PTSD (Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder) is a mental health condition that can have a profound impact on a person’s life, causing them to feel trapped in their own emotions and experiences. Understanding the intricacies of PTSD and the feeling of being trapped is crucial in the journey of recovery.
PTSD is a psychiatric disorder that occurs in individuals who have experienced or witnessed a traumatic event. It can manifest in various symptoms such as flashbacks, nightmares, hypervigilance, and emotional numbness. Feeling trapped, in the context of PTSD, refers to the persistent sense of being overwhelmed and unable to move forward from the traumatic experience.
The impact of feeling trapped in PTSD recovery is significant. It can hinder progress and exacerbate symptoms, leading to avoidance behaviors and the constant reliving of traumatic experiences. The feeling of being trapped often fuels a sense of hopelessness, making it challenging for individuals to seek help and find a way out of their emotional confinement.
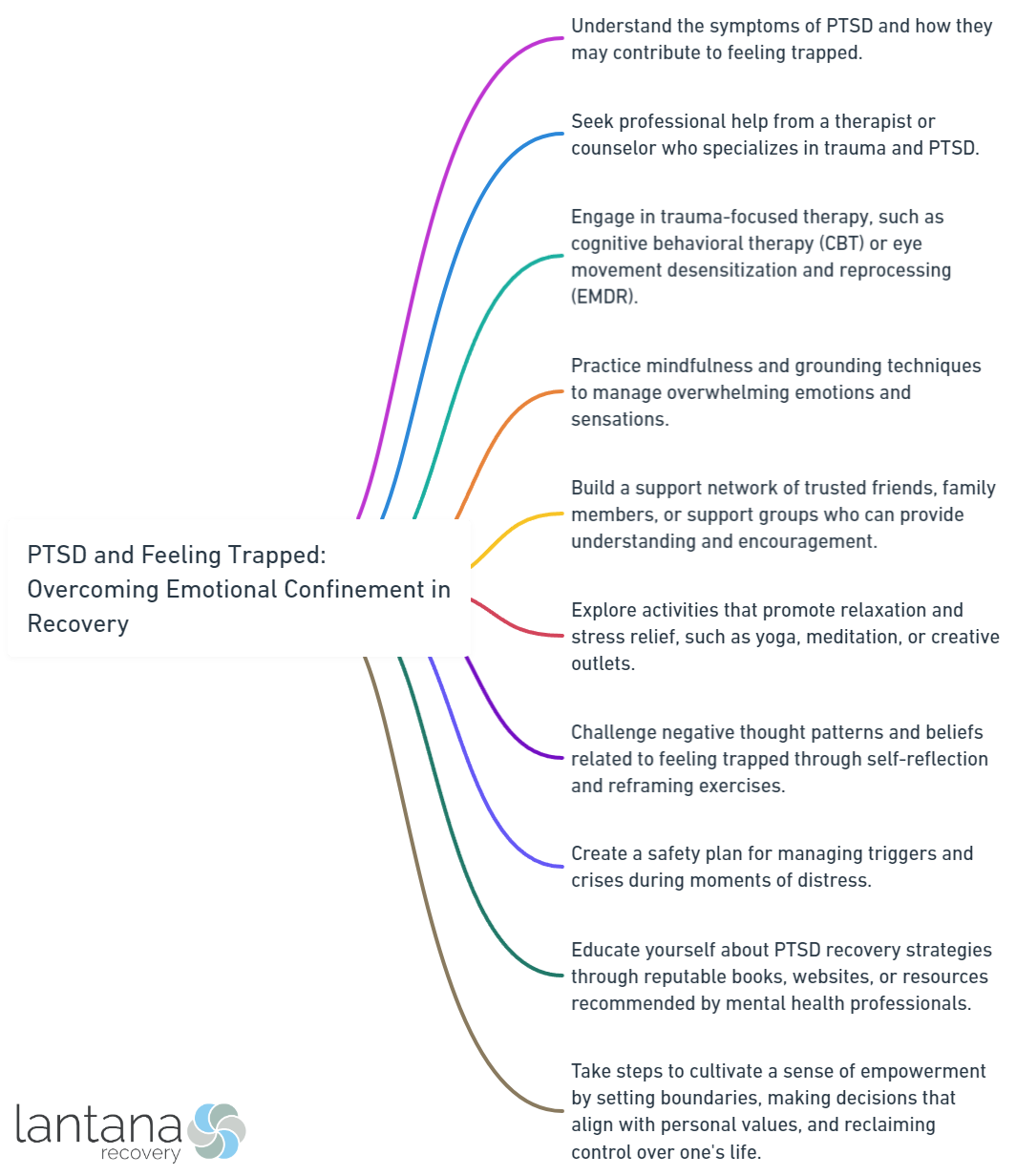
Fortunately, there are strategies and techniques that can help individuals overcome the emotional confinement of PTSD. Seeking professional help, such as therapy and counseling, is essential in addressing the underlying issues and developing effective coping mechanisms. Building a support network of understanding and empathetic individuals provides a safe space for healing. Engaging in self-care practices, such as mindfulness and relaxation techniques, allows for the nurturing of emotional well-being.
The journey towards overcoming emotional confinement in PTSD recovery involves rebuilding a sense of freedom and empowerment. This can be achieved by reframing negative thoughts and beliefs, setting achievable goals, taking small steps forward, and exploring new activities and hobbies. Focusing on personal growth and resilience is also crucial in regaining control over one’s life.
By understanding the impact of feeling trapped in PTSD recovery and implementing strategies to overcome emotional confinement, individuals can gradually heal and reclaim their lives, moving towards a brighter and more empowered future.
Understanding PTSD and Feeling Trapped
Understanding PTSD and feeling trapped are critical elements to consider when addressing and overcoming emotional confinement in recovery. PTSD, also known as Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder, is a mental health condition that may develop following the experience or observation of a traumatic event. This condition is characterized by symptoms such as flashbacks, nightmares, anxiety, and depression, all of which significantly impact daily life.
It is quite common for individuals with PTSD to feel trapped. Their traumatic experiences often contribute to a sensation of being stuck, making it difficult to progress and break free from emotional confinement. In order to truly grasp the nature of PTSD and feeling trapped, it is imperative to acknowledge the importance of providing support and empathy.
Creating a secure and non-judgmental environment is key to enabling individuals to share their experiences and emotions. There are numerous treatment options available to those who suffer from PTSD and feel trapped. Therapeutic methods like cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) can be instrumental in processing trauma and developing effective coping mechanisms. Support groups and peer support are also invaluable, as they provide validation and a sense of community. Recovery from PTSD and the process of overcoming feeling trapped is a journey that requires time and effort. Patience, compassion, and understanding are fundamental when supporting individuals during their recovery process.
What is PTSD?
PTSD, or Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder, is a mental health condition that can develop in individuals who have experienced or witnessed a traumatic event. It is a serious condition that can significantly impact a person’s daily life.
What is PTSD? Feeling trapped in the context of PTSD refers to being unable to escape or move on from the traumatic event. This feeling can manifest in difficulty processing emotions, recurring nightmares or flashbacks, and avoiding situations or triggers related to the trauma.
It is important to understand that PTSD is a natural response to an overwhelming and traumatic experience, not a sign of weakness or character flaw. It can affect anyone, regardless of age, gender, or background. To address PTSD, seeking professional help is crucial. Therapies like Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR), and medication can effectively manage symptoms and aid in recovery. Developing coping mechanisms, building a support network, and engaging in self-care activities are also beneficial for overcoming emotional confinement.
Overcoming PTSD is a gradual process that requires time, patience, and support. With the right treatment and support system, individuals can regain a sense of freedom and empowerment, leading to a better quality of life. It’s important to remember that each person’s journey is unique, and what works for one may not work for another.
What Does Feeling Trapped Mean in the Context of PTSD?
Feeling trapped in the context of PTSD refers to being stuck in the emotional and psychological effects of the disorder. It is a common symptom of PTSD and can greatly affect a person’s well-being and recovery. Those with PTSD constantly relive their trauma through intrusive thoughts, nightmares, or flashbacks, and may avoid triggers or situations that remind them of their trauma, which leads to isolation and difficulties in daily life.
To overcome this feeling of entrapment, seeking professional help like therapy or counseling is crucial. These therapies provide tools and strategies to cope with and overcome the feelings of being trapped. Developing coping mechanisms and healthy habits, as well as building a support network, can contribute to breaking free from this feeling. Engaging in self-care activities like mindfulness and relaxation techniques can also help in managing symptoms and regaining control.
Fact: Approximately 6% of the U.S. population will experience PTSD at some point in their lives, according to the National Center for PTSD.

The Impact of Feeling Trapped in PTSD Recovery
The Impact of Feeling Trapped in PTSD Recovery can have detrimental effects on an individual’s journey towards healing and restoring a sense of self. Those who experience PTSD may encounter difficulties in actively participating in therapy, establishing meaningful connections, and reintegrating into society.
The sensation of being trapped can lead individuals to engage in avoidance behaviors, purposely evading situations or triggers that remind them of their traumatic experiences. By avoiding these stimuli, they inadvertently impede their ability to confront and process their emotions, consequently hindering their path to recovery.
Additionally, feeling trapped can intensify feelings of seclusion and solitude. People with PTSD may encounter challenges in establishing connections with others and cultivating relationships, which results in a sense of being misunderstood or isolated in their struggles.
Moreover, feeling trapped can impede an individual’s capacity to trust and seek assistance. They may hold the belief that attaining recovery is unattainable or that they are destined to remain ensnared in their traumatic past indefinitely.
A vital component in overcoming the sensation of feeling trapped is the existence of a strong support system. Understanding and empathetic individuals, including friends, family, or support groups, can provide the essential encouragement and validation needed to pursue recovery.
For instance, Sam, a survivor of PTSD, battled with a feeling of entrapment within her own mind for several years following a traumatic event. It wasn’t until she sought professional assistance and became a part of a support group that she discovered she was not alone. Through therapy, she acquired coping mechanisms and gradually regained control over her life. Sam‘s story serves as a testament that with the right support and treatment, feeling trapped in PTSD recovery can be overcome, enabling individuals to heal and reclaim their lives.
How Does Feeling Trapped Affect PTSD Recovery?
How does feeling trapped affect PTSD recovery? Feeling trapped can have a significant impact on the recovery process of individuals with PTSD. This feeling of being trapped contributes to feelings of helplessness and hopelessness, making it challenging for them to envision a way out or believe in the possibility of recovery. Consequently, this can hinder their motivation to seek help and engage in necessary treatments.
Moreover, feeling trapped often leads to avoidance behaviors. Individuals may actively avoid triggers that are associated with their traumatic experiences in an attempt to escape the distressing emotions that arise. Unfortunately, this avoidance strategy can prevent them from fully processing and healing from the trauma.
Furthermore, feeling trapped causes individuals to frequently relive their traumatic experiences through various means such as flashbacks, nightmares, or intrusive thoughts. These re-experiences can be overwhelming and perpetuate the sensation of being trapped within their own minds.
To overcome the debilitating impact of feeling trapped in the context of PTSD recovery, it is essential for individuals to seek professional help through therapy and counseling. These interventions provide the necessary support, guidance, and effective coping mechanisms required for their healing journey.
In addition to seeking professional help, developing coping mechanisms and healthy habits can be instrumental in managing the feelings of being trapped. Engaging in relaxation techniques, practicing mindfulness exercises, and prioritizing self-care activities promote emotional well-being, which in turn helps individuals regain a sense of control.
Building a strong support network is also crucial. Surrounding oneself with understanding friends, family, or support groups provides a safe space where experiences can be shared and support can be received. This sense of understanding and support is paramount in alleviating the perception of feeling trapped, allowing individuals to embark on their recovery journey with renewed hope and determination.
The Link Between Feeling Trapped and Avoidance Behaviors
The link between feeling trapped and avoidance behaviors in PTSD recovery is significant. These avoidance behaviors are a natural response to feeling trapped in PTSD, according to the book Trauma-Informed Care in Behavioral Health Services by SAMHSA. They serve as a way for individuals to cope with trauma and overwhelming emotions. Individuals engage in these behaviors to avoid situations, people, or places that remind them of their traumatic experiences. The goal is to minimize distress and anxiety. However, it’s important to acknowledge that this avoidance can hinder the recovery process. By suppressing emotions and prolonging the healing journey, individuals may find it difficult to overcome PTSD.
There are various ways in which avoidance behaviors can manifest. For instance, individuals may isolate themselves from social activities or events. They may also avoid discussing their trauma or seeking professional help. While engaging in these behaviors might temporarily alleviate distress, it is important to recognize that individuals miss out on opportunities for growth and healing.
Overcoming emotional confinement requires individuals to confront and process their traumatic experiences. Seeking professional help, developing coping mechanisms, and building a support network are essential steps in gradually confronting triggers and establishing healthier ways of managing PTSD symptoms. It is important to acknowledge the impact of avoidance and actively take steps towards facing trauma, seeking support, and engaging in strategies for emotional well-being. These actions are essential for recovery in PTSD.
The Connection Between Feeling Trapped and Reliving Traumatic Experiences
Feeling trapped in PTSD is closely connected to reliving traumatic experiences. The Connection Between Feeling Trapped and Reliving Traumatic Experiences can be distressing and overwhelming for individuals with PTSD. The connection between feeling trapped and reliving traumatic experiences stems from the way the brain processes and stores memories. In PTSD, traumatic memories can become fragmented and disorganized, making it difficult to distinguish between past and present. Triggers or reminders of the trauma can elicit intense emotional and physiological reactions, causing individuals to relive the event.
Reliving traumatic experiences can take various forms: intrusive thoughts, flashbacks, nightmares, or intense emotional and physical distress. Situations, people, places, or sensory stimuli associated with the trauma can trigger these experiences.
Understanding The Connection Between Feeling Trapped and Reliving Traumatic Experiences is crucial for recovery. Therapeutic interventions, such as trauma-focused therapy or eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR), help reprocess and integrate traumatic memories into one’s life narrative, reducing the intensity and frequency of reliving experiences.
By addressing The Connection Between Feeling Trapped and Reliving Traumatic Experiences, individuals with PTSD can regain control and freedom in their lives. Therapy, coping mechanisms, and support networks all contribute to overcoming the emotional confinement associated with feeling trapped and moving towards healing and recovery.

Overcoming Emotional Confinement in PTSD Recovery
Feeling trapped by the weight of PTSD is a daunting challenge, but there is hope for overcoming emotional confinement in recovery. This section will guide you through the path of liberation, exploring various strategies that can empower you. From seeking professional help in therapy and counseling, to developing coping mechanisms and healthy habits, building a support network, and embracing self-care techniques like mindfulness and relaxation. Each sub-section holds a key to breaking free from the confines of PTSD, paving the way toward healing and renewal.
Seeking Professional Help: Therapy and Counseling
Seeking professional help, such as therapy and counseling, is crucial for individuals with PTSD. Through therapy, individuals can address their trauma and work towards healing. Trained therapists or counselors guide individuals in exploring and processing their traumatic experiences, helping them understand their reactions and emotions. Evidence-based approaches like cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) or eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR) are often used to manage symptoms and develop coping strategies.
Counseling provides emotional support and guidance on the PTSD journey, helping individuals develop healthy coping mechanisms, improve self-esteem, and build resilience.
It’s important to remember that seeking treatments for PTSD is not a sign of weakness, but a brave step towards recovery. Therapy and counseling can greatly reduce PTSD symptoms, enhance well-being, and improve quality of life.
When searching for a therapist or counselor, it is recommended to find someone specializing in trauma and PTSD. Establishing a strong therapeutic alliance with someone who creates a safe and empathetic space is crucial. With professional help, individuals can gain the necessary tools and support to overcome the emotional toll of PTSD and start their healing journey.
Developing Coping Mechanisms and Healthy Habits
When recovering from PTSD, it is crucial for individuals to develop coping mechanisms and healthy habits. These strategies play a vital role in managing symptoms, enhancing well-being, and promoting resilience. Here are some effective ways to naturally incorporate developing coping mechanisms and healthy habits:
- Engage in regular physical exercise: Incorporate physical activities like walking, jogging, yoga, or swimming into the routine. These activities help reduce stress, anxiety, and improve mental health, especially for individuals with PTSD.
- Practice relaxation techniques: Learn various relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing exercises, progressive muscle relaxation, or guided imagery. By incorporating these techniques, individuals can effectively reduce tension and promote a calm state.
- Maintain a balanced diet: Ensure that the diet includes nutritious foods like fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains. By avoiding excessive caffeine and alcohol, individuals with PTSD can prevent the worsening of anxiety and sleep disturbances while supporting overall health and well-being.
- Establish a routine: Create a structured daily routine that provides stability and control. Consistently following a schedule for meals, sleep, and activities can significantly reduce stress and increase feelings of security.
- Seek social support: Build a support network consisting of trusted friends, family members, or support groups. This network will provide emotional support and understanding, which is crucial for individuals dealing with PTSD.
- Practice self-care: Engage in activities that bring joy and relaxation, such as hobbies, spending time in nature, or practicing mindfulness and meditation. These activities contribute to overall well-being and promote a sense of calm and happiness.
- Develop healthy coping strategies: Identify and adopt healthy coping mechanisms such as journaling, practicing gratitude, listening to music, or engaging in hobbies. These strategies can effectively manage stress and help individuals navigate difficult emotions.
By incorporating these coping mechanisms and healthy habits into daily life, individuals can enhance their resilience and improve their overall well-being as they recover from PTSD.
Building a Support Network
Building a support network is crucial in the recovery process of PTSD. A strong support system provides comfort, understanding, and encouragement. Here are steps to build a support network:
1. Identify trustworthy individuals: Reach out to trusted and comfortable people in your life, such as family, close friends, or support group members with similar experiences. Building a support network is essential in the journey of PTSD recovery.
2. Communicate your needs: Openly express your concerns and needs to your support network. Let them know how they can help you, whether it’s listening or assisting with tasks. Effective communication is key to building a strong support network.
3. Attend support groups: Join PTSD-specific support groups to connect with others who understand. Share experiences, gain insights, and offer support to fellow members in a safe space. Joining these groups is an important step in building a support network.
4. Seek professional support: In addition to your personal network, consider professional help from therapists and counselors who can offer guidance and support throughout your recovery. Professional support plays a significant role in building a comprehensive support network.
5. Participate in community activities: Get involved in volunteering, joining clubs, or organizations to expand your social circle, meet new people, and engage in enjoyable activities. Participating in community activities is a great way to enhance your support network.
Remember, building a support network takes time and effort. Be patient with yourself and others as you navigate recovery. With the support of your network, you can overcome PTSD challenges and find a sense of community and understanding. Building a support network is an essential part of the healing process.
Engaging in Self-Care: Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques
Engaging in self-care is crucial for individuals recovering from PTSD. Mindfulness and relaxation techniques can greatly benefit symptom management and overall well-being.
Practicing mindfulness allows individuals to focus on the present moment, increasing self-awareness and reducing stress. Activities such as meditation or deep breathing can create calm and relaxation. Mindfulness also helps in accepting thoughts and emotions associated with PTSD without judgment.
Relaxation techniques are essential in reducing anxiety and promoting relaxation. Progressive muscle relaxation or guided imagery can release tension and promote a sense of calmness. These techniques aim to decrease the physical and psychological arousal often experienced in PTSD.
“Several studies have highlighted associations between mindfulness and changes in patterns of brain activation in regions impacted in patients with PTSD. Specifically, increased activation of the prefrontal cortex (including the dorsomedial PFC [dmPFC]) during expectation of negative pictures and reduced activation in the amygdala and parahippocampal gyrus following perception of negative stimuli has been observed following brief mindfulness training among healthy controls,” suggests a study. (Mindfulness-based treatments for posttraumatic stress disorder: a review of the treatment literature and neurobiological evidence, Boyd et al., 2018)
This means the parts of the brain called the amygdala and parahippocampal gyrus became less active when they actually saw the negative pictures. These areas are typically involved in processing emotions, so their reduced activity might mean that the individuals were better at handling negative stimuli after the mindfulness training.
Engaging in self-care through mindfulness and relaxation techniques should be tailored to individual preferences and needs. Find techniques that resonate with you and can be incorporated into daily routines. Regular practice can enhance overall well-being and cope more effectively with the challenges of PTSD.
Incorporating self-care activities into daily life can boost emotional and psychological well-being. Building upon these techniques enhances the ability to manage PTSD symptoms and cultivates self-awareness and resilience. Seek professional guidance to ensure techniques are appropriate for specific needs and circumstances.

Rebuilding a Sense of Freedom and Empowerment
Rebuilding a sense of freedom and empowerment after trauma is a crucial step in the recovery process. In this section, we’ll uncover powerful strategies to help overcome emotional confinement. We’ll explore the art of reframing negative thoughts and beliefs, setting meaningful goals, diving into new activities, and fueling personal growth. By taking these small but impactful steps, individuals can reclaim their sense of agency and resilience, ultimately finding liberation on their path to healing.
Reframing Negative Thoughts and Beliefs
Reframing negative thoughts and beliefs is crucial for individuals undergoing PTSD recovery, as it allows them to overcome emotional confinement. The process entails actively challenging and replacing negative thoughts with positive and realistic ones.
By engaging in the practice of reframing negative thoughts and beliefs, individuals with PTSD can alter their perspective and foster resilience and empowerment. One highly effective approach is cognitive restructuring, which involves identifying negative thoughts and critically examining the evidence that supports them. Through this process of acknowledgment and challenge, individuals can substitute these thoughts with positive and adaptive beliefs.
In addition, practicing self-compassion proves to be immensely helpful. Many people with PTSD tend to hold themselves responsible or experience shame. By treating themselves kindly and with understanding, individuals can reduce the impact of negative thoughts and beliefs.
Moreover, incorporating positive self-talk plays a vital role. By replacing negative self-talk with affirmations and encouraging statements, individuals can boost their self-esteem and develop a more optimistic outlook on life.
Although reframing negative thoughts and beliefs requires effort and persistence, it plays a significant role in the recovery process for individuals with PTSD. Through actively challenging and replacing negative thoughts, individuals can liberate themselves from emotional confinement and embrace a positive and fulfilling life.
Setting Goals and Taking Small Steps Forward
Setting goals and taking small steps forward is crucial for overcoming emotional confinement in PTSD recovery. It allows individuals to regain control and make progress towards healing. Here are some steps to guide this process:
1. Reflect on personal values and aspirations. Identify what is important to you and what you want to achieve in life.
2. Break down larger goals into smaller, manageable tasks. This reduces overwhelm and increases the chances of success.
3. Create a timeline or schedule. Set specific deadlines or milestones for each step to stay focused and motivated.
4. Track progress regularly. Keep a record of achievements, no matter how small, to observe growth over time.
5. Seek support and accountability. Share goals with a trusted friend, therapist, or support group who can provide encouragement and help you stay on track.
6. Celebrate achievements along the way. Acknowledge and reward yourself for each milestone reached to boost motivation and confidence.
7. Adjust goals as needed. Be flexible and willing to adapt if circumstances or priorities change. Remember that goals can evolve over time.
Setting goals and taking small steps forward is a powerful tool in the recovery process. It helps individuals regain purpose, build resilience, and cultivate a positive mindset towards their healing journey.
Read our article on Ketamine treatment for PTSD to learn more about the benefits as well as side effects of this drug for treating PTSD.
Exploring New Activities and Hobbies
Exploring new activities and hobbies is vital for individuals undergoing PTSD recovery as it helps them overcome emotional confinement. These activities not only provide a sense of purpose and enjoyment but also promote empowerment. Let’s explore the ways in which these activities benefit individuals on their healing journey:
1. Expanding horizons: When individuals try out different activities and hobbies, they are able to step outside their comfort zones and uncover hidden talents or passions.
2. Positive distractions: Engaging in enjoyable activities serves as a form of positive distraction from negative thoughts and trauma triggers. It offers a healthy outlet for emotions and redirects focus towards fulfilling experiences.
3. Cultivating achievement: By learning new skills through various activities and hobbies, individuals foster a sense of accomplishment and boost self-confidence. Achieving both big and small goals contributes to progress and empowerment.
4. Connection and community: Participation in group activities or joining hobby-based communities cultivates a sense of belonging and support. It allows individuals to connect with like-minded people, share experiences, and build relationships.
5. Stress reduction: Engaging in joyful and relaxing activities such as painting, gardening, or hiking can significantly reduce stress levels. These hobbies promote healthy coping mechanisms and contribute to overall well-being.
Actively exploring new activities and hobbies enhances the PTSD recovery journey for individuals. It aids in finding sources of happiness and fulfillment, ultimately helping them break free from emotional confinement.
Focusing on Personal Growth and Resilience
Focusing on personal growth and resilience is crucial for the recovery from PTSD. Engaging in activities that support self-improvement and emotional strength can help overcome the feeling of being trapped.
To promote personal growth and resilience, it is important to embrace positivity. Cultivating a positive mindset involves reframing negative thoughts and beliefs that hinder progress. By replacing negative self-talk with uplifting statements, individuals can boost their confidence and motivation.
Developing emotional intelligence is another key aspect of personal growth and resilience. Building emotional intelligence enhances self-awareness, empathy, and effective emotion management. By recognizing and understanding emotions, individuals can foster personal growth and resilience.
Building mental and physical strength is also necessary for personal growth and resilience. Regular exercise and a healthy lifestyle have a positive impact on mental and physical well-being. Physical activity releases endorphins, which reduce stress and improve mood. Taking care of the body and mind is crucial for personal growth and resilience.
Setting realistic goals is another important factor in personal growth and resilience. Achievable goals encourage progress and resilience. Breaking down large goals into manageable steps provides a sense of accomplishment and motivates individuals to continue moving forward.
Seeking support is also vital for personal growth and resilience. Building a support network of trusted individuals who understand and validate experiences offers invaluable strength and resilience. Connecting with support groups, therapy, or counseling provides guidance, encouragement, and a safe space to share.
By focusing on personal growth and resilience, individuals can gradually overcome emotional confinement and regain control and freedom in their lives. Embracing positive attitudes, developing emotional intelligence, maintaining physical and mental well-being, setting goals, and seeking support are key elements in the journey towards PTSD recovery.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How does post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) affect relationships and family life?
PTSD can have a significant impact on relationships and family life, as individuals with PTSD may have difficulty controlling their behavior due to their nervous system being in a constant state of alertness.
2. How can loved ones support someone with PTSD?
Face-to-face support from loved ones is crucial for recovery from PTSD. It is important to respect boundaries but also offer comfort and support. Engaging in normal activities unrelated to PTSD can help the person feel more engaged and accepted.
3. What can I do to support someone with PTSD?
Managing your own stress and being patient are important in supporting someone with PTSD. Educating yourself about PTSD can help you understand what your loved one is going through. Listening attentively without judgment is more helpful than giving advice.
4. How should I respond to triggers for someone with PTSD?
Triggers can set off PTSD symptoms, so it is helpful to have a plan for how to respond. Grounding techniques can help during a flashback. It is important to be aware of the person’s triggers and provide a supportive and calming environment.
5. Is professional therapy necessary for individuals with PTSD?
Professional therapy even at an outpatient treatment center may be necessary for some individuals with PTSD. It is important to approach the topic sensitively and encourage the person to seek help from healthcare providers. Therapies like virtual reality exposure therapy can be effective in treating trauma-related memories and reducing symptoms.
6. How can I take care of myself while supporting someone with PTSD?
Taking care of yourself is crucial in order to support your loved one without becoming overwhelmed. Seek out friends and healthy relationships, pursue hobbies and self-care activities, and consider attending therapy or support groups yourself. Remember, self-care is not selfish but necessary for both you and your loved one’s well-being.