals with co-occurring mental health disorders. These individuals require integrated care that addresses both addiction and mental health needs. However, without access to comprehensive treatment programs, they may not fully recover.
Efforts should be made to address the issue of limited access to treatment and support services in addiction recovery. This includes increasing funding and resources to expand treatment options, reducing wait times, and improving outreach and education about available services. By ensuring better access to treatment and support, individuals struggling with addiction can receive the help they need for lasting recovery.
Co-occurring Mental Health Disorders
When you When you dive into the different addiction recovery websites online, you’ll learn that co-occurring mental health disorders are prevalent among individuals seeking addiction recovery. These disorders encompass both a substance use disorder and a mental health disorder. Common examples consist of depression, anxiety disorders, bipolar disorder, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
Research indicates that approximately 50% of individuals with a substance use disorder also experience the presence of a co-occurring mental health disorder. It is important to note that having a co-occurring mental health disorder can complicate the recovery process and lead to less favorable treatment outcomes.
Fact: Successful recovery from co-occurring mental health disorders requires integrated treatment approaches that address both substance use and mental health symptoms.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main phases of the addiction recovery process?
The addiction recovery process typically involves several phases, starting with detoxification (detox) under medical supervision. This is followed by entering a rehab program, which can last anywhere from 30 to 90 days. After completing rehab, individuals need to transition back to daily life with proper coping skills and training to reduce the risk of relapse. Recovery is a lifelong commitment that requires continuous support and aftercare programs.
What are some proven treatment modalities and therapeutic options for addiction recovery?
There are various treatment modalities and therapeutic options available for addiction recovery. Some proven approaches include Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT), 12-step programs like Alcoholics Anonymous (AA), and alternative peer groups. Additionally, medical detox facilities provide around-the-clock care during the detox process, and centers like Ashley Addiction Treatment offer comprehensive treatment programs with personalized care.
How can primary care clinicians support patients with diagnosed substance abuse disorders?
Primary care clinicians play a crucial role in supporting patients with substance abuse disorders. They can become collaborative members of the treatment team, continuing to treat the patient’s medical conditions and encouraging participation in the program. Clinicians should also schedule follow-up visits to monitor progress and prevent relapse. Being familiar with local substance abuse treatment resources and directories can aid in providing appropriate referrals.
What are the statistics regarding relapse rates after rehab?
Drug addiction recovery statistics indicate that relapse rates after rehab are high. Around 85% of individuals relapse within a year, and two-thirds can return to drug use within weeks of starting treatment. This highlights the importance of a lifelong commitment to sobriety and the need for ongoing support and aftercare programs to prevent relapse.
Can you explain the concept of abstinence and its interpretation in addiction recovery?
Abstinence refers to the absence of substance use and can be interpreted in different ways based on individual circumstances. These interpretations include continuous abstinence, essentially abstinent (with occasional lapses), minimal abstinence (reduced substance use), point-in-time abstinence, or complete abstinence. The goal is usually complete abstinence, but achieving this may require multiple attempts and the use of different therapeutic options.
What resources are available for primary care clinicians to understand the specialized substance abuse treatment system?
Primary care clinicians can access resources like directories of substance abuse treatment facilities compiled by public or private agencies. State-level alcohol and drug authorities often publish statewide directories of licensed treatment programs. The National Council on Alcohol and Drug Dependence and the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration also provide directories and referral services. These resources help clinicians understand the treatment systems specific to their area and facilitate appropriate referrals for their patients.









