Mushroom withdrawal symptoms can have a significant impact on individuals who have used psychedelic mushrooms. It is important to understand the effects of these substances and how they can lead to withdrawal symptoms. The following provides an overview of mushroom withdrawal symptoms and their implications for users.
Psychedelic mushrooms, also known as magic mushrooms, contain a naturally occurring compound called psilocybin. These mushrooms have been used for centuries in spiritual and cultural practices due to their hallucinogenic properties. When consumed, psilocybin is converted to psilocin, which interacts with serotonin receptors in the brain, resulting in altered perception, mood changes, and heightened sensory experiences.
While psychedelic mushrooms are not physically addictive like certain substances, they can still lead to psychological dependence. Sudden cessation or reduction of mushroom use after regular or prolonged use can result in withdrawal symptoms. The intensity and duration of these symptoms can vary depending on factors such as individual tolerance, frequency of use, and dosage.
Common mushroom withdrawal symptoms include psychological symptoms such as anxiety, depression, irritability, and disturbances in perception. Emotional symptoms may manifest as mood swings, increased sensitivity, and difficulty regulating emotions. Physical symptoms can include headaches, fatigue, changes in appetite, and sleep disturbances.
Managing mushroom withdrawal symptoms requires a supportive approach. It is important to remember that withdrawal symptoms are temporary and will gradually diminish over time. Engaging in self-care practices such as maintaining a healthy lifestyle, practicing stress-reduction techniques, and seeking social support can help alleviate withdrawal symptoms.
However, self-managed withdrawal can have potential risks. Individuals may experience intense cravings or emotional distress, which could lead to relapse. It is crucial to seek professional help when the severity of withdrawal symptoms becomes overwhelming or when relapse is a concern.

Overview of Psychedelic Mushrooms
Psychedelic mushrooms, also known as magic mushrooms, have a long history of use in spiritual and cultural contexts. They are natural psychedelics that can induce altered states of consciousness and profound psychedelic experiences. These mushrooms contain varying levels of the compound psilocybin, which is converted to psilocin in the body. Psilocin is responsible for the hallucinogenic effects. When consumed, psychedelic mushrooms can result in hallucinations, altered perception, intense emotions, and spiritual experiences. The effects can vary based on mindset, environment, and dosage.
Research by Jeremy Daniel from South Dakota State University suggests that psychedelic mushrooms may have therapeutic potential for mental health conditions such as depression, anxiety, and substance use disorders. They may also enhance creativity and promote personal growth. While they are generally considered safe when used responsibly, there are risks associated with their use. These risks include potential for psychological distress, accidents, and negative interactions with certain medications or mental health conditions.
I had the opportunity to try psychedelic mushrooms during a camping trip. We carefully planned our dosage, set, and setting for a safe and meaningful experience. As we consumed the mushrooms, we embarked on a journey of self-discovery and introspection. The world around us transformed into a vibrant tapestry of colors, shapes, and patterns. Our senses heightened, and we gained insights into ourselves and our relationships. The experience was awe-inspiring and humbling, leaving us with a newfound appreciation for the mysteries of the mind and the interconnectedness of all things. It sparked a lifelong interest in exploring the potential of psychedelics for personal growth and well-being.
What Are Psychedelic Mushrooms?
Psychedelic mushrooms, also known as magic mushrooms or psilocybin mushrooms, offer a mind-altering experience. When consumed, these hallucinogenic fungi induce profound changes in perception, mood, and consciousness. The mushrooms contain psilocybin, a psychoactive compound that, upon metabolism, converts into psilocin. In the body, psilocin interacts with serotonin receptors in the brain, resulting in altered sensory perception, hallucinations, and shifts in thought processes and emotions.
For centuries, indigenous cultures have incorporated psychedelic mushrooms into their spiritual and religious ceremonies. More recently, these mushrooms have gained popularity for recreational use, self-exploration, and potential therapeutic purposes. Their appearance varies, encompassing a range of colors and sizes.
The effects of psychedelic mushrooms can differ based on factors such as dosage, mindset, and environment. Individuals may experience feelings of euphoria and gain spiritual insights, but there is also the potential for anxiety, confusion, and a distorted sense of reality.
It is crucial to recognize the potential risks associated with the use of psychedelic mushrooms. These risks include psychological distress and the potential for triggering underlying mental health conditions. Furthermore, it is essential to note that psychedelic mushrooms are illegal in many countries, including the United States. Possessing, selling, or cultivating these mushrooms can result in legal consequences.
Therefore, individuals who are contemplating using psychedelic mushrooms must fully understand the potential risks and effects. They should seek accurate information, embrace harm reduction strategies, and obtain professional guidance to ensure their well-being and safety.
How Do Psychedelic Mushrooms Work?
Psychedelic mushrooms, also known as magic mushrooms or shrooms, work by affecting the brain’s serotonin receptors. The active ingredient, psilocybin, is converted into psilocin in the body. Psilocin then binds to serotonin receptors, specifically the 5-HT2A receptors, which results in altered perception, mood changes, and hallucinations.
When consumed, psychedelic mushrooms are metabolized by the liver and broken down into psilocin quickly. This psilocin then travels to the brain and binds to serotonin receptors. This binding stimulates the receptors and disrupts the normal functioning of serotonin, a neurotransmitter responsible for regulating mood, appetite, sleep, and cognitive functions.
The altered state of consciousness that occurs from consuming psychedelic mushrooms leads to changes in perception, including visual and auditory hallucinations, synesthesia, and an altered sense of time and self. The exact mechanisms through which psilocybin produces these effects are not fully understood but may involve changes in communication between different regions of the brain.
It is important to note that the effects of psychedelic mushrooms can vary depending on factors such as dosage, set, and setting. Set refers to the mindset and psychological state of the individual consuming the mushrooms, while setting refers to the environment in which the experience takes place.
Fact: Psychedelic mushrooms have a long history of use in various cultural and religious practices. Indigenous peoples have used them for centuries for spiritual and healing purposes.

Understanding Mushroom Withdrawal
Understanding mushroom withdrawal is crucial for those who have used psychedelics and are discontinuing their use. Here are key points to consider:
- Physical symptoms: Mushroom withdrawal can cause headaches, fatigue, decreased appetite, and gastrointestinal issues. These symptoms vary in intensity and duration.
- Psychological effects: Users may experience mood swings, irritability, anxiety, and depression during withdrawal. Seeking support from mental health professionals may be necessary.
- Timeline: Mushroom withdrawal symptoms typically begin a few days after discontinuation and can last up to a week or more. Severity and duration vary based on dosage, frequency of use, and individual differences.
- Supportive measures: Engaging in healthy lifestyle practices, such as exercise, proper nutrition, and sufficient sleep, can help alleviate withdrawal symptoms. Seeking emotional support from friends, family, or support groups is also valuable.
- Professional help: If managing withdrawal symptoms or experiencing severe psychological distress becomes difficult, it is important to seek professional help. Mental health professionals can provide guidance, therapy, and support for individuals going through mushroom withdrawal.
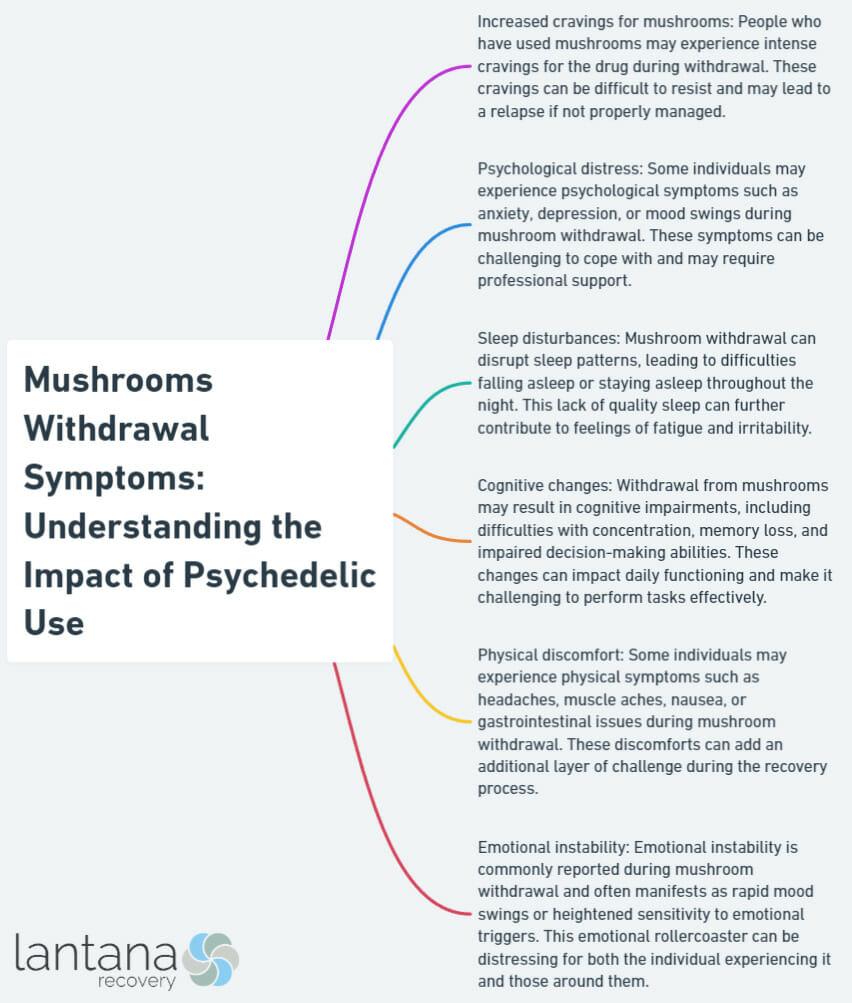
Can One Develop Withdrawal Symptoms from Mushroom Use?
Yes, it is possible to develop withdrawal symptoms from mushroom use. Some individuals may experience a range of physical, psychological, and emotional symptoms when they stop using psychedelic mushrooms.
Physical withdrawal symptoms may include headaches, muscle aches, fatigue, and gastrointestinal discomfort. These symptoms can make the process of quitting mushroom use challenging.
Psychological symptoms such as irritability, mood swings, anxiety, and difficulty concentrating are also common during mushroom withdrawal. These symptoms can significantly impact a person’s daily life and well-being.
Emotional symptoms may manifest as depression, sadness, and a general sense of unease. It is important to recognize and address these emotional challenges during the withdrawal process.
The exact causes of mushroom withdrawal symptoms are not fully understood, but it is believed that prolonged mushroom use can lead to dependence. When mushrooms are abruptly stopped, the brain may struggle to adapt to the lack of psychedelic effects, which can result in withdrawal symptoms.
Managing mushroom withdrawal symptoms involves various strategies. Getting enough rest, maintaining a healthy diet, and engaging in stress-reducing activities can help alleviate symptoms. Additionally, seeking professional help is crucial, especially if the symptoms become severe or if there is a risk of relapse.
What Causes Mushroom Withdrawal Symptoms?
Mushroom withdrawal symptoms can be caused by psychedelic use on the brain and body. The active ingredient in psychedelic mushrooms, psilocybin, interacts with serotonin receptors in the brain, resulting in altered perception, mood changes, and hallucinations. When individuals stop using psychedelic mushrooms regularly and for a prolonged period of time, their brains need to adjust to the lack of psilocybin, leading to withdrawal symptoms.
There are many reason why people start using psychedelic mushroom. However, a recent study reports, “General mental health and well-being were popular reasons for psychedelic mushroom (PM) use (63.6%), although use for medically-diagnosed (31.8%) and self-diagnosed (19.0%) conditions was also common.” (Psychedelic Mushrooms in the USA: Knowledge, Patterns of Use, and Association With Health Outcomes, Matzopoulos et al., 2022)
The exact causes of mushroom withdrawal symptoms are not fully understood, but it is believed that they are a combination of psychological and physiological factors. Psychologically, individuals may crave the hallucinogenic effects and altered perception provided by mushrooms. Physiologically, prolonged mushroom use can desensitize or downregulate serotonin receptors in the brain, causing imbalances in serotonin levels and resulting in withdrawal symptoms.
Common mushroom withdrawal symptoms include cravings, anxiety, depression, mood swings, irritability, difficulty concentrating, headaches, fatigue, and gastrointestinal issues. The severity and duration of these symptoms can vary depending on the frequency and duration of mushroom use.
It’s important to note that supportive measures, such as making healthy lifestyle choices, seeking emotional support, and consulting with professionals, can help manage mushroom withdrawal symptoms. However, attempting to manage withdrawal without professional guidance can be risky and increase the chances of relapse.
Common Mushroom Withdrawal Symptoms
Common psychological withdrawal symptoms of mushroom use include anxiety, depression, mood swings, irritability, and cognitive difficulties. Emotional symptoms during mushroom withdrawal include intense drug cravings, restlessness, difficulty sleeping, and feelings of emptiness or sadness. Physical symptoms of mushroom withdrawal can include headaches, nausea, sweating, tremors, muscle aches, and changes in appetite or weight.
The severity and duration of these common mushroom withdrawal symptoms vary among individuals. Some may experience more intense withdrawal symptoms, and the withdrawal period’s duration may differ. Seek support from healthcare professionals or addiction support groups for guidance and assistance during the recovery process. Self-managed withdrawal can be dangerous and increase the risk of relapse. Prioritize mental health and physical well-being, and seek professional help if needed. Treatment and support are available to help individuals overcome addiction and effectively manage these common mushroom withdrawal symptoms.
Psychological Symptoms
Psychological symptoms are common during mushroom withdrawal. Symptoms like mood swings, irritability, depression, anxiety, emotional detachment, and difficulty concentrating can vary in severity and duration depending on the individual and extent of mushroom use. Each person may experience different psychological symptoms during withdrawal.
It is important to seek professional help, such as counseling or therapy, to manage these psychological symptoms during withdrawal. Professionals can provide guidance and support in navigating the challenges. Engaging in activities like exercise, mindfulness, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle can also contribute to a smoother withdrawal process.
Being patient and understanding is crucial, as psychological symptoms may take time to improve. Surrounding yourself with a supportive network who can offer understanding and encouragement during mushroom withdrawal is a pro-tip. They can provide valuable emotional support and assist in maintaining a positive mindset.
With proper support and self-care, individuals can overcome these challenges and move toward a healthier life.
Emotional Symptoms
Emotional symptoms are a prevalent occurrence when going through mushroom withdrawal. These symptoms manifest in various ways but typically involve changes in mood, feelings, and overall emotional well-being. Emotional symptoms can be intense and have a profound impact on daily life.
It is common for individuals to experience increased anxiety or heightened fear and paranoia during this time. Some may also feel sadness, depression, or mood swings. Emotional instability and irritability are frequently reported during mushroom withdrawal. These symptoms can be difficult to manage and may have an effect on relationships and social interactions.
It is crucial to acknowledge that emotional symptoms during mushroom withdrawal are temporary and will gradually lessen over time. Engaging in self-care practices, such as regular exercise, sufficient sleep, and relaxation techniques, can help alleviate some of these symptoms.
If emotional symptoms become severe or persist for an extended period, seeking professional help can be beneficial. Mental health professionals can offer support and guidance in navigating the challenges of mushroom withdrawal and effectively managing emotional symptoms.
Remember that experiencing emotional symptoms during mushroom withdrawal is normal. Be patient and prioritize self-care to enhance emotional well-being during this period.
Physical Symptoms
Physical symptoms associated with mushroom withdrawal can vary in severity and duration.
Common physical symptoms experienced during mushroom withdrawal include headaches, fatigue, nausea and stomach discomfort, sweating and chills, and muscle aches and pains.
These physical symptoms can range from mild discomfort to more severe migraines and can be the body’s way of adjusting to the absence of the drug.
It is important to note that the severity and duration of physical symptoms may vary depending on the individual and their pattern of mushroom use.
If severe physical symptoms are experienced during mushroom withdrawal, it is recommended to seek professional help for support and guidance.

Managing Mushroom Withdrawal Symptoms
Managing mushroom withdrawal symptoms can be challenging, but it is possible to alleviate discomfort and navigate this period. Here are steps to help you manage mushroom withdrawal symptoms:
- Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of water to flush out toxins and minimize withdrawal symptoms. Aim for at least 8 glasses of water per day.
- Eat a balanced diet: Consume nutritious meals to support your body’s healing process. Include foods rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants to boost your overall well-being.
- Engage in physical activity: Regular exercise releases endorphins, natural mood-boosting chemicals. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise, such as brisk walking or cycling, every day.
- Practice relaxation techniques: Use deep breathing, meditation, or yoga to reduce stress and promote calmness. These mindfulness based relaxation techniques have been proven effective in managing withdrawal by a clinical trial conducted by experts at University of Washington.
- Seek support: Reach out to friends, family, or a support group for understanding and encouragement. Talking about your experiences and emotions can alleviate psychological symptoms of withdrawal.
- Establish a daily routine: Create structure in your day to distract your mind from withdrawal symptoms and provide stability. Plan activities, set goals, and follow a regular sleep schedule.
- Practice self-care: Engage in activities that bring joy and relaxation, such as reading, listening to music, taking baths, or practicing hobbies.
- Stay positive: Remember that withdrawal symptoms are temporary and your body and mind will gradually adjust. Focus on your progress towards a healthier lifestyle and celebrate achievements along the way.
How Long Do Mushroom Withdrawal Symptoms Last?
Mushroom withdrawal symptoms can vary in duration depending on various factors. How long do mushroom withdrawal symptoms last? There is no fixed timeframe for these symptoms, but understanding the general timeline is important. Typically, mushroom withdrawal symptoms can last for several days to a couple of weeks.
Factors that can influence the duration of withdrawal symptoms include overall health, frequency and duration of mushroom use, dosage, and personal tolerance levels.
During the initial phase of withdrawal, which may last a few days, individuals may experience psychological symptoms such as mood swings, anxiety, and irritability. These symptoms can gradually subside over time.
In the second phase, emotional symptoms like depression and cravings may persist for a week or more. It’s important to note that withdrawal symptoms can vary in severity and duration for each person.
Physical symptoms, such as headaches, fatigue, and changes in appetite, may also be present and can last for several weeks. Proper rest, a healthy diet, and staying hydrated can help alleviate these symptoms.
Seeking professional help is crucial if the symptoms become overwhelming or there is a risk of relapse. How long do mushroom withdrawal symptoms last? A healthcare provider or addiction specialist can offer guidance, support, and appropriate treatment options to manage mushroom withdrawal symptoms effectively.
Remember, the duration of mushroom withdrawal symptoms may vary from person to person, so seeking professional help is essential for a safe and successful recovery.
Supportive Measures for Mushroom Withdrawal
When dealing with mushroom withdrawal symptoms, several measures can help individuals cope with the challenges they may face. These measures include:
- Creating a support system: Surrounding oneself with a supportive network of friends, family, or a therapist can offer emotional support during this difficult time.
- Seeking professional help: Consulting with a healthcare professional or addiction specialist can provide guidance and assistance throughout the withdrawal process. They can offer personalized treatment plans and support tailored to individual needs.
- Engaging in healthy coping mechanisms: Finding healthy ways to manage stress and cravings, such as mindfulness, exercise, or hobbies, can contribute to a successful withdrawal process.
- Adopting a healthy lifestyle: Prioritizing physical health through regular exercise, proper nutrition, and adequate sleep can help restore balance and improve overall well-being.
- Considering support groups: Joining a support group, such as Narcotics Anonymous (NA), can provide a sense of community and understanding as individuals share their experiences and strategies for overcoming addiction.
It is important to remember that everyone’s journey is unique, and what works for one person may not work for another. Implementing supportive measures along with professional guidance can increase the chances of a successful withdrawal process and overall recovery.
When to Seek Professional Help?
Knowing when to seek professional help is crucial when dealing with mushroom withdrawal symptoms. Severe psychological symptoms such as hallucinations, delusions, or intense anxiety require immediate professional help. Additionally, physical symptoms like severe headaches, nausea, vomiting, or tremors should prompt medical attention.
If mushroom withdrawal symptoms persist for a prolonged period without improvement, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional. Professional help can provide necessary resources and strategies to effectively manage withdrawal symptoms and address underlying health issues. Seeking professional help for withdrawal is a proactive step towards overall well-being and recovery.

Potential Risks of Mushroom Withdrawal
When considering mushroom withdrawal, individuals may experience physical and psychological symptoms. The risks can vary based on dosage, frequency of use, overall health, and predisposition to addiction.
- Psychological symptoms: Mushroom withdrawal may cause mood swings, anxiety, depression, irritability, and difficulty concentrating. It is crucial to seek support from a healthcare professional or addiction counselor.
- Physical symptoms: Some individuals may experience discomfort, such as headache, nausea, sweating, and tremors, during mushroom withdrawal. These symptoms generally subside over time but can be distressing initially.
- Relapse potential: Mushroom withdrawal is challenging, and the risk of relapse is significant. Establishing a strong support system and developing coping strategies can minimize the risk and maintain long-term recovery.
- Underlying mental health conditions: Mushroom withdrawal can worsen underlying mental health conditions like depression or anxiety. Individuals with pre-existing mental health conditions should seek professional help.
- Long-term effects: Limited research suggests individuals may experience persistent psychological symptoms or cravings after the acute withdrawal phase. Continued support and therapy can manage these effects and increase successful recovery.
What are the Dangers of Self-Managed Withdrawal?
Self-managed withdrawal from psychedelic mushrooms poses serious risks to individuals. It is important to understand the potential dangers and seek professional help.
- Psychological risks: Self-managed withdrawal for drug addiction can cause intense psychological symptoms such as anxiety, depression, and mood swings. These symptoms may require professional guidance.
- Physical risks: Withdrawal symptoms from psychedelic mushrooms can include headaches, nausea, sweating, and insomnia. Without proper supervision, individuals may not have access to medical attention to alleviate these symptoms.
- Lack of support: Self-managed withdrawal may lack the necessary support systems to navigate the challenges. Having a support network is crucial for a safe and successful withdrawal process.
- Relapse potential: Without professional guidance, the risk of relapse is higher during self-managed withdrawal. It can be challenging to resist the temptation to use psychedelic mushrooms again.
- Unsafe detoxification methods: Self-managed withdrawal may involve unsafe detoxification methods that put individuals at risk. Medical supervision is essential for physical and mental well-being.
To ensure a safe and successful withdrawal, it is recommended to seek professional help and engage with addiction support services. Professional guidance provides necessary resources and support to navigate the withdrawal process effectively and reduce potential risks.
Could Mushroom Withdrawal Lead to Relapse?
Mushroom withdrawal can indeed lead to relapse, although the likelihood and severity vary from person to person. It is crucial to understand that any type of substance withdrawal, including mushrooms, has the potential to trigger a relapse. Consider the following essential points:
- Individual susceptibility: Some individuals are more vulnerable to relapse due to various factors, such as genetic predisposition, mental health conditions, or a history of substance abuse.
- Psychological withdrawal: Mushroom withdrawal can give rise to cravings, depression, anxiety, and irritability. Managing these symptoms can be challenging and can heighten the risk of relapse.
- Physical symptoms: While mushrooms are not physically addictive, certain individuals may experience discomfort during withdrawal, including headaches, nausea, and fatigue. If these symptoms are not properly addressed, they may lead to relapse.
- Supportive measures: To minimize the risk of relapse, it is crucial to seek professional assistance and establish a support system. Therapy, counseling, and support groups can offer guidance and aid during the withdrawal process.
- Dangers of self-management: Attempting to manage mushroom withdrawal without professional guidance is hazardous and increases the risk of relapse. It is essential to consult healthcare professionals who specialize in addiction treatment.
Ultimately, the risk of relapse depends on the individual and the availability of support and resources during the withdrawal period. Taking proactive steps to address both the physical and psychological aspects of withdrawal can significantly decrease the likelihood of relapse.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the short-term symptoms of using psilocybin mushrooms?
The short-term symptoms of using psilocybin mushrooms include hallucinations, altered perception of time, inability to distinguish fantasy from reality, panic, muscle relaxation or weakness, loss of coordination, enlarged pupils, nausea, vomiting, and drowsiness.
Are psilocybin mushrooms considered addictive substances?
Psilocybin mushrooms have a low risk of addiction, but some individuals may develop a psychological dependence on them, especially if they are used to maintain happiness or a sense of enlightenment.
What are the withdrawal symptoms associated with psilocybin mushrooms?
The withdrawal symptoms of psilocybin mushrooms may include headaches, depression, anxiety, and exhaustion. Flashbacks, triggered by stress or the use of other drugs, may also occur and may be linked to Hallucinogen Persisting Perception Disorder (HPPD).
How long does a psilocybin mushrooms withdrawal typically last?
A psilocybin mushrooms withdrawal typically lasts 24 hours or less. However, extended periods of psilocybin mushroom abuse may lead to hallucinatory flashbacks and can result in Hallucinogen Persisting Perception Disorder (HPPD), which can persist for up to 12 months after multiple doses.
Is it safe to combine psilocybin mushrooms with other substances of abuse?
No, combining psilocybin mushrooms with other substances of abuse can exacerbate health risks. It is important to avoid combining psilocybin mushrooms with other substances for safety reasons.
What treatment options are available for psilocybin mushrooms withdrawal?
To safely manage psilocybin mushrooms detox, it is recommended to seek professional help, especially if other substances of abuse are involved or there are underlying mental health issues. Treatment should be individualized and holistic, addressing both substance use and mental health concerns.









