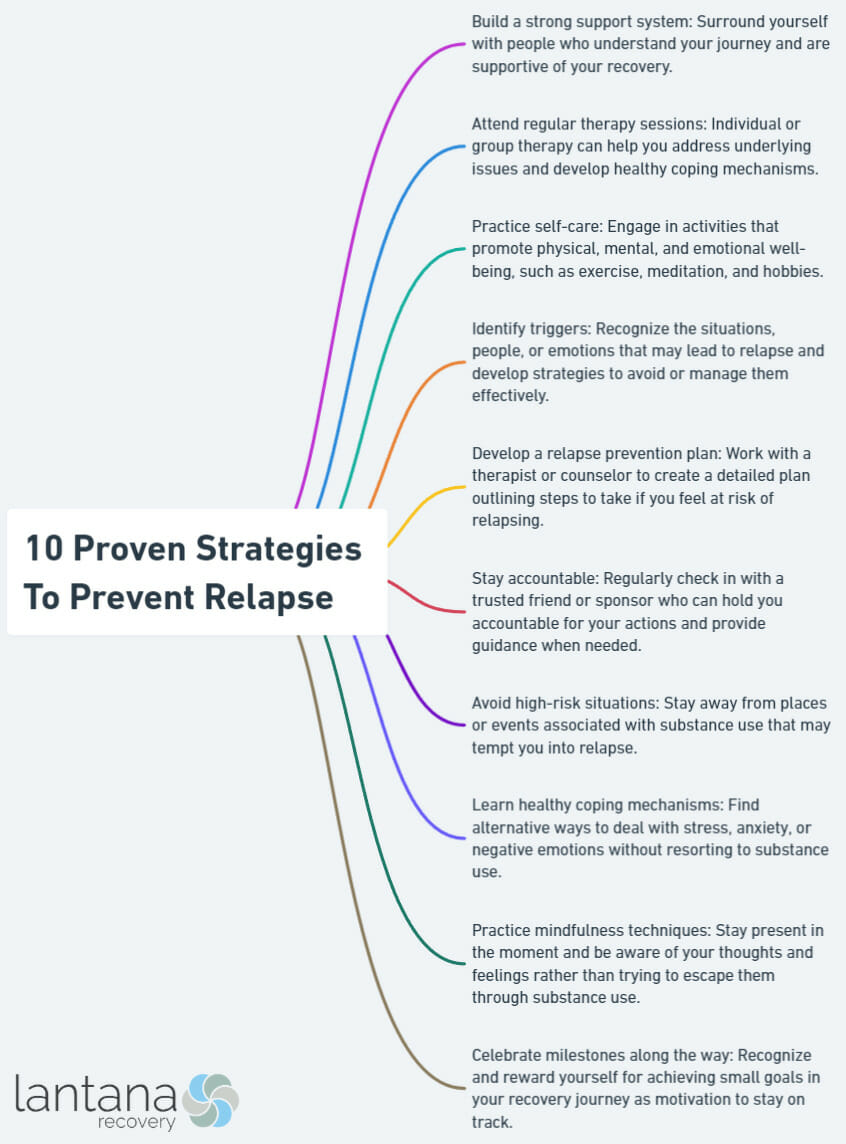
The journey of addiction recovery is filled with ups and downs, challenges, and triumphs. One of the most critical aspects of this journey is relapse prevention, as it helps individuals maintain their hard-earned sobriety and continue on the path to a healthier, happier life. In this blog post, we will explore 10 proven strategies to prevent relapse, delve into each strategy’s importance, and provide practical tips on how to implement them in your life. By understanding and applying these strategies, you can increase your chances of long-lasting recovery and minimize the risk of relapse.
From understanding the stages of relapse to staying engaged in recovery, each section of this blog post will focus on a specific aspect of relapse prevention. You will learn how to recognize and handle triggers, build a strong support system, and prioritize self-care. Let’s embark on this journey together and discover how you can stay committed to long-term recovery.
Key Takeaways
- Understand relapse and its stages to prevent it.
- Develop a personalized plan with the help of healthcare professionals.
- Build resilience through self-care, mindfulness, and commitment for long term recovery.
Understanding Relapse and Its Stages

Relapse frequently occurs in addiction recovery, thus being aware of its nature aids in implementing effective relapse prevention strategies. In fact, relapse is often seen as a learning opportunity that can provide valuable insights into one’s recovery process. Recognizing that relapse is not a singular event, but a three-stage process encompassing emotional, mental, and physical relapse is vital. The stages of relapse include:
- Emotional relapse: This stage involves feelings of anxiety, anger, or depression, often due to unresolved issues or poor self-care.
- Mental relapse: In this stage, there is an internal struggle between the desire to use substances and the commitment to stay sober.
- Physical relapse: This stage occurs when an individual returns to substance use, often due to a lack of coping skills or exposure to high-risk situations.
Grasping these stages is key to spotting early warning signs and applying useful relapse prevention skills.
Substance abuse treatment programs recognize the importance of relapse prevention techniques and incorporate them into their curriculum. An excellent relapse prevention technique focuses on promoting recovery by addressing the underlying causes of substance dependence, such as unresolved emotional issues or unmet needs. Treatment programs that address these issues can assist individuals in building resilience and forming strategies to bolster their long-term recovery.
Alcohol use disorders, in particular, present unique challenges when it comes to relapse prevention. Alcohol is a widely accepted and available substance, making it difficult for individuals in recovery to avoid exposure to alcohol-related triggers. In these cases, it is especially important to develop a personalized relapse prevention plan that includes strategies for managing high-risk situations and staying committed to sobriety.
Developing a Personalized Relapse Prevention Plan

Formulating a tailor-made relapse prevention plan is a key step in sustaining long-term sobriety. A well-rounded plan will include:
- Names and contact information of key people in your support system
- A description of internal and external triggers
- Identification of healthy coping skills
- A personalized plan on how to intervene when relapse triggers are activated
A customized plan allows you to foresee challenges and equip yourself to tackle them effectively.
One of the fundamental aspects of a relapse prevention plan is identifying your specific triggers. Triggers can be internal, such as feelings of stress or loneliness, or external, like being around people who still use substances. Identifying your triggers enables the development of strategies to circumvent or handle them, thereby lowering the risk of relapse. For instance, you can alter your daily routine, distance yourself from individuals or places associated with substance use, or practice healthy coping strategies to manage stress.
High-risk situations are another crucial element to address in your relapse prevention plan. These situations can significantly increase the likelihood of relapse, especially during early recovery. By actively avoiding high-risk situations and establishing boundaries, you can protect your sobriety and focus on your recovery goals.
It is advisable to work with a healthcare professional or counselor from an institution like Lantana Recovery when creating a personalized relapse prevention plan. They can provide expert guidance, help you identify your triggers, and suggest coping strategies that are tailored to your needs. By working together, you can create a plan that is both effective and sustainable in the long run.
Recognizing and Handling Triggers

Comprehending the role of triggers and warning signs in relapse is fundamental for successful relapse prevention. Triggers act as internal or external cues that can activate the urge to use substances, increasing the risk of relapse. Some common triggers include:
- encountering people from one’s past drug experiences who are still using substances
- visiting places associated with drug or alcohol use
- experiencing negative emotions such as stress, anger, or sadness
For efficient trigger management, it’s necessary to pinpoint them and devise strategies for their avoidance or handling. Some strategies for managing triggers include:
- Changing your daily routine or surroundings
- Abstaining from individuals or locations related to substance abuse
- Developing alternative methods to cope with stress
By being proactive in handling triggers, you can reduce the likelihood of returning to substance use.
In addition to avoiding triggers, it’s essential to develop healthy coping strategies to manage them when they arise. Some relapse prevention skills that can help you manage triggers include implementing relaxation techniques, engaging in mindfulness practices, or seeking assistance from your support network. By honing these skills, you can better cope with triggers and maintain your sobriety.
Staying aware of both internal and external triggers is a crucial element of relapse prevention. By recognizing and addressing triggers, you can take control of your recovery journey and minimize the risk of relapse.
Building a Strong Support System
A robust support system is an essential component of addiction recovery. Support networks can consist of:
- Friends
- Family members
- Addiction medicine specialists
- Addiction treatment programs such as Alcoholics Anonymous or SMART Recovery
McCrady & Flanagan discuss how alcohol use disorder (AUD) and family well-being are closely linked, with AUD having a negative impact on families. However, families tend to experience significant improvements when there is recovery from AUD. These connections can provide you with healthy coping strategies, encouragement, and understanding, all of which are vital in maintaining sobriety.
Establishing and maintaining a support network requires proactive effort and communication. Reach out to loved ones, join self-help groups, or seek professional assistance to build a robust support system. It’s important to be honest and open with your support network, as well as understanding that they may need support too.
Actively engaging in self-help groups can offer numerous benefits for individuals with substance use disorders. By participating in these groups, you can gain a sense of solidarity, learn from others’ experiences, and find a non-judgmental environment to share your own struggles and successes related to substance use disorder. The support and camaraderie found in these groups can be invaluable in maintaining long-term recovery.
Keep in mind that constructing a robust support system is a continuous process. As you progress through your recovery journey, your support network may evolve and change. Regularly evaluate your support system and make adjustments as needed to ensure you have the resources and connections that best support your sobriety.
Prioritizing Self-Care in Recovery

Self-care is a vital part of relapse prevention, aiding individuals in sustaining their physical, emotional, and mental health. By prioritizing self-care, you can better manage stress, negative emotions, and other challenges that may arise during recovery. Some self-care practices that can help prevent relapse include:
- Exercise
- Proper nutrition
- Sleep
- Stress management
Exercise is an excellent self-care practice that can help improve mood, reduce stress, and promote overall well-being. Regular physical activity can also help prevent relapse by providing a positive outlet for stress and negative emotions. Implementing physical exercise into your daily routine doesn’t have to be complicated; even simple activities like walking, swimming, or yoga can provide significant benefits.
Proper nutrition is another vital component of self-care. Consuming a healthy diet can support your physical and mental health, providing the necessary energy and nutrients for your body to function optimally. A well-balanced diet can also help reduce cravings and stabilize mood, reducing the risk of relapse.
Stress management is also essential in maintaining sobriety and preventing relapse. Developing healthy coping strategies to manage stress, such as mindfulness techniques or deep breathing exercises, can help you navigate challenges without resorting to substance use. By prioritizing self-care in your recovery journey, you can build a strong foundation for long-term sobriety and overall well-being.
Enhancing Coping Mechanisms
It’s essential to develop and hone coping skills for managing stress and negative emotions that might surface during recovery. By enhancing your coping mechanisms, you can better handle challenges and avoid relapse. Some examples of coping skills include:
- Distraction techniques
- Relaxation techniques
- Problem-solving skills
- Assertiveness training
- The ability to identify and challenge negative thoughts
These can be useful tools to help manage distressful situations.
Cooperating with a healthcare professional or counselor can be tremendously advantageous in identifying and cultivating coping skills that are appropriate for your situation after you’ve gone through the first step to recovery: denial. They can help you consistently apply and refine these skills throughout your recovery journey. By working together, you can create a personalized set of coping strategies that effectively address your unique needs and challenges.
Practicing and refining your coping skills over time is essential for long-term success. Here are some steps to help you improve your coping abilities.
- Set goals for yourself.
- Track your progress.
- Seek feedback from your healthcare professional or counselor.
- Continuously work on improving your coping skills.
The more you practice, the more effective your coping skills will become, better preparing you for any challenges that may arise.
It’s important to remember that building effective coping mechanisms is a gradual process that requires ongoing effort and dedication. By consistently working on your coping skills and adapting them to your evolving needs, you can enhance your resilience and ability to maintain sobriety in the face of adversity.
Navigating High-Risk Situations

High-risk situations can considerably increase the probability of relapse, hence it’s crucial to recognize and handle them effectively. By constructing a plan for evading high-risk circumstances, you can decrease the likelihood of physical relapse and remain focused on your recovery objectives.
To navigate high-risk situations, it’s important to establish boundaries and communicate them to others. This may involve distancing yourself from certain individuals or places or avoiding situations where substances are present. It’s important to recognize that setting boundaries may require making difficult but necessary decisions to protect your sobriety.
Another strategy for managing high-risk situations is to engage in sober activities. By participating in activities that do not involve substance use, you can reduce the risk of relapse and build a fulfilling life without drugs or alcohol. Sober activities can include:
- Hobbies
- Sports
- Volunteer work
- Spending time with supportive friends and family
Remember, navigating high-risk situations is an ongoing process that requires vigilance and adaptability. By regularly evaluating your risk factors and adjusting your strategies as needed, you can minimize the likelihood of relapse and maintain your commitment to recovery.
Staying Engaged in Recovery
Staying actively involved in your recovery journey is pivotal for enduring success. By regularly participating in support groups, therapy sessions, and other recovery-oriented activities, you can continuously learn new skills, gain insights, and stay committed to your sobriety.
Support groups, such as Alcoholics Anonymous or SMART Recovery, can provide invaluable resources and connections for individuals in recovery. “Developed as an alternative to 12-step approaches, SMART Recovery incorporates both motivational interviewing and cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) to promote positive behavioral change for a range of addictive behaviors” (A qualitative exploration of SMART Recovery meetings, Gray et al., 2020.) By attending meetings, sharing your experiences, and listening to others, you can gain a deeper understanding of your addiction, learn new strategies for managing triggers and high-risk situations, and build a supportive community.
Therapy sessions, whether individual or group, can also play a crucial role in relapse prevention. Working with a therapist can help you address underlying issues that may contribute to substance use, develop healthy coping strategies, and improve your overall mental health.
Staying engaged in your recovery is an ongoing commitment that requires dedication and effort. By actively participating in recovery-oriented activities and maintaining a strong support network, you can continue to grow and develop the skills necessary for long-term sobriety.
Practicing Mindfulness and Gratitude

Incorporating mindfulness and gratitude practices into your daily life can have a profound impact on your mental well-being and overall recovery journey. Mindfulness-based relapse prevention techniques promote self-awareness and help individuals to accept cravings rather than battling them. This can provide a healthier approach to managing triggers. By practicing mindfulness, you can develop the ability to observe your thoughts and emotions without judgment, allowing you to respond to cravings and triggers more effectively.
Gratitude practices can also support your recovery by fostering a more positive outlook on life and promoting overall well-being. Here are some examples of how to practice gratitude.
- Maintaining a gratitude journal
- Expressing gratitude through acts of kindness or words of appreciation
- Taking time to appreciate the positive aspects of life
By cultivating gratitude, you can counteract the negative feelings and thoughts that may arise during recovery and build a more resilient mindset. Practicing gratitude can also help prevent emotional relapse by strengthening your overall mental health and well-being.
Incorporating mindfulness and gratitude practices into your recovery journey can provide numerous benefits, from improved mental health to reduced risk of relapse. By dedicating time and effort to these practices, you can support your long-term recovery and enhance your overall quality of life.
Committing to Long-Term Recovery
Remaining committed to your recovery journey is key to preventing relapses and upholding long-term sobriety. This commitment involves continuously learning new skills, building resilience, and adapting to the challenges that may arise during your recovery journey.
One essential aspect of long-term recovery is the development of a personalized relapse prevention plan. By devising a plan that addresses your unique triggers, high-risk situations, and coping strategies, you can better anticipate challenges and prepare yourself to face them effectively.
Building resilience is another critical component of long-term recovery. By constructing resilience, you can better handle difficult situations and stay dedicated to your sobriety. Developing healthy coping skills, engaging in self-care practices, and maintaining a strong support network are all essential components of building resilience.
Committing to long-term recovery requires ongoing effort, dedication, and adaptation. By staying focused on your recovery goals, actively engaging in support networks and recovery-oriented activities, and continuously refining your coping skills, you can build a strong foundation for lasting sobriety and overall well-being.
The Bottom Line
In conclusion, preventing relapse is a crucial aspect of addiction recovery that requires ongoing effort, dedication, and the implementation of various strategies. By understanding the stages of relapse, developing a personalized relapse prevention plan, recognizing and handling triggers, building a strong support system, and prioritizing self-care, you can enhance your chances of maintaining recovery.
Remember, the journey towards recovery is not a linear path, but rather a continuous process of learning about what relapse is and growth. By staying committed to your recovery, actively engaging in support networks and recovery-oriented activities, and continuously refining your coping skills, you can build a strong foundation for lasting sobriety and overall well-being. Keep pushing forward and remember that you are not alone in this journey – together with experts at Lantana, we can overcome the challenges of addiction and embrace a healthier, happier future.
Frequently Asked Questions
How can relapse be prevented?
To prevent relapse, it is essential to engage in self-care, recognize triggers, join a support group, practice mindfulness meditation, and take steps to increase self-awareness, life balance, nutrition, exercise, and sleep.
Additionally, it is important to build healthy relationships with others and form a recovery support network.
What are the 4 D’s of relapse prevention?
Relapse prevention involves utilizing the 4 Ds: delay, distraction, stress management, and de-catastrophizing. Through using these tools, we can reduce the likelihood of relapses occurring, even when triggers or cravings arise.
What is a good relapse prevention plan?
Creating a personalized plan for relapse prevention is key to successful recovery. This should include identifying personal goals in recovery, planning ways to manage cravings and triggers, improving self-care, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
What are the three stages of relapse?
The three stages of relapse are emotional, mental, and physical, representing a gradual deterioration of self-control. These stages can leave an individual increasingly vulnerable to lapsing into substance use. It is important to recognize the signs of relapse in order to prevent it from happening. Early recognition of the signs can help an individual take steps to prevent a full relapse.
How can I identify my triggers and high-risk situations?
Identifying triggers and high-risk situations can be done by working with a healthcare professional or counselor, who can provide individualized assistance.









