How does alcoholism impair the capacity to love? The answer lies deeper than mere intoxication—it’s in the tangled web of emotional unavailability, broken trust, and the profound impact on mental health. This article navigates through these intricate issues, paving the way for understanding why an alcoholic cannot love, and what hope there may be for healing.
Key Takeaways
- Alcoholism significantly diminishes emotional availability, leading to impaired ability to love and connect, with intoxication masking true emotions and fostering emotional detachment and negative emotions like guilt and shame.
- Substance abuse disorder disrupts relationship dynamics through neglect, codependency, loss of trust, and financial instability, with Behavioral Couples Therapy offering potential improvements.
- Alcoholism negatively affects mental health and behavior, aggravating mental disorders, perpetuating a progressive disease that increases risk-taking and emotional instability, and often resulting in confrontations and legal issues.
Alcohol Rehab South Carolina
Finding the right alcohol rehab in South Carolina can be a pivotal step towards recovery for individuals struggling with alcohol addiction. With a range of treatment options available, tailored to meet individual needs, those seeking help can find solace in knowing there are resources designed to support their journey to sobriety. South Carolina offers various rehab facilities equipped with professional staff members who specialize in addiction recovery, providing comprehensive care and support throughout the rehabilitation process. Whether one requires inpatient treatment for severe addiction or outpatient programs for more flexibility, there are options available to suit different circumstances and preferences. Additionally, many alcohol rehab centers in South Carolina incorporate therapy and counseling sessions, helping individuals address the underlying causes of their addiction and develop coping strategies for long-term sobriety. By accessing these resources, individuals can embark on a path towards healing and a brighter, substance-free future.
The Struggle with Emotional Availability in Active Alcoholism

In the throes of active alcoholism, emotional availability becomes as elusive as a mirage in the desert. The alcoholic’s inner turmoil, laden with guilt and shame, erodes their self-esteem and distorts their ability to love and be present emotionally. The chemical impact of alcohol on the brain further complicates matters; neurotransmitters are hijacked, and the decrease in ‘feel-good’ chemicals such as serotonin and dopamine creates a barrier to maintaining loving relationships.
The temporary solace found in alcohol’s calming effects is fleeting, and dependence only grows, leaving behind a husk of emotional detachment that stifles intimacy and genuine connection. Those who abuse alcohol often find themselves trapped in this cycle.
The Mask of Intoxication
Intoxication conceals the true emotions of an alcoholic behind a mask, obscuring the ability to communicate effectively and connect on a deep level. The result is a facade that not only masks the individual’s true feelings but also prevents the establishment of an emotional bond that is essential for a healthy and loving relationship.
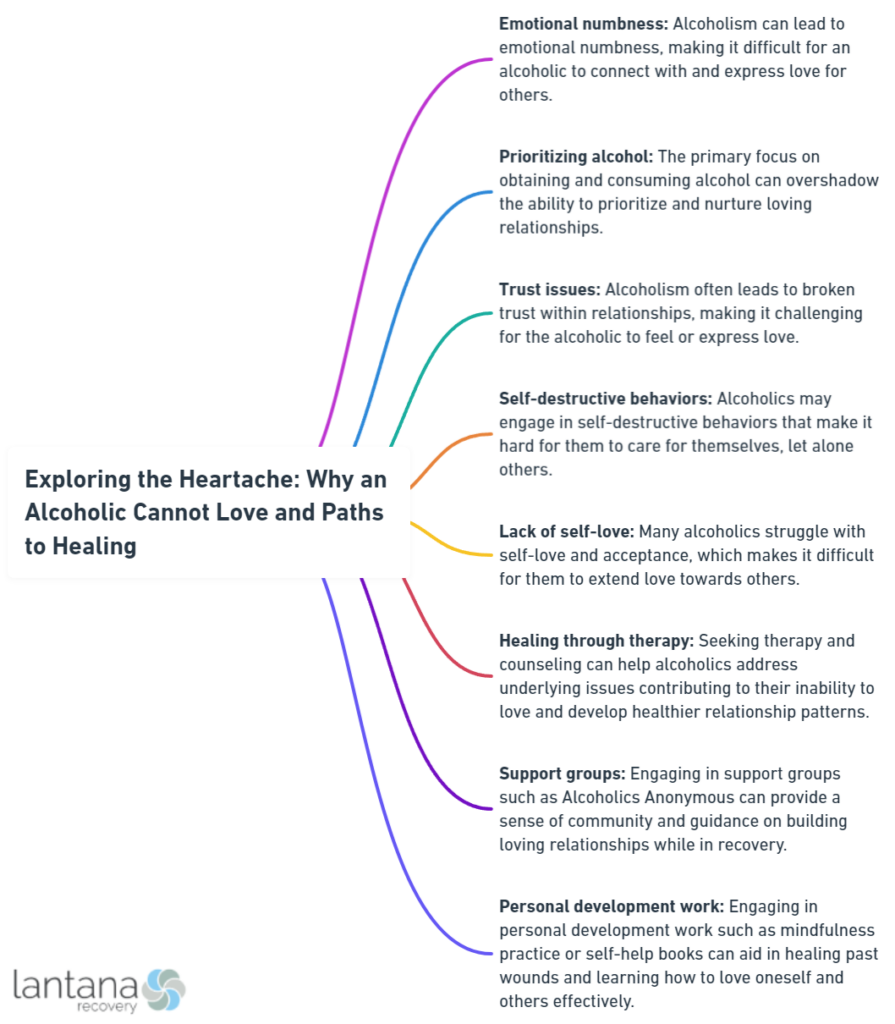
The Cycle of Emotional Detachment
The path of active alcoholism, a form of active addiction, is marked by a gradual retreat from emotional expression, leading to a state of emotional unavailability. This detachment is a significant barrier to forming and maintaining the connections that are the bedrock of any healthy relationship.
The Burden of Negative Emotions
Amplified by alcohol abuse, negative emotions such as guilt and shame form a chasm between the alcoholic and their ability to experience and express love. The weight of these emotions acts as a barrier to empathy and connection, making emotional well-being a distant goal.
Why is Alcohol Addictive
Why is alcohol addictive? Alcohol addiction, also known as alcoholism, is a complex issue influenced by various factors. One reason lies in the way alcohol affects the brain’s chemistry. It interacts with neurotransmitters, such as dopamine, which play a crucial role in pleasure and reward pathways. This leads to feelings of euphoria and relaxation, reinforcing the desire to consume more alcohol. Additionally, genetics and environmental factors can contribute to the development of alcohol addiction. Over time, regular alcohol consumption can lead to tolerance and dependence, making it difficult for individuals to control their intake. Moreover, societal and cultural norms surrounding alcohol use can further perpetuate addictive behaviors. Understanding these factors is essential for addressing alcohol addiction effectively.
The Impact of Substance Abuse Disorder on Relationship Dynamics

Substance abuse disorder wreaks havoc on the dynamics of a relationship, creating a chasm where trust and mutual respect once stood. Alcohol abuse leads to neglect of responsibilities, causing the alcoholic to withdraw from activities and time spent with their partner. This neglect fosters feelings of hopelessness and worry, which further strain the relationship, potentially leading to verbal abuse.
Behavioral Couples Therapy (BCT) offers a glimmer of hope, yielding greater reductions in substance use and improvements in relationship satisfaction than typical individual-based treatment. However, the key ingredients to healthy relationships are often eroded by the behavioral impacts of Alcohol Use Disorder.
Codependent Relationship Patterns
Codependency is a common pattern in relationships affected by alcohol addiction. One partner may become excessively dependent on the alcoholic, reinforcing an unhealthy dynamic that masquerades as love but is rooted in mutual dysfunction. The thrival of addiction is facilitated in such a relationship, where enabling behaviors further entrench the addiction, and true intimacy is impeded.
Addressing codependency may involve setting boundaries, sometimes without explicitly sharing them to avoid resistance, and seeking Behavioral Couples Therapy to build support for abstinence and improve relationship functioning.
Trust Erosion and Broken Promises
At the heart of healthy relationships lie trust and promises, both of which are often casualties of alcoholism. The secrecy of substance use and the tendency of the alcoholic to deny the problem obstruct the development of trust and intimacy. The habitual dishonesty and failure to fulfill responsibilities or keep promises further damage the trust, leaving the partner feeling insecure and destabilized.
Financial Instability and Its Ripple Effects
The financial instability caused by alcoholism creates a domino effect that extends far beyond the wallet. Excessive spending on alcohol affects the ability to pay bills and make necessary purchases, leading to job loss and potentially homelessness.
The diversion of funds towards alcohol use often takes away from critical areas like housing and education, creating a cycle of debt and long-term financial issues within the relationship.
Alcohol’s Grip on Mental Health and Behavior

Alcoholism extends its grip beyond the bottle, grasping tightly at the mental health and behavior of the afflicted individual. Long-term use of alcohol as a coping mechanism exacerbates mental health issues like depression and anxiety, leading to emotional instability and a chaotic home environment. Personality changes, including increased aggression and impulsivity, are common in alcoholics, impacting their ability to form genuine connections.
The complex relationship between alcohol consumption, alcohol use disorder, and aggression is bidirectional, increasing the risk of developing AUD and vice versa.
The Role of Co-Existing Mental Disorders
Co-existing mental disorders greatly complicate the progression and treatment of alcohol use disorders. Conditions such as major depressive disorder, bipolar disorder, and other substance use disorders exhibit high prevalence rates with AUD, adding layers of complexity to the individual’s already precarious situation.
The co-occurrence of these disorders leads to frequent alcohol use and severe psychiatric symptoms, escalating consequences such as higher hospitalization rates and increased suicide risk.
The Path of Progressive Disease
AUD is insidious in its progression, as the individual develops increased tolerance to alcohol and experiences withdrawal symptoms, a clear indication of deepening reliance. This progressive disease is characterized by:
- repeated unhealthy drinking behaviors
- increased risk-taking
- straining relationships
- leading to impulsive conduct.
From Emotional Instability to Physical Altercations
Emotional instability in alcoholics often results in:
- Diminished capacity to manage interpersonal conflicts
- Verbal and physical altercations
- Unreliable and raw emotions
- Abusive behavior which masks underlying emotional issues
Intoxication exacerbates these issues and makes it even more difficult to manage emotions and conflicts.
The serious consequences of alcohol-induced confrontations may include legal problems, heavy fines, and jail time.
Navigating the Complexities of Loving an Alcoholic
Loving an alcoholic is akin to navigating a labyrinth, where understanding the challenges and developing coping mechanisms are crucial for traversing its twists and turns. Compassionate strategies, self-care, and creating a solid support network are key elements in supporting an alcoholic’s journey to recovery and maintaining a loving approach.
Understanding the Alcoholic Love Paradox
The “alcoholic cannot love” paradox is a complex interplay of emotions and behaviors that require acknowledgment and understanding for effective coping.
Partners of alcoholics, who may also be a family member, must navigate this terrain with patience and compassion to maintain a loving relationship.
Setting Boundaries for Emotional Well Being
Setting boundaries is an act of self-preservation, a necessary step to prevent personal detriment in dysfunctional relationships.
Establishing healthy relationship boundaries is crucial for managing personal well-being and maintaining respect within the relationship, which ultimately helps to maintain healthy relationships.
Seeking Professional Help Together

Seeking professional help together provides a structured approach to address alcohol-related relationship issues and ensures that both partners are involved in the recovery journey. Couples therapy and support services offer significant relief from the cycle of broken promises and build a pathway for genuine progress and healing.
What is Binge Drinking
Binge drinking is a pattern of excessive alcohol consumption characterized by consuming large quantities of alcohol within a short period, typically leading to a blood alcohol concentration (BAC) of 0.08 grams per deciliter or higher. This behavior often occurs with the intention of becoming intoxicated quickly. While there isn’t a universally agreed-upon definition of binge drinking in terms of specific quantities or timeframes, it generally involves consuming enough alcohol to significantly impair judgment and physical coordination. Binge drinking poses serious health risks, including alcohol poisoning, liver disease, cardiovascular problems, and an increased likelihood of accidents or injuries. It’s particularly prevalent among young adults and college students, often associated with social gatherings or peer pressure. Effective prevention strategies and education campaigns aim to raise awareness about the risks associated with binge drinking and promote responsible alcohol consumption habits.
Recovery: A Journey Toward Regaining Control and Rebuilding Love
Recovery is a transformative journey that enables individuals to regain control over their lives and rebuild relationships through comprehensive addiction treatment and mutual support. There is always hope for healing and reconnection, which can rebuild the emotional bonds previously strained by alcoholism.
Committing to healthy coping mechanisms and establishing a relationship dynamic that supports emotional availability and care is essential for sustaining sobriety.
The Transformation through Addiction Treatment
Acknowledging the problem and seeking help are the first steps toward recovery for an alcoholic. Comprehensive addiction treatment enables the transformation of the individual’s life and encourages relational rebuilding.
Support Groups as a Pillar of Recovery
Support groups provide a community of empathy and mutual support for both the alcoholic and their partner, playing a crucial role in the recovery process. These groups foster an environment of understanding and accountability, crucial for maintaining sobriety after an alcohol intervention.
The Importance of Individual and Joint Therapy
Individual and joint therapy offer spaces for personal healing and relationship rehabilitation, playing crucial roles in the recovery process.
Behavioral Couples Therapy (BCT) utilizes various techniques to bolster positive activities and communication, facilitating the rehabilitation of relationships.
Summary
As we bring this exploration to a close, it is clear that the grip of alcoholism on love is both powerful and destructive. Yet, amidst the chaos and heartache, there lies a beacon of hope in recovery. The journey towards healing is not a solitary one; it is paved with the support, understanding, and commitment of both the alcoholic and their loved ones. The transformation through addiction treatment, the solidarity found in support groups, and the guided path offered by professional therapy illuminate the way to reclaiming control and rekindling the embers of love that alcoholism once threatened to extinguish.
Let this be a message of hope and a call to action for those entangled in the web of alcoholism. The struggle is real, but so too is the potential for healing and the restoration of loving relationships. May the insights shared here inspire and empower you to embark on the path to recovery, knowing that love, though challenged, can endure and flourish once again.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does alcohol affect personality?
Alcohol can affect personality by increasing traits like impulsivity, aggression, and neuroticism, while also lowering conscientiousness and agreeableness. These changes may manifest as mood swings, hostility, and increased risk of negative mental health symptoms.
What are the 4 types of wives of alcoholics?
The four types of wives of alcoholics are Suffering Susan, controlling Catherine, wavering Winifred, and punitive Polly, as described by Whalen in 1983. These types highlight the significant contribution of the wife’s personality to her husband’s alcoholism.
Does alcohol affect love?
Yes, alcohol can affect love by causing feelings of detachment and disinterest when consumed in excess. It’s important to be mindful of the impact of alcohol on your relationship.
Can someone with alcohol use disorder still experience genuine love?
Yes, someone with alcohol use disorder can still experience genuine love, although alcohol may affect their capacity to express it.
How does alcoholism affect the mental health of the alcoholic?
Alcoholism exacerbates mental health issues, leading to emotional instability and a chaotic home environment for the individual struggling with alcohol addiction. It can worsen conditions like depression and anxiety, affecting the overall mental health of the alcoholic.








