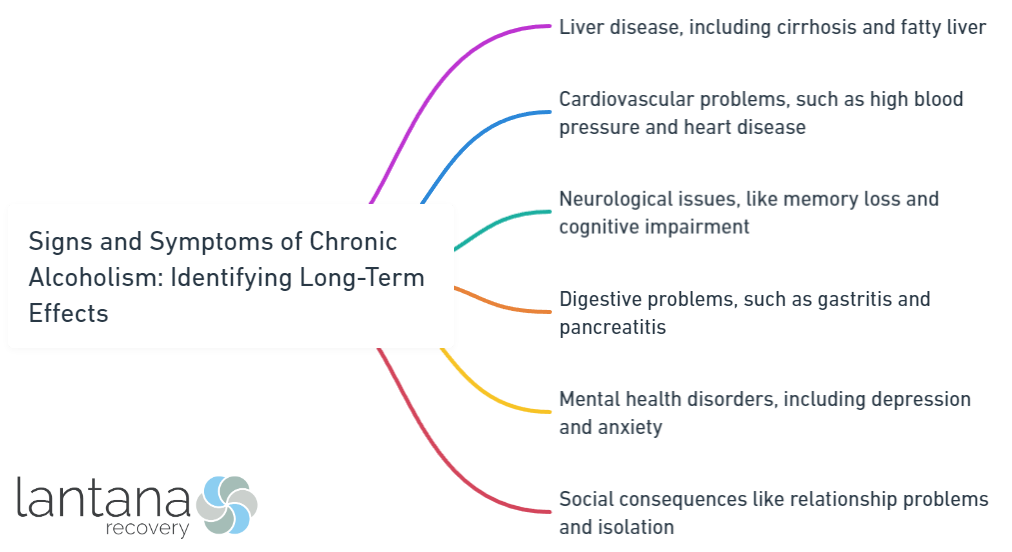
Chronic alcoholism is a serious condition characterized by the excessive and prolonged consumption of alcohol, leading to severe physical, psychological, and social consequences. Understanding the long-term effects of chronic alcoholism is crucial in identifying and addressing this issue effectively.
Research conducted by the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism has shown that chronic alcoholism can have detrimental effects on the body, including liver damage, cardiovascular issues, cognitive impairment, and the development of mental health disorders.
Chronic alcoholism can manifest in various signs and symptoms, both physical and psychological. Recognizing these indicators is essential in identifying individuals who may be struggling with chronic alcoholism. Some common signs include changes in appearance, frequent cravings for alcohol, withdrawal symptoms, tolerance to alcohol, neglecting responsibilities, and experiencing relationship problems.
The impact of chronic alcoholism on health and well-being is significant and can have long-lasting consequences. Seeking help for chronic alcoholism is crucial for recovery. Treatment options may include detoxification and rehabilitation, therapy, support groups, and maintenance for relapse prevention. By recognizing the signs, understanding the long-term effects, and seeking assistance, individuals with chronic alcoholism can take steps towards recovery and improving their overall well-being.
What is Chronic Alcoholism?
Chronic alcoholism, also known as alcohol use disorder, is a serious condition characterized by the excessive and prolonged consumption of alcohol. This chronic pattern of alcohol abuse can lead to both physical and psychological dependence. It is important to note that chronic alcoholism is not the same as occasional heavy drinking; it is a persistent and harmful behavior over an extended period of time.
The effects of chronic alcoholism can be detrimental to both physical and mental health. It can seriously damage vital organs such as the liver, heart, and brain. This can result in serious medical conditions including liver cirrhosis, pancreatitis, cardiovascular diseases, and cognitive impairment.
Furthermore, chronic alcoholism can have negative impacts on personal relationships, work performance, and overall quality of life. It can lead to financial difficulties, legal problems, and social isolation.
If left untreated, chronic alcoholism can have severe consequences, including an increased risk of death due to organ failure or alcohol-related accidents. However, it is important to know that recovery is possible with appropriate treatment and support.
If you suspect that someone you know may be struggling with chronic alcoholism, it is crucial to seek help from healthcare professionals or support groups. There are various treatment options available, such as detoxification, counseling, and medication, which can effectively manage the condition and promote a healthier lifestyle. Remember, the journey to recovery takes time, but with the right support, it is possible to overcome chronic alcoholism and improve overall well-being.

Understanding the Long-Term Effects of Chronic Alcoholism
Understanding the long-term effects of chronic alcoholism is crucial in recognizing the impact of prolonged alcohol abuse on an individual’s health and well-being. By exploring these consequences, we can comprehend the severity of this condition.
Chronic alcoholism can cause liver damage, such as alcoholic hepatitis and cirrhosis, which hinder the liver’s function and potentially lead to liver failure. Excessive alcohol consumption can also damage the brain and impair cognitive function, resulting in memory loss, difficulty concentrating, decreased coordination, and psychiatric disorders.
Moreover, chronic alcoholism increases the risk of cardiovascular issues, including high blood pressure, irregular heart rhythms, and an increased risk of heart attacks and strokes. Alcohol can irritate the gastrointestinal tract, causing digestive disorders like gastritis, ulcers, and pancreatitis.
Apart from these health complications, long-term alcohol abuse is associated with a higher risk of developing various types of cancer, such as liver, mouth, throat, esophageal, and breast cancer. Research demonstrates that chronic alcoholism can shorten an individual’s lifespan by an average of 10 to 15 years.
Therefore, it is crucial to address alcohol abuse and provide support for those affected by this condition, considering the detrimental effects of alcohol on the body.
How Does Chronic Alcoholism Affect the Body?
Chronic alcoholism significantly affects the body. Excessive and prolonged alcohol consumption can impact various bodily systems. How Does Chronic Alcoholism Affect the Body?
- Liver damage: Chronic alcoholism can cause fatty liver, alcoholic hepatitis, and cirrhosis, impairing liver function and detoxification.
- Cardiovascular issues: Alcohol abuse contributes to cardiovascular disease, including high blood pressure, irregular heart rhythms, and weakened heart muscles, increasing the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
- Cognitive impairment: Long-term alcohol abuse damages the brain, impairing cognitive functions like memory, attention, and problem-solving abilities. It also increases the risk of developing conditions such as dementia.
- Mental health disorders: Chronic alcoholism often leads to depression, anxiety, and increased suicide risk. Alcohol worsens pre-existing mental health conditions and complicates treatment.
- Social problems: Alcohol abuse strains relationships, causes social isolation, conflicts, communication impairment, and financial difficulties.
Recognize the harmful effects of chronic alcoholism on the body and seek help if struggling with alcohol use disorder. Detoxification, rehabilitation programs, therapy, and support groups are available to overcome alcohol addiction and minimize long-term health risks.
What are the Physical Signs of Chronic Alcoholism?
- Chronic alcoholism can have various physical signs, including:
- Jaundice: Yellowing of the skin and eyes caused by liver damage and a buildup of bilirubin in the blood.
- Weight loss: The body’s ability to absorb nutrients from food can be hindered, leading to weight loss.
- Appearance of broken blood vessels: Spider-like blood vessels may appear on the skin, particularly on the face and nose.
- Swollen or tender abdomen: The liver can become enlarged due to alcohol-related liver disease, resulting in a swollen or tender abdomen.
- Tremors or shaking: Alcohol withdrawal tremors can cause tremors or shaking, especially in the hands.
- Poor coordination and balance: Chronic alcohol consumption can lead to poor coordination and balance due to its impact on the central nervous system.
- Redness or flushing of the skin: Alcohol can cause blood vessels to dilate, resulting in a flushed appearance of the skin, particularly on the face.
It is important to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis if chronic alcoholism is suspected, as these physical signs may also indicate other health conditions.
Pro-tip: If you or someone else displays these physical signs and chronic alcoholism is suspected, seeking help and support from healthcare professionals or support groups is crucial. Early intervention and treatment can significantly improve outcomes and quality of life.
What are the Psychological Signs of Chronic Alcoholism?
Chronic alcoholism is characterized by various psychological signs that are important to recognize in order to address the condition effectively. Understanding these signs is crucial for identifying and addressing the problem of chronic alcoholism.
Let’s explore the psychological signs of chronic alcoholism:
1. Impaired judgment: Chronic alcoholism leads to impaired decision-making and poor judgment. Individuals may engage in risky behaviors without considering the consequences of their actions.
2. Mood swings: Frequent and extreme changes in mood, ranging from depression and anxiety to irritability and even euphoria and aggression, are common psychological signs of chronic alcoholism.
3. Memory problems: Alcohol affects the brain and can result in memory impairment. Those struggling with chronic alcoholism may experience blackouts or have difficulties recalling events, conversations, or important details.
4. Increased tolerance and cravings: Development of a higher tolerance to alcohol and experiencing strong cravings are psychological signs of chronic alcoholism. This often leads individuals to consume larger quantities of alcohol in order to achieve the desired effects.
5. Isolation and social withdrawal: Chronic alcoholism can cause social problems, leading to isolation and withdrawal from friends, family, and social activities. Individuals may prioritize alcohol over personal relationships, straining or even breaking them.
6. Mental health issues: Chronic alcoholism often contributes to the development or worsening of mental health disorders such as depression, anxiety, and bipolar disorder. Alcohol can temporarily mask the symptoms, leading individuals to self-medicate and become dependent on alcohol.
Recognizing these psychological signs of chronic alcoholism is crucial in identifying the problem. It is essential to seek appropriate help and treatment. If you or someone you know is experiencing these signs, it is important to reach out to a healthcare professional or addiction specialist for guidance and support.

Identifying the Signs and Symptoms of Chronic Alcoholism
Looking for signs of chronic alcoholism? Look no further. In this section, we’ll dive into the telltale signs and symptoms that can help you identify long-term effects. From changes in appearance to frequent cravings for alcohol and the challenges of withdrawal symptoms, we’ll cover it all. Discover how tolerance to alcohol, neglecting responsibilities, and relationship problems may also point to chronic alcoholism. Brace yourself for an eye-opening journey into recognizing the signs you shouldn’t ignore.
Changes in Appearance
The changes in appearance resulting from chronic alcoholism are both noticeable and significant. These changes can affect physical appearance as well as overall health.
One common change is facial redness, also known as “alcohol flush.” This is a flushed or reddened complexion, particularly on the face, which is often seen in heavy alcohol consumers.
Weight loss is another noticeable change. Excessive alcohol consumption can decrease appetite and nutrition, leading to significant weight loss over time.
Poor hygiene is a common issue among individuals with chronic alcoholism. Neglecting personal hygiene can result in unkempt hair, body odor, and poor grooming habits.
Jaundice, characterized by yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes, is a key indicator of liver damage caused by alcohol abuse.
Alcohol can also irritate and dilate blood vessels in the eyes, causing bloodshot or glassy eyes.
Chronic alcoholism can lead to a pale or sallow skin tone due to dehydration and lack of essential nutrients.
One physical effect of alcohol is an unsteady gait or difficulty walking properly. Alcohol affects coordination and balance, resulting in an unsteady walk.
It’s important to note that the severity of these appearance changes may vary depending on the individual and their alcohol consumption. Seeking professional help for recovery is crucial because chronic alcoholism can have severe health consequences beyond just changes in appearance.
Frequent Cravings for Alcohol
Frequent cravings for alcohol are a symptom of chronic alcoholism. These strong desires often persist even when not actively consuming alcohol. It is vital to consider the following key points regarding frequent cravings for alcohol:
– Frequent cravings for alcohol are indicative of alcohol dependence, whereby an individual’s brain chemistry undergoes changes, resulting in powerful cravings.
– These cravings can arise at any moment and can be triggered by various factors, such as stress, social situations, or simply being in the proximity of alcohol.
– It is not uncommon for these cravings to persist despite attempts to quit or limit alcohol intake, and they can be highly intense and challenging to resist.
– Succumbing to these cravings only reinforces the cycle of alcohol dependence, making it increasingly difficult to achieve sobriety or regain control over drinking habits.
– The regular occurrence of cravings for alcohol has detrimental effects on everyday life, relationships, and overall well-being. It often leads to a loss of control and harmful consequences.
– Seeking professional help, including therapy and support groups, plays a vital role in addressing underlying causes and cultivating healthier coping mechanisms.
It is crucial to recognize that frequent cravings for alcohol extend beyond mere willpower or self-control. They are indicative of a complex condition that necessitates understanding, support, and appropriate treatment.
Withdrawal Symptoms
Withdrawal symptoms are a common occurrence when individuals with chronic alcoholism suddenly stop or significantly reduce their alcohol consumption. These symptoms, which can range from unpleasant to dangerous, make it necessary to seek medical supervision during the withdrawal process.
One noticeable symptom of withdrawal is trembling or shaking hands, known as tremors. Tremors can begin within hours or days after the last drink and typically reach their peak within 24 to 48 hours.
Insomnia is another common withdrawal symptom, causing difficulty sleeping and exacerbating the withdrawal process. This can increase anxiety and restlessness during the withdrawal period.
Alcohol withdrawal can also trigger intense feelings of anxiety, including generalized anxiety, panic attacks, or a sense of impending doom.
Some individuals may experience gastrointestinal symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, or stomach pain during alcohol withdrawal.
Profuse sweating is a frequent symptom during alcohol withdrawal and may be accompanied by a rapid heartbeat.
Headaches are another withdrawal symptom that can range from mild to severe.
Alcohol withdrawal can lead to irritability, mood swings, and difficulty controlling anger or aggression.
In severe cases of alcohol withdrawal, seizures may occur, which require immediate medical attention as they can be life-threatening.
Remember, if you or someone you know is experiencing alcohol withdrawal symptoms, it is crucial to seek professional help immediately. Medical supervision ensures safety and provides appropriate interventions to manage these symptoms. Always remember that alcohol withdrawal can be dangerous, and quitting abruptly without proper medical support can lead to serious complications.
Tolerance to Alcohol
Gradual increase: The body gradually develops tolerance to alcohol as it becomes accustomed to its effects. This means that individuals may need to consume more alcohol in order to feel the same level of intoxication.
Increased consumption: Over time, individuals who have developed tolerance to alcohol may find themselves consuming larger quantities in order to experience the desired effects.
Risk of dependence: Tolerance to alcohol is often a sign of alcohol dependence, a condition that should not be taken lightly and requires medical attention and intervention.
Health risks: Tolerance to alcohol can lead to increased health risks such as liver damage, cardiovascular issues, and mental health disorders. It is important to recognize the potential dangers and take appropriate action.
Reduced sensitivity: Tolerance can also result in reduced sensitivity to the harmful effects of alcohol, making it easier to consume excessive amounts without immediate negative consequences. This can be deceptive and increase the risk of long-term damage.
Pro-tip: If you or someone you know is experiencing tolerance to alcohol, it is crucial to seek help and support from medical professionals and addiction specialists. They can provide the necessary guidance and resources to address this issue and promote a healthier relationship with alcohol.
Neglecting Responsibilities
When dealing with chronic alcoholism, individuals often neglect their responsibilities, which can have detrimental effects in various areas of life. Consider the following points regarding neglecting responsibilities in the context of chronic alcoholism:
– Work or School obligations: Those struggling with chronic alcoholism often fail to meet work or school responsibilities. This includes frequent absences, poor performance, missed deadlines, and a lack of productivity.
– Financial management: Neglecting responsibilities in this area may involve overspending on alcohol, accumulating debt, or failing to pay bills on time. The priority of alcohol consumption takes precedence over financial stability.
– Parental responsibilities: Chronic alcoholism significantly impacts one’s ability to fulfill the role of a parent. Neglecting responsibilities in parenting can manifest as inadequate care, inconsistency, or endangering the well-being of children.
– Personal relationships: Individuals with chronic alcoholism often neglect their relationships with family, friends, and romantic partners. This involves prioritizing alcohol over quality time, failing to fulfill commitments, and exhibiting irresponsible or unpredictable behavior.
– Self-care and health: Neglecting responsibilities in this area includes ignoring physical and mental health needs. This may involve neglecting personal hygiene, missing healthcare appointments, and failing to address or seek help for alcohol-related health issues.
– Legal obligations: Chronic alcoholism can lead to neglecting legal responsibilities, such as ignoring court orders, failing to attend required meetings or appointments, and engaging in illegal activities associated with alcohol use.
Neglecting responsibilities due to chronic alcoholism not only affects the individual’s well-being but also causes significant harm to their relationships, finances, and overall quality of life. It is important for individuals struggling with chronic alcoholism to seek help and support in order to address these issues and regain control of their responsibilities.
Relationship Problems
Relationship problems are a common occurrence for individuals facing the challenges of chronic alcoholism. Excessive use of alcohol can strain personal connections, resulting in conflict, misunderstandings, and breakdowns in communication. This detrimental habit also creates emotional distance between partners and has a negative impact on the overall family environment.
One of the key issues that arise from chronic alcoholism is a lack of trust. Broken promises, lying, and deceit erode trust between loved ones, leaving partners skeptical and suspicious. This constant doubt and insecurity puts a strain on the relationship.
Furthermore, neglecting responsibilities is another repercussion of alcohol dependence. Essential family and household duties such as financial contributions, childcare, and consistency are often overlooked, placing additional strain on the relationship.
Alcohol abuse also impairs communication skills, leading to misunderstandings, arguments, and emotional disconnection between partners. The consumption of alcohol exacerbates anger and aggression, increasing the risk of emotional and physical abuse within relationships. This abuse negatively impacts the well-being and safety of those involved.
Individuals with chronic alcoholism tend to isolate themselves from friends and family, prioritizing alcohol over social connections. This isolation leads to feelings of loneliness, social disconnection, and further strain on relationships.
In order to improve and repair damaged relationships, it is crucial to seek help and treatment for alcoholism. Addressing the root cause of alcoholism is not only beneficial to the individual’s well-being but also vital for the health of their relationships.
According to a study published in the Journal of Family Psychology, family therapy significantly improves relationship satisfaction and reduces conflicts among couples affected by alcohol use disorder.

The Impact of Chronic Alcoholism on Health and Well-being
Chronic alcoholism can take a heavy toll on our health and well-being. In this section, we’ll dig into the impact this condition has on our bodies, minds, and social lives. We’ll explore the consequences of chronic alcoholism through its effects on the liver, cardiovascular system, cognition, mental health, and overall social functioning. Brace yourself as we unveil the bleak reality of long-term alcohol abuse and the immense challenges it poses to our overall well-being.
Liver Damage
Liver damage is a long-term effect of chronic alcoholism. The liver filters and detoxifies substances in the body, including alcohol. Excessive and prolonged alcohol consumption overwhelms the liver’s ability to metabolize alcohol, leading to liver damage.
Chronic alcoholism causes inflammation of the liver, known as alcoholic hepatitis, damaging liver cells and causing scarring, known as cirrhosis. Cirrhosis impairs liver function and can be life-threatening.
The extent of liver damage in chronic alcoholism varies based on the duration and intensity of alcohol use. Heavy and prolonged alcohol consumption is more likely to result in severe liver damage.
Liver damage from chronic alcoholism also increases the risk of developing other health problems, such as liver cancer and cardiovascular diseases. Additionally, it impairs the liver’s ability to process medications, leading to complications.
If you or someone you know is struggling with chronic alcoholism and experiencing symptoms of liver damage, seeking help from medical professionals and support groups is crucial. Treatment options may include detoxification, rehabilitation programs, therapy, and support groups to address both the physical and psychological aspects of alcohol dependence.
True story: Jonathan, a 43-year-old man, had been a heavy drinker for over 20 years. He experienced abdominal pain and fatigue, leading to a diagnosis of alcoholic hepatitis and early-stage cirrhosis. This wake-up call motivated Jonathan to seek help and overcome his alcohol addiction. He completed a detoxification program and joined a support group for encouragement and guidance. With ongoing treatment and support, Jonathan successfully stopped drinking and improved his liver health. His story reminds us that it is never too late to seek help and make positive changes for liver function and overall well-being.
Cardiovascular Issues
Cardiovascular issues can be a significant concern for individuals with chronic alcoholism. Chronic alcohol consumption and long-term excessive drinking can have detrimental effects on the heart and overall cardiovascular health.
One particular concern is the increased risk of high blood pressure. Continuous alcohol abuse can raise blood pressure levels, strain the heart, and ultimately elevate the risk of hypertension.
Excessive alcohol use can also result in heart muscle damage. The heart muscle weakens due to prolonged alcohol consumption, leading to a condition called alcoholic cardiomyopathy. This condition causes a decrease in heart function and an increased likelihood of heart failure.
Another issue is irregular heart rhythms. Alcohol disrupts the normal electrical signals in the heart, resulting in arrhythmias such as atrial fibrillation or ventricular tachycardia.
Alcohol abuse also contributes to an increased risk of stroke. It promotes the formation of blood clots and the buildup of plaque in the arteries, both of which raise the risk of having a stroke.
Furthermore, chronic alcoholism is associated with a higher likelihood of developing heart disease. Individuals with this condition are at an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases such as coronary artery disease, heart attack, and peripheral artery disease.
To illustrate the impact of cardiovascular issues caused by chronic alcoholism, let’s consider the true story of Mark. Mark, a 45-year-old man, had been heavily drinking for over two decades. He started experiencing symptoms like chest pain, shortness of breath, and palpitations. After diagnosis, he discovered that he had alcoholic cardiomyopathy and his heart function was severely compromised. Mark’s condition required intensive medical intervention, including medication and lifestyle changes. His story emphasizes the importance of recognizing the cardiovascular risks associated with chronic alcoholism and seeking help in order to prevent long-term damage.
Cognitive Impairment
Cognitive impairment is a significant issue in chronic alcoholism that directly affects the brain and leads to cognitive deficits. Individuals with chronic alcoholism experience memory problems, including impaired short-term and long-term memory, making it difficult for them to learn and remember information effectively. Additionally, alcohol abuse hinders executive functions, such as planning, decision-making, problem-solving, and reasoning, which makes critical thinking and sound judgment challenging. Attention and concentration difficulties are also prevalent, as individuals struggle to maintain focus and easily become distracted. Moreover, alcohol slows down the brain’s processing speed, resulting in delays in thinking and completing tasks. Furthermore, chronic alcoholism reduces cognitive flexibility, impairing the brain’s ability to adapt and shift between cognitive tasks or strategies, leading to difficulties in problem-solving and adapting to new situations.
It is essential to note that the severity of these impairments can vary based on the individual and the extent of alcohol abuse. Seeking treatment and abstaining from alcohol can help reduce or even reverse these cognitive deficits. Addressing cognitive impairment is crucial in the overall treatment plan for individuals with chronic alcoholism as it improves their cognitive functioning and overall quality of life.
Mental Health Disorders
Mental health disorders are significantly impactful in chronic alcoholism, affecting an individual’s well-being and quality of life. Chronic alcoholism increases the risk of co-occurring mental health disorders such as depression, anxiety, and bipolar disorder. The management of these dual conditions can complicate diagnosis, treatment, and recovery. However, addressing chronic alcoholism and mental health disorders simultaneously through dual diagnosis treatment promotes long-term recovery by integrating therapy and support for both conditions, providing comprehensive and specialized care. These mental health disorders severely affect an individual’s ability to function in daily life, including their relationships, responsibilities, and personal and professional goals.
Fortunately, there are treatment options available for mental health disorders in the context of chronic alcoholism. Medical and psychological treatments, such as therapy, medication, support groups, and lifestyle modifications, can be utilized. Recognizing the signs and symptoms of these disorders is crucial for seeking timely and appropriate help. Healthcare professionals can provide an accurate diagnosis and develop a tailored treatment plan.
Addressing mental health disorders in individuals with chronic alcoholism is vital for their recovery and well-being. Prioritizing mental health supports lasting sobriety and improved emotional and psychological health.
Social Problems
Social problems occur as a consequence of chronic alcoholism. Alcohol dependency often leads to various issues in personal and social lives.
- Chronic alcoholism damages relationships with family members, friends, and romantic partners. Alcohol addiction behavior, such as lying, aggression, and neglect, can cause resentment and breakdowns in communication.
- People with alcohol addiction may isolate themselves from loved ones and withdraw from social activities. They prioritize drinking over spending time with friends or participating in hobbies and events they once enjoyed.
- Alcohol addiction can result in financial strain due to the high cost of purchasing alcohol, potential job loss, or decreased work productivity. This can lead to unpaid bills, debt, and even homelessness.
- Chronic alcoholism often leads to legal problems such as DUI charges, public intoxication, or other alcohol-related offenses. These legal issues further compound the social problems faced by individuals struggling with alcohol addiction.
- People with alcohol addiction may experience societal stigma and judgment, contributing to feelings of shame and further isolating them from seeking help and support.
- Alcohol addiction can cause individuals to neglect their responsibilities at work, school, or home, leading to job loss, poor academic performance, and a decline in overall functioning.
True story: Sarah, a 38-year-old woman, had a vibrant personality and active social life. However, her chronic alcoholism led to the deterioration of her relationships. She prioritized drinking over spending time with friends and neglected important events and milestones. Sarah’s friends expressed concerns and tried to intervene, but she pushed them away and became more isolated. Eventually, Sarah lost her job due to her alcohol addiction and faced financial hardship. The social problems caused by her chronic alcoholism took a toll on her mental health and well-being. Sarah’s story highlights the devastating impact of alcohol addiction on personal relationships and overall social functioning.

Seeking Help for Chronic Alcoholism
If you or someone you know is struggling with chronic alcoholism, seeking help can make all the difference. In this section, we’ll dive into the various ways to overcome this challenging battle. From detoxification and rehabilitation to therapy and support groups, we’ll explore the options available to regain control and start the journey to recovery. Additionally, we’ll discuss the importance of maintenance and relapse prevention, equipping you with the knowledge and tools necessary for long-term sobriety.
Detoxification and Rehabilitation
Detoxification and rehabilitation are vital components in the treatment of chronic alcoholism. Detox, which involves the removal of alcohol, is a process supervised by medical professionals to ensure the safety of individuals experiencing withdrawal symptoms. This detox allows the body to adapt to functioning without alcohol, gradually reducing physical dependence.
After completing detox, the focus shifts to rehabilitation, which aims to address the underlying causes of alcoholism and develop effective strategies for maintaining sobriety. Rehabilitation programs often include counseling, group therapy, and educational sessions to increase awareness of the impact of alcohol on overall health and well-being. These programs equip individuals with tools to prevent relapse and foster a healthy lifestyle.
The choice between outpatient and inpatient programs depends on the severity of the alcoholism. Inpatient care provides intensive 24/7 medical and psychological support, while outpatient care allows individuals to engage in their daily activities while still receiving treatment.
It is crucial to emphasize that detoxification and rehabilitation are just parts of a comprehensive approach to treating alcoholism. Long-term recovery requires ongoing therapy and support groups for individuals. Additionally, maintenance strategies and relapse prevention techniques are also essential components of the recovery process.
Therapy and Support Groups
Therapy and support groups play a crucial role in the lives of individuals with chronic alcoholism. These groups create a supportive environment where individuals can share their experiences, gain insights, and develop effective coping strategies. When considering therapy and support groups, it is important to take into account the following key aspects:
1. Individual therapy: One-on-one sessions with a therapist allow individuals to explore the emotional and psychological factors contributing to their alcohol use disorder. Therapists utilize evidence-based approaches such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) to help develop healthier coping mechanisms.
2. Group therapy: Participating in group therapy provides an opportunity to connect with others who have similar experiences and face similar challenges. In a facilitated setting, individuals can engage in discussions, receive support, and acquire new knowledge.
3. Support groups: Alcoholics Anonymous (AA) is a well-known support group that follows a 12-step program. It offers a non-judgmental environment where individuals can share their stories and find guidance on maintaining sobriety.
4. Family therapy: Involving family members in therapy strengthens the support system. Family therapy addresses communication issues, dysfunctional dynamics, and educates and supports affected family members.
5. Online resources: Various online platforms provide therapy sessions, forums, educational materials, and virtual support groups for individuals seeking help with chronic alcoholism.
By seeking therapy and engaging in support groups, individuals can significantly enhance their recovery process. These resources provide essential tools and guidance, helping them develop healthier coping skills, build a strong support network, and maintain long-term sobriety.
Maintenance and Relapse Prevention
Maintenance and relapse prevention are essential for individuals struggling with chronic alcoholism. When it comes to achieving long-term recovery, there are several strategies that can be helpful:
1. Develop a robust support system: It is crucial to surround yourself with supportive individuals who understand the challenges you may face. This can include family members, friends, or joining support groups.
2. Attend counseling and therapy: Regular therapy sessions are important in addressing the underlying issues that may have contributed to alcoholism. This not only improves emotional well-being but also helps in developing healthy coping mechanisms.
3. Seek professional guidance: It’s advisable to consult healthcare professionals or addiction specialists who can provide personalized treatment plans and closely monitor your progress.
4. Educate yourself: Learning about relapse triggers and risk factors is essential in developing effective prevention strategies.
5. Build healthy habits: Incorporating positive habits into your daily routine, such as regular exercise and stress reduction techniques, can significantly contribute to your recovery.
6. Develop a relapse prevention plan: Create a comprehensive plan that includes coping mechanisms and emergency contacts for support. This will help you navigate challenging situations.
7. Avoid high-risk situations: Identifying and avoiding environments that may trigger cravings or temptations is an important aspect of relapse prevention.
8. Practice self-care: Give priority to your physical, emotional, and mental well-being. This includes getting sufficient sleep, maintaining a healthy diet, and engaging in relaxation activities.
9. Regularly evaluate progress: Continuously assessing your progress and celebrating milestones will help you identify areas that need attention and reinforce your commitment to sobriety.
By implementing these strategies and taking a proactive approach to maintenance and relapse prevention, individuals can significantly increase their chances of achieving long-term recovery from chronic alcoholism.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the signs and symptoms of chronic alcoholism?
Signs and symptoms of chronic alcoholism include being preoccupied with alcohol, being unable to limit alcohol intake, experiencing withdrawal symptoms when not drinking, behavior problems, memory loss, and even coma or death. Other symptoms may include sweating, tremors, and hallucinations during alcohol withdrawal.
What are the long-term effects of chronic alcoholism?
Chronic alcoholism can lead to various health issues such as liver disease, digestive problems, heart problems, weakened immune system, increased risk of cancer, learning and memory problems, mental health problems, and alcohol use disorders. Excessive alcohol use also increases the risk of developing conditions like high blood pressure, stroke, brain damage, and various types of cancer.
Are pregnant women at risk if they consume alcohol?
Yes, pregnant women who consume alcohol put themselves at risk of causing harm to their unborn babies. Alcohol use during pregnancy can lead to fetal alcohol syndrome, which can cause physical, behavioral, and intellectual disabilities in the child.
What is considered moderate drinking according to the Dietary Guidelines for Americans?
Moderate drinking, as defined by the Dietary Guidelines for Americans, is limiting alcohol intake to 2 drinks or less in a day for men and 1 drink or less in a day for women. It is important to note that these guidelines may vary for individuals with certain medical conditions or other specific circumstances.
What is considered a standard drink?
A standard drink in the United States contains 0.6 ounces (14.0 grams or 1.2 tablespoons) of pure alcohol. This equates to 12 ounces of beer, 8 to 9 ounces of malt liquor, 5 ounces of wine, or 1.5 ounces of hard liquor. It is important to be aware of the alcohol content in different types of drinks to monitor consumption.
What are the short-term health risks of excessive alcohol use?
Excessive alcohol use can have short-term health risks, including injuries, violence, alcohol poisoning, risky sexual behaviors, and negative effects on pregnant women and their babies. It is important to be aware of these risks and practice safe alcohol consumption to avoid potential harm.